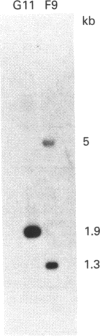
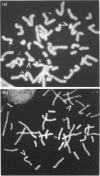
Abstract
Arylamine N-acetyltransferase is encoded at two loci, AAC-1 and AAC-2, on human chromosome 8. The products of the two loci are able to catalyse N-acetylation of arylamine carcinogens, such as benzidine and other xenobiotics. AAC-2 is polymorphic and individuals carrying the slow-acetylator phenotype are more susceptible to benzidine-induced bladder cancer. We have identified yeast artificial chromosome clones encoding AAC-1 and AAC-2 and have used the cloned DNAs as fluorescent probes for in situ hybridization. The hybridization patterns allow assignment of AAC-1 and AAC-2 to chromosome 8p21.3-23.1, a region in which deletions have been associated with bladder cancer [Knowles, Shaw and Proctor (1993) Oncogene 8, 1357-1364].
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand R., Riley J. H., Butler R., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. A 3.5 genome equivalent multi access YAC library: construction, characterisation, screening and storage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):1951–1956. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum M., Demierre A., Grant D. M., Heim M., Meyer U. A. Molecular mechanism of slow acetylation of drugs and carcinogens in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5237–5241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum M., Grant D. M., McBride W., Heim M., Meyer U. A. Human arylamine N-acetyltransferase genes: isolation, chromosomal localization, and functional expression. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;9(3):193–203. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright R. A., Glashan R. W., Rogers H. J., Ahmad R. A., Barham-Hall D., Higgins E., Kahn M. A. Role of N-acetyltransferase phenotypes in bladder carcinogenesis: a pharmacogenetic epidemiological approach to bladder cancer. Lancet. 1982 Oct 16;2(8303):842–845. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90810-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coroneos E., Gordon J. W., Kelly S. L., Wang P. D., Sim E. Drug metabolising N-acetyltransferase activity in human cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 9;1073(3):593–599. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coroneos E., Sim E. Arylamine N-acetyltransferase activity in human cultured cell lines. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):481–486. doi: 10.1042/bj2940481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribb A. E., Grant D. M., Miller M. A., Spielberg S. P. Expression of monomorphic arylamine N-acetyltransferase (NAT1) in human leukocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Dec;259(3):1241–1246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribb A. E., Nakamura H., Grant D. M., Miller M. A., Spielberg S. P. Role of polymorphic and monomorphic human arylamine N-acetyltransferases in determining sulfamethoxazole metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 24;45(6):1277–1282. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90280-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Mashimo M., Suzuki T. Correlation between acetylator phenotypes and genotypes of polymorphic arylamine N-acetyltransferase in human liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12757–12760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T. Sequences and expression of alleles of polymorphic arylamine N-acetyltransferase of human liver. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18140–18147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisawa T., Deguchi T. Structure and restriction fragment length polymorphism of genes for human liver arylamine N-acetyltransferases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1252–1257. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90676-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards Y. H., Barlow J. H., Konialis C. P., Povey S., Butterworth P. H. Assignment of the gene determining human carbonic anhydrase, CAI, to chromosome 8. Ann Hum Genet. 1986 May;50(Pt 2):123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1986.tb01030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flammang T. J., Yamazoe Y., Guengerich F. P., Kadlubar F. F. The S-acetyl coenzyme A-dependent metabolic activation of the carcinogen N-hydroxy-2-aminofluorene by human liver cytosol and its relationship to the aromatic amine N-acetyltransferase phenotype. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Dec;8(12):1967–1970. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.12.1967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. M. Molecular genetics of the N-acetyltransferases. Pharmacogenetics. 1993 Feb;3(1):45–50. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199302000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman D., Risch A., Camilleri J. P., Sim E. Genotyping human polymorphic arylamine N-acetyltransferase: identification of new slow allotypic variants. Pharmacogenetics. 1992 Oct;2(5):217–226. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199210000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman D., Sim E. N-acetyltransferase polymorphism. Comparison of phenotype and genotype in humans. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 8;42(5):1007–1014. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90282-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells: genetic, immunologic, and biochemical analysis with Chinese hamster cell hybrids containing selected human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):193–197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly S. L., Sim E. Expression of N-acetyl transferase in a human monocytic cell-line, U937. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1991 Jan;10(1):33–38. doi: 10.1177/096032719101000106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. A., Shaw M. E., Proctor A. J. Deletion mapping of chromosome 8 in cancers of the urinary bladder using restriction fragment length polymorphisms and microsatellite polymorphisms. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1357–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J., Han C. Y., Lin B. K., Hardy S. Slow acetylator mutations in the human polymorphic N-acetyltransferase gene in 786 Asians, blacks, Hispanics, and whites: application to metabolic epidemiology. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):827–834. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsako S., Deguchi T. Cloning and expression of cDNAs for polymorphic and monomorphic arylamine N-acetyltransferases from human liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4630–4634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst M. R., Blum M., Fasshauer I., D'Orazio D., Meyer U. A., Wild D. The role of the human acetylation polymorphism in the metabolic activation of the food carcinogen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ). Carcinogenesis. 1992 Oct;13(10):1713–1717. doi: 10.1093/carcin/13.10.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard E. A., Povey S., Spurr N. K., Phillips I. R. Chromosomal localization of a cytochrome b5 gene to human chromosome 18 and a cytochrome b5 pseudogene to the X chromosome. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):302–308. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim E., Hickman D., Coroneos E., Kelly S. L. Arylamine N-acetyltransferase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):304–309. doi: 10.1042/bst0200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., Solomon E., Pajunen L. Immunochemical analysis of the N-acetyl hexosaminidases in human-mouse hybrids made using a double selective system. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;18(3):136–148. doi: 10.1159/000130758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatsis K. P., Martell K. J., Weber W. W. Diverse point mutations in the human gene for polymorphic N-acetyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6333–6337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatsis K. P., Weber W. W. Structural heterogeneity of Caucasian N-acetyltransferase at the NAT1 gene locus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Feb 15;301(1):71–76. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A., Hickman D., Gordon J. W., Sim E. Arylamine N-acetyltransferase in human red blood cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 25;44(6):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90373-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong S., Wolf C. R., Spurr N. K. Chromosomal assignment and linkage analysis of the human glutathione S-transferase mu gene (GSTM1) using intron specific polymerase chain reaction. Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;90(4):435–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00220473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]