Abstract
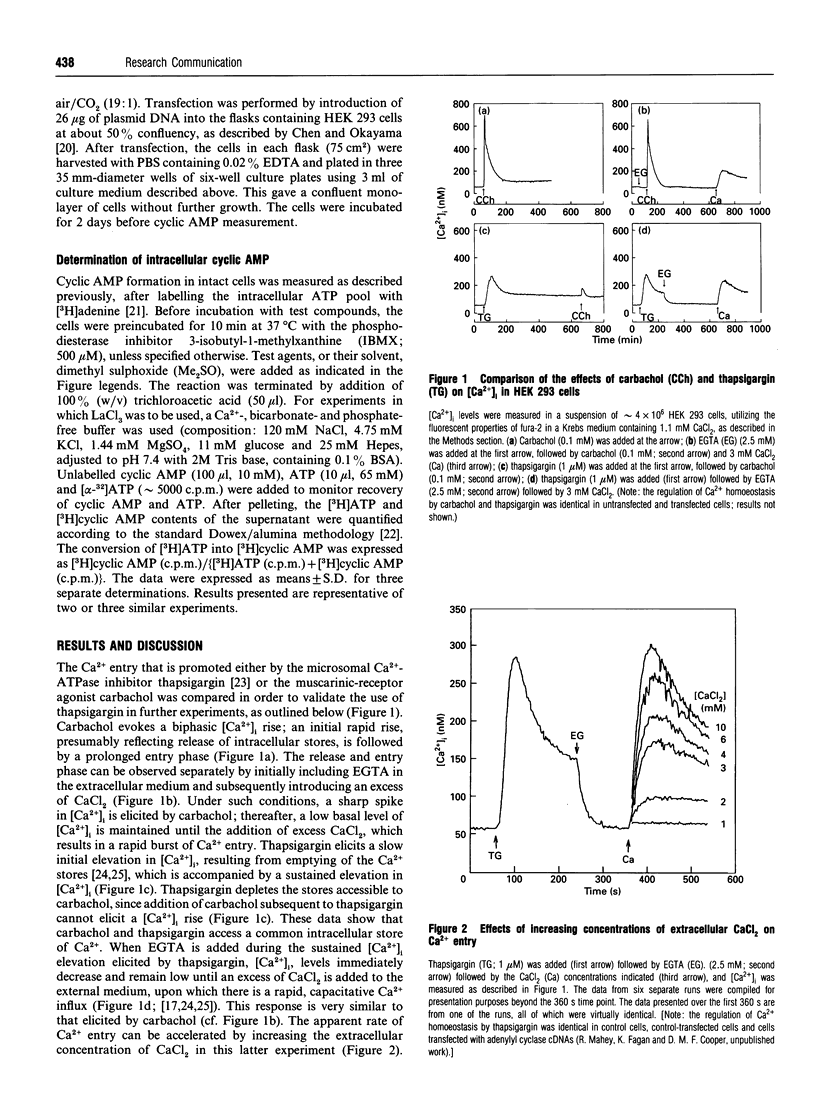
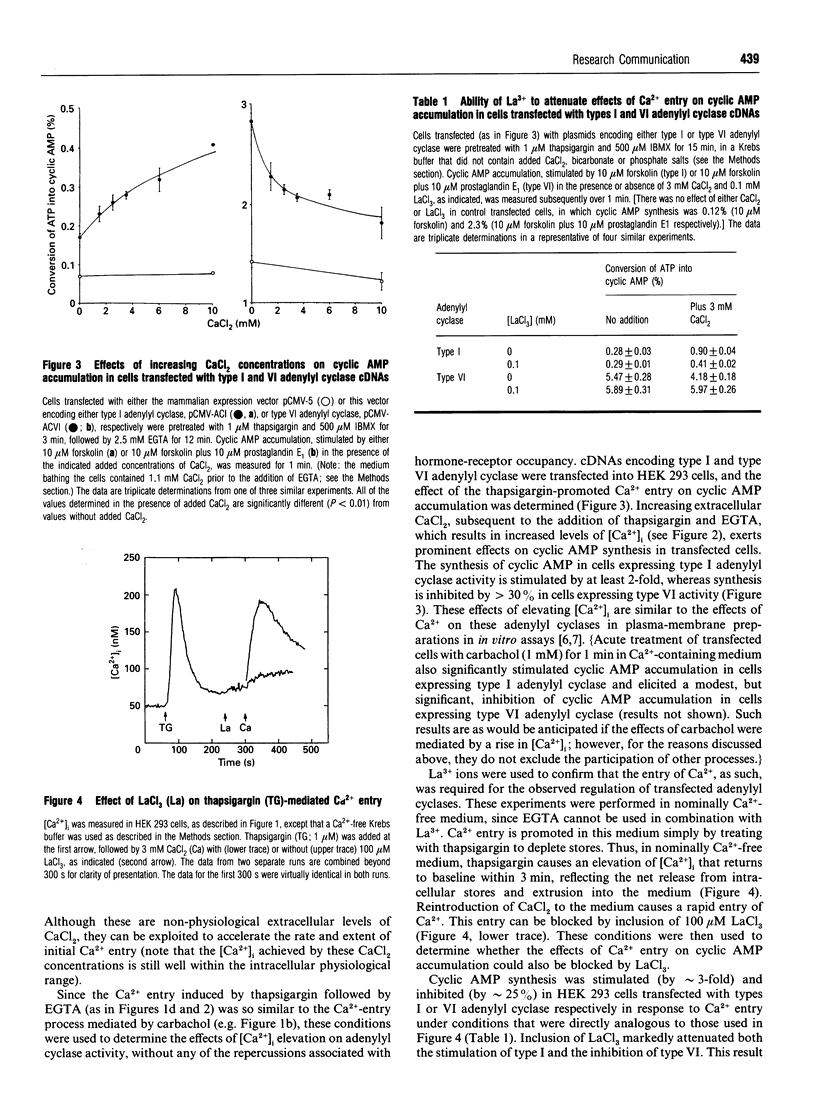
A number of the currently described adenylyl cyclase species can be regulated by Ca2+ in the submicromolar concentration range in in vitro assays. The regulatory significance of these observations hinges on whether a physiological elevation in intracellular Ca2+ can regulate these cyclase activities in intact cells. However, achieving a physiological elevation in cytosolic Ca2+ is complicated by the fact that hormonal increases in cytosolic Ca2+ can be accompanied by additional effects, such as liberation of beta gamma-subunits of G-proteins and activation of protein kinase C, which can have disparate type-specific effects on cyclase activities. Therefore we have devised a strategy based on capacitative Ca2+ entry to show that, when types I and VI adenylyl cyclase are expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells, they are stimulated and inhibited respectively by Ca2+ entry. Blockade of Ca2+ entry by La3+ ions blocks the effects of Ca2+ entry on cyclic AMP synthesis. These studies establish that adenylyl cyclases deemed to be sensitive to Ca2+ in in vitro assays can be regulated by physiological Ca2+ entry, and therefore, such cyclases are poised to respond to changes in intracellular Ca2+ in tissues in which they are expressed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin R. A., Oibo J. A., Allen R. A. Calcium inhibition of cardiac adenylyl cyclase. Evidence for two distinct sites of inhibition. Cell Calcium. 1991 Jan;12(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90081-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M., Brooker G. Ca(2+)-inhibited adenylyl cyclase in cardiac tissue. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Feb;14(2):34–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90027-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Smith M. M., Tanner L. I., Harden T. K. Muscarinic cholinergic receptors of two cell lines that regulate cyclic AMP metabolism by different molecular mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):395–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federman A. D., Conklin B. R., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R., Bourne H. R. Hormonal stimulation of adenylyl cyclase through Gi-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):159–161. doi: 10.1038/356159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garritsen A., Zhang Y., Firestone J. A., Browning M. D., Cooper D. M. Inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation in intact NCB-20 cells as a direct result of elevation of cytosolic Ca2+. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1630–1639. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):353–356. doi: 10.1038/355353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz O., Chen J., Premont R. T., Iyengar R. Stimulation of specific types of Gs-stimulated adenylyl cyclases by phorbol ester treatment. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3829–3832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsushika S., Chen L., Kawabe J., Nilakantan R., Halnon N. J., Homcy C. J., Ishikawa Y. Cloning and characterization of a sixth adenylyl cyclase isoform: types V and VI constitute a subgroup within the mammalian adenylyl cyclase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8774–8778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Coussen F., Bakalyar H. A., Tang W. J., Feinstein P. G., Orth K., Slaughter C., Reed R. R., Gilman A. G. Adenylyl cyclase amino acid sequence: possible channel- or transporter-like structure. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1558–1564. doi: 10.1126/science.2472670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Lehman T. C., Frankenfield C. D., Zwaagstra J. C., Watson P. A. Molecular diversity in the adenylylcyclase family. Evidence for eight forms of the enzyme and cloning of type VI. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24858–24862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. Y., Takemura H., Obie J. F., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Effects of MeCh, thapsigargin, and La3+ on plasmalemmal and intracellular Ca2+ transport in lacrimal acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1006–C1015. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. R., Han P. L., Hwang P. M., Feinstein P. G., Davis R. L., Reed R. R. The Drosophila learning and memory gene rutabaga encodes a Ca2+/Calmodulin-responsive adenylyl cyclase. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90185-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M. S., Sziber P. P., Quinn W. G. Loss of calcium/calmodulin responsiveness in adenylate cyclase of rutabaga, a Drosophila learning mutant. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig K. D., Conklin B. R., Herzmark P., Taussig R., Bourne H. R. Type II adenylylcyclase integrates coincident signals from Gs, Gi, and Gq. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13900–13905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mons N., Yoshimura M., Cooper D. M. Discrete expression of Ca2+/calmodulin-sensitive and Ca(2+)-insensitive adenylyl cyclases in the rat brain. Synapse. 1993 May;14(1):51–59. doi: 10.1002/syn.890140108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premont R. T., Chen J., Ma H. W., Ponnapalli M., Iyengar R. Two members of a widely expressed subfamily of hormone-stimulated adenylyl cyclases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9809–9813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Inositol phosphates and calcium entry. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;26:143–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sihra T. S., Bogonez E., Nicholls D. G. Localized Ca2+ entry preferentially effects protein dephosphorylation, phosphorylation, and glutamate release. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1983–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Type-specific regulation of adenylyl cyclase by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1500–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.1962211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Krupinski J., Gilman A. G. Expression and characterization of calmodulin-activated (type I) adenylylcyclase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8595–8603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O. Role of Ca2(+)-ATPases in regulation of cellular Ca2+ signalling, as studied with the selective microsomal Ca2(+)-ATPase inhibitor, thapsigargin. Agents Actions. 1990 Jan;29(1-2):8–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01964706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Cooper D. M. Cloning and expression of a Ca(2+)-inhibitable adenylyl cyclase from NCB-20 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6716–6720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Cooper D. M. Type-specific stimulation of adenylylcyclase by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4604–4607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


