Abstract
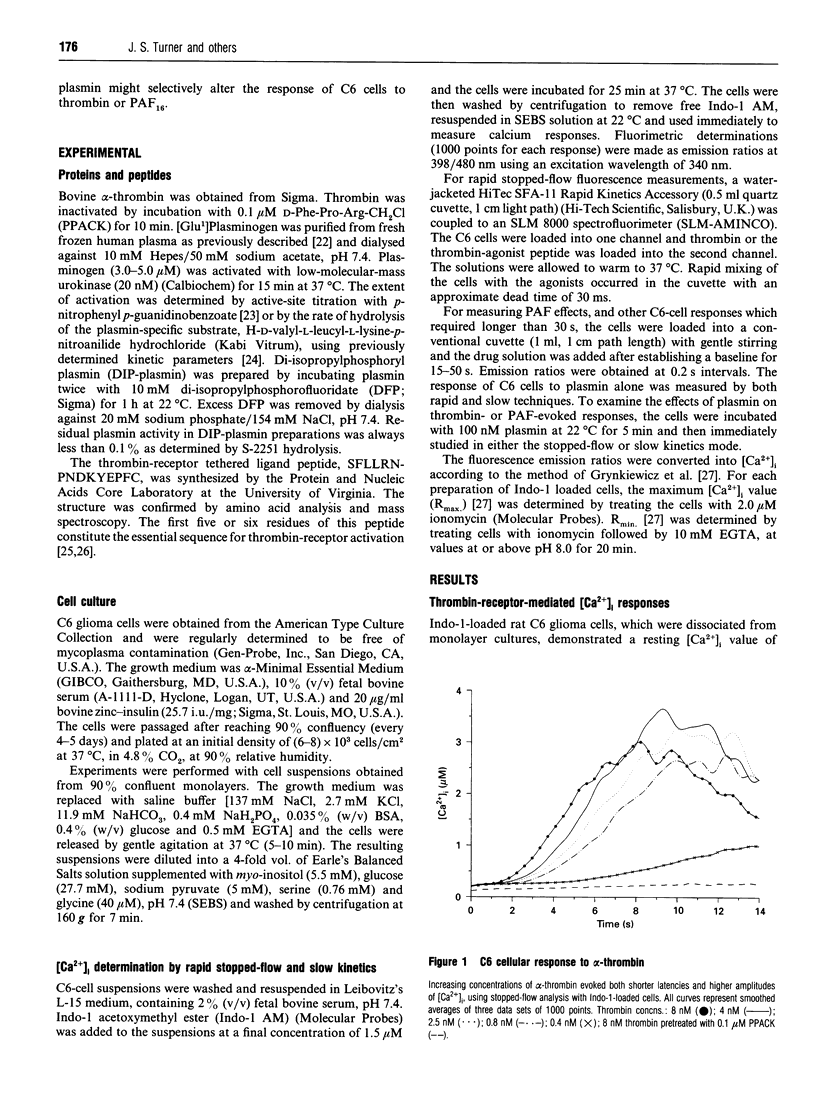
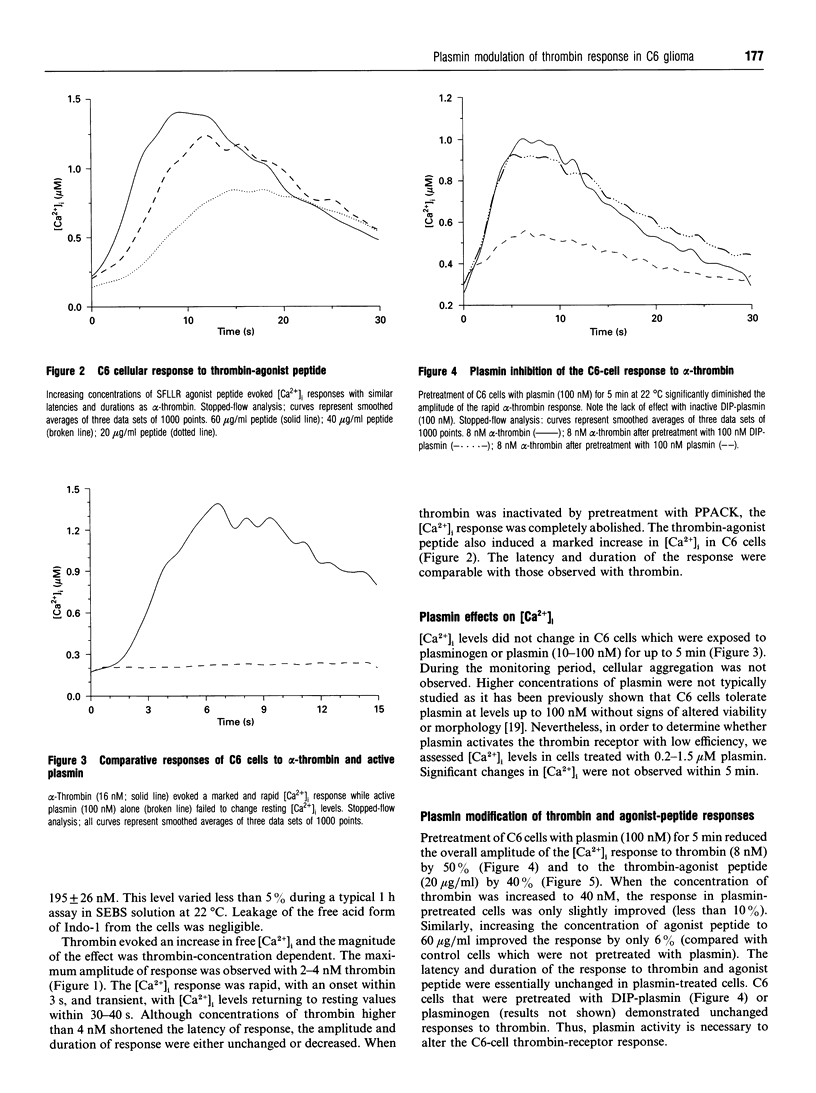
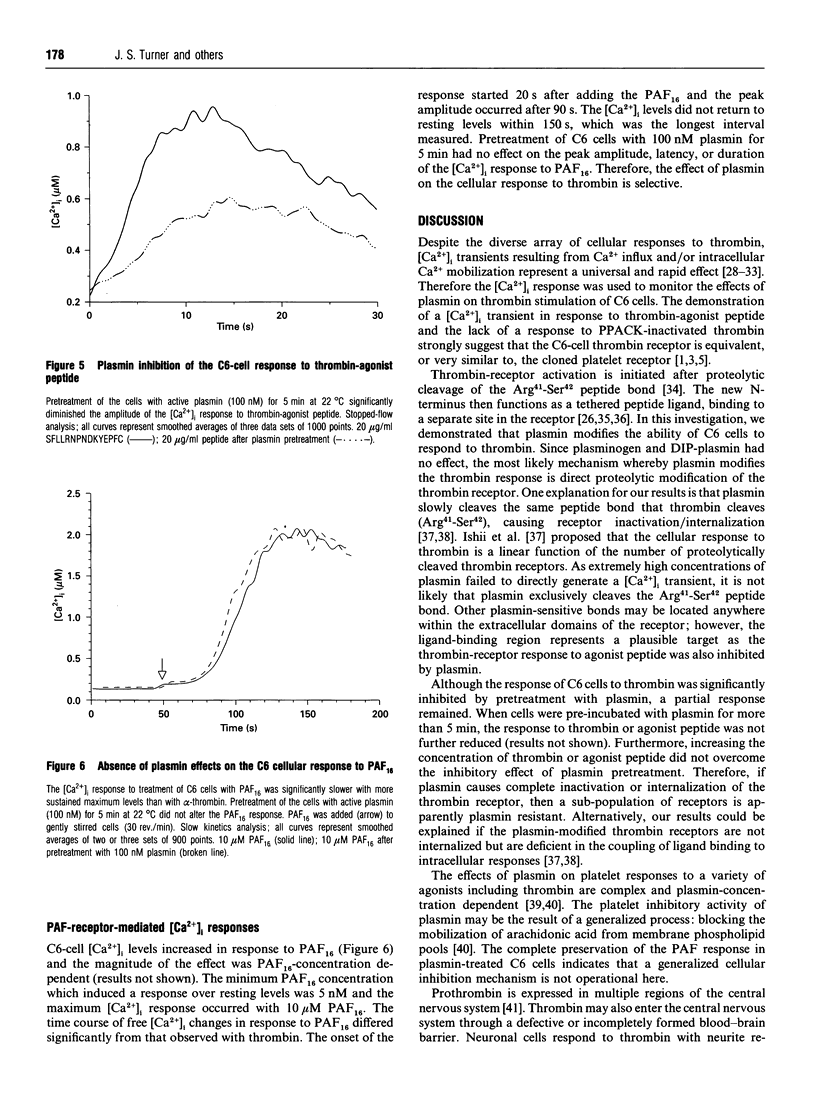
Extracellular proteinases may be selectively targeted to cell surfaces by specific receptors or binding sites. In previous studies, we have characterized cellular binding sites for plasminogen and plasmin on rat C6 glioma cells. In this investigation, we studied the response of C6 cells to alpha-thrombin and plasmin by measuring the rapid kinetics of free intracellular Ca2+ concentrations ([Ca2+]i). Thrombin produced a strong, concentration-dependent rise in [Ca2+]i with an onset within 3 s and peak levels achieved in less than 10 s. A similar response was also evoked by an SFLLRN-containing thrombin-agonist peptide. C6 cells did not respond to plasmin (25 nM-1.5 microM). By contrast, pretreatment of C6 cells with 100 nM plasmin significantly inhibited the [Ca2+]i response to thrombin and the thrombin-agonist peptide. The peak [Ca2+]i response to thrombin, in cells pretreated with plasmin, was reduced by approx. 50%. The effect of plasmin on the cellular response to thrombin was selective, as pretreatment of the cells with plasmin did not affect the [Ca2+]i response to platelet-activating factor. Di-isopropylphosphorylplasmin and plasminogen did not inhibit the cellular response to thrombin, indicating that plasmin activity is required and that occupancy of cellular plasmin(ogen)-binding sites alone is insufficient. These studies demonstrate that plasmin does not directly induce a response in C6 cells, but may affect cellular function by specifically modulating the thrombin response.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anonick P. K., Gonias S. L. Soluble fibrin preparations inhibit the reaction of plasmin with alpha 2-macroglobulin. Comparison with alpha 2-antiplasmin and leupeptin. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 1;275(Pt 1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2750053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Vassallo R. R., Jr, Belmonte E., Ahuja M., Cichowski K., Hoxie J. A. Structure and function of the human platelet thrombin receptor. Studies using monoclonal antibodies directed against a defined domain within the receptor N terminus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13795–13798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh K. P., Gurwitz D., Cunningham D. D., Bradshaw R. A. Reciprocal modulation of astrocyte stellation by thrombin and protease nexin-1. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1735–1743. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. p-Nitrophenyl-p'-guanidinobenzoate HCl: a new active site titrant for trypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I. Characterization of a functional thrombin receptor. Issues and opportunities. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):351–355. doi: 10.1172/JCI115592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dihanich M., Kaser M., Reinhard E., Cunningham D., Monard D. Prothrombin mRNA is expressed by cells of the nervous system. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):575–581. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90060-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich H., Costa T., Clouse K. A., Pluta R. M., Ogino Y., Coligan J. E., Burd P. R. Thrombin is a regulator of astrocytic endothelin-1. Brain Res. 1993 Jan 15;600(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91374-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Ofosu F. A., Moon D. G., Maraganore J. M. Thrombin structure and function: why thrombin is the primary target for antithrombotics. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1991 Feb;2(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerichs K. U., Feuerstein G. Z. Platelet-activating factor--key mediator in neuroinjury? Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1990 Summer;2(2):148–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurwitz D., Cunningham D. D. Thrombin modulates and reverses neuroblastoma neurite outgrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3440–3444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall S. W., Humphries J. E., Gonias S. L. Inhibition of cell surface receptor-bound plasmin by alpha 2-antiplasmin and alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12329–12336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J. Platelet-activating factor: a novel lipid agonist. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1992;33:65–78. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152833-1.50010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick-Davis K., Camussi G., Bussolino F., Baglioni C. Modulation of neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells by protein kinase C and platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18620–18625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Ahuja M., Belmonte E., Pizarro S., Parton R., Brass L. F. Internalization and recycling of activated thrombin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13756–13763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Wong Y. H., Vu T. K., Coughlin S. R. The cloned platelet thrombin receptor couples to at least two distinct effectors to stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and inhibit adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20831–20834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B. Specific receptors of platelet-activating factor, receptor heterogeneity, and signal transduction mechanisms. J Lipid Mediat. 1990 May-Jul;2(3-4):123–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Hein L., Kobilka B., Coughlin S. R. Kinetics of thrombin receptor cleavage on intact cells. Relation to signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9780–9786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., Moolenaar W. H. Thrombin receptor activation causes rapid neural cell rounding and neurite retraction independent of classic second messengers. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):411–419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. G., McDonough P. M., Brown J. H. Thrombin and trypsin act at the same site to stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and calcium mobilization. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):142–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kentroti S., Baker R., Lee K., Bruce C., Vernadakis A. Platelet-activating factor increases glutamine synthetase activity in early and late passage C-6 glioma cells. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Apr;28(4):497–506. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490280406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács T., Tordai A., Szász I., Sarkadi B., Gárdos G. Membrane depolarization inhibits thrombin-induced calcium influx and aggregation in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81532-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magócsi M., Sarkadi B., Kovács T., Gárdos G. Thrombin-induced activation of calcium transport pathways and their role in platelet functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 21;984(1):88–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neveu I., Jehan F., Jandrot-Perrus M., Wion D., Brachet P. Enhancement of the synthesis and secretion of nerve growth factor in primary cultures of glial cells by proteases: a possible involvement of thrombin. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):858–867. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni F., Ripoll D. R., Martin P. D., Edwards B. F. Solution structure of a platelet receptor peptide bound to bovine alpha-thrombin. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 24;31(46):11551–11557. doi: 10.1021/bi00161a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Felez J., Miles L. A. Cellular regulation of fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponting C. P., Marshall J. M., Cederholm-Williams S. A. Plasminogen: a structural review. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1992 Oct;3(5):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabo T., Gurwitz D., Motola L., Brodt P., Barak R., Elhanaty E. Structure-activity studies of the thrombin receptor activating peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 30;188(2):604–610. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91099-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Naughton M. A., Teng W., Hung D. T., Rose J., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Turck C. W., Coughlin S. R. Tethered ligand agonist peptides. Structural requirements for thrombin receptor activation reveal mechanism of proteolytic unmasking of agonist function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13146–13149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer A. I., Adelman B. Plasmin inhibition of platelet function and of arachidonic acid metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):456–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI111720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer A. I., Maas A. K., Ware J. A., Johnson P. C., Rittenhouse S. E., Salzman E. W. Platelet protein phosphorylation, elevation of cytosolic calcium, and inositol phospholipid breakdown in platelet activation induced by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):73–79. doi: 10.1172/JCI112576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi G. Y., Hau J. S., Wang S. J., Wu I. S., Chang B. I., Lin M. T., Chow Y. H., Chang W. C., Wing L. Y., Jen C. J. Plasmin and the regulation of tissue-type plasminogen activator biosynthesis in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19363–19368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D. Inositol phospholipid turnover in PAF transmembrane signalling. Lipids. 1991 Dec;26(12):1028–1033. doi: 10.1007/BF02536496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder F. Platelet-activating factor and related acetylated lipids as potent biologically active cellular mediators. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 1):C697–C708. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.5.C697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturk A., ten Cate J. W., Hosford D., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Braquet P. The synthesis, catabolism, and pathophysiological role of platelet-activating factor. Adv Lipid Res. 1989;23:219–276. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024923-7.50010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tas P. W., Koschel K. Thrombin reverts the beta-adrenergic agonist-induced morphological response in rat glioma C6 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Jul;189(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiruppathi C., Lum H., Andersen T. T., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Malik A. B. Thrombin receptor 14-amino acid peptide binds to endothelial cells and stimulates calcium transients. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):L595–L601. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.5.L595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trejo J., Chambard J. C., Karin M., Brown J. H. Biphasic increase in c-jun mRNA is required for induction of AP-1-mediated gene transcription: differential effects of muscarinic and thrombin receptor activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4742–4750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassallo R. R., Jr, Kieber-Emmons T., Cichowski K., Brass L. F. Structure-function relationships in the activation of platelet thrombin receptors by receptor-derived peptides. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6081–6085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Hung D. T., Charo I., Coughlin S. R. Domains specifying thrombin-receptor interaction. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):674–677. doi: 10.1038/353674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong C., Hayzer D. J., Corson M. A., Runge M. S. Molecular cloning of the rat vascular smooth muscle thrombin receptor. Evidence for in vitro regulation by basic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16975–16979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


