Abstract
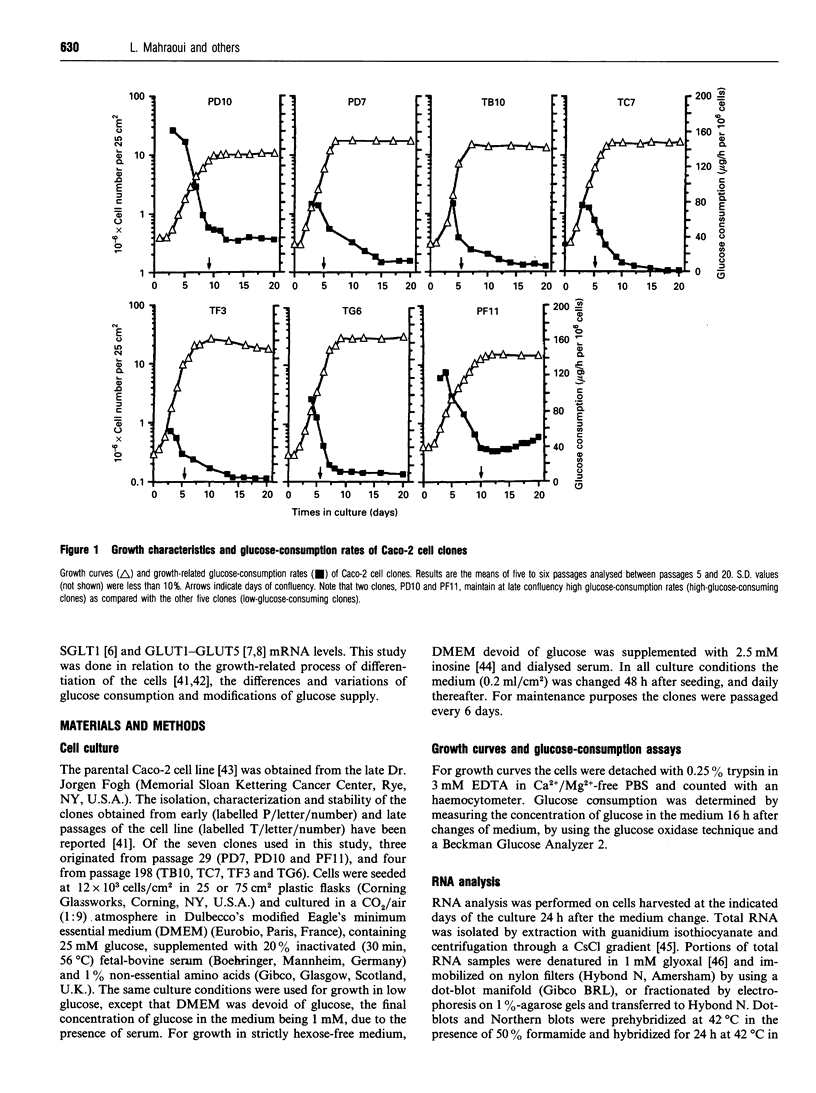
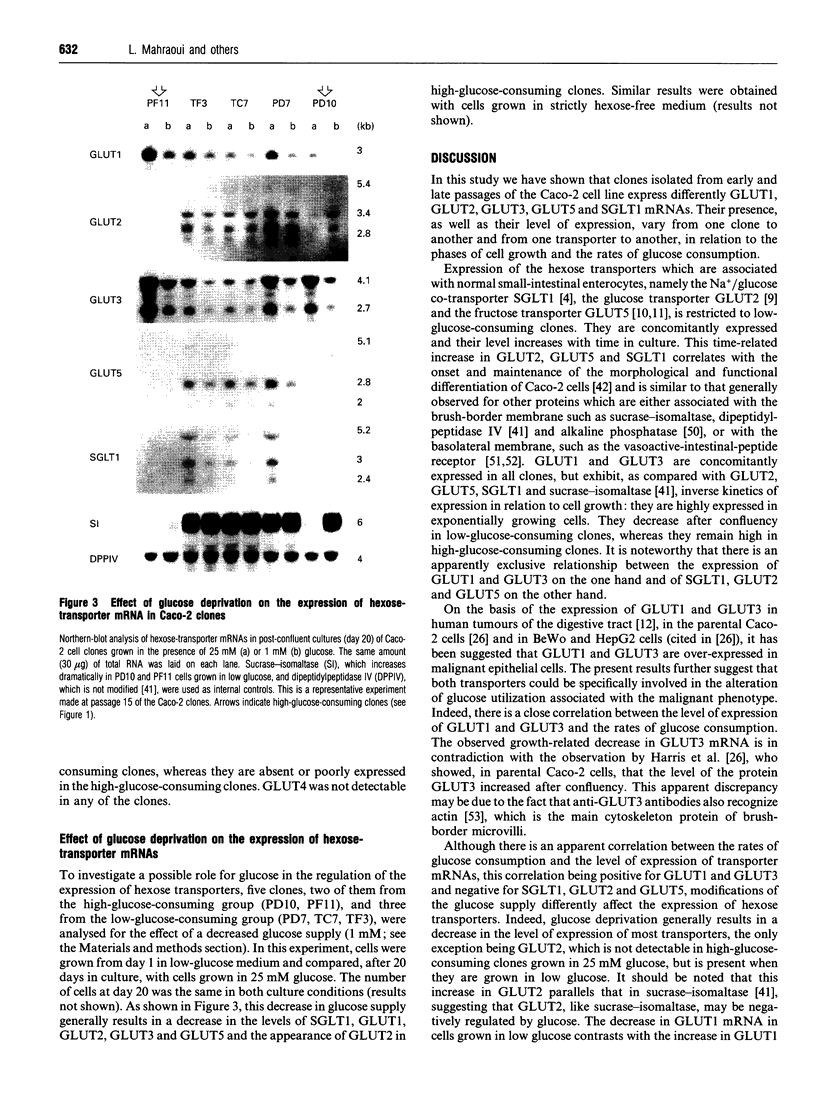
Seven clones from the Caco-2 cell line, three isolated from passage 29 (PD7, PD10, PF11) and four from passage 198 (TB10, TC7, TF3, TG6), all of them selected on the basis of differences in the levels of expression of sucrase-isomaltase and rates of glucose consumption, were analysed for the expression of hexose-transporter mRNAs (SGLT1, GLUT1-GLUT5) in relation to the phases of cell growth and the associated variations of the rates of glucose consumption. All clones showed a similar pattern of evolution of the rates of glucose consumption, which decreased from the exponential to the late-stationary phase, but differed, in a 1-40-fold range, in the values observed at late postconfluency. According to these values, clones could be divided into high- (PD10, PF11) and low-glucose-consuming cells (PD7, TB10, TC7, TF3 and TG6). GLUT1 and GLUT3 mRNAs were expressed in all clones and showed a similar pattern of evolution: their level decreased, from the exponential to the stationary phase, in close correlation with the decrease in rates of glucose consumption, with only high-glucose-consuming clones maintaining high levels in the stationary phase. In contrast, SGLT1, GLUT2 and GLUT5 mRNAs were only expressed, like sucrase-isomaltase mRNA, in the low-glucose-consuming clones, and their level increased from the exponential to the stationary phase, in parallel with the differentiation of the cells. GLUT4 was undetectable in all the clones. Glucose deprivation generally resulted in a discrete decrease in the levels of all transporter mRNAs in all clones, one exception being GLUT2, which in the high-glucose-consuming clones is only detectable when the cells are grown in low glucose. These clones should be ideal tools with which to study in vitro, at the single-cell level, how these transporters concur to the utilization and transport of hexoses and how their exclusive or co-ordinated expression is regulated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Burant C. F., Takeda J., Lin D., Fukumoto H., Seino S. Molecular biology of mammalian glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):198–208. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Transformation of rat fibroblasts by FSV rapidly increases glucose transporter gene transcription. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1495–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.3029870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blais A., Bissonnette P., Berteloot A. Common characteristics for Na+-dependent sugar transport in Caco-2 cells and human fetal colon. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01871231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burant C. F., Takeda J., Brot-Laroche E., Bell G. I., Davidson N. O. Fructose transporter in human spermatozoa and small intestine is GLUT5. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14523–14526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantret I., Lacasa M., Chevalier G., Ruf J., Islam I., Mantei N., Edwards Y., Swallow D., Rousset M. Sequence of the complete cDNA and the 5' structure of the human sucrase-isomaltase gene. Possible homology with a yeast glucoamylase. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 1;285(Pt 3):915–923. doi: 10.1042/bj2850915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantret I., Lacasa M., Chevalier G., Swallow D., Rousset M. Monensin and forskolin inhibit the transcription rate of sucrase-isomaltase but not the stability of its mRNA in Caco-2 cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 9;328(1-2):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80964-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantret I., Trugnan G., Dussaulx E., Zweibaum A., Rousset M. Monensin inhibits the expression of sucrase-isomaltase in Caco-2 cells at the mRNA level. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross H. S., Quaroni A. Inhibition of sucrose-isomaltase expression by EGF in the human colon adenocarcinoma cells Caco-2. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):C1173–C1183. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.6.C1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmoul D., Lacasa M., Chantret I., Swallow D. M., Trugnan G. Isolation of a cDNA probe for the human intestinal dipeptidylpeptidase IV and assignment of the gene locus DPP4 to chromosome 2. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;54(Pt 3):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. O., Hausman A. M., Ifkovits C. A., Buse J. B., Gould G. W., Burant C. F., Bell G. I. Human intestinal glucose transporter expression and localization of GLUT5. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C795–C800. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Mueckler M. M., Usher P., Lodish H. F. Elevated levels of glucose transport and transporter messenger RNA are induced by ras or src oncogenes. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1492–1495. doi: 10.1126/science.3103217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Fogh J. M., Orfeo T. One hundred and twenty-seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):221–226. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Bell G. I. Facilitative glucose transporters: an expanding family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jan;15(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90125-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasset E., Bernabeu J., Pinto M. Epithelial properties of human colonic carcinoma cell line Caco-2: effect of secretagogues. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C410–C418. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green F., Edwards Y., Hauri H. P., Povey S., Ho M. W., Pinto M., Swallow D. Isolation of a cDNA probe for a human jejunal brush-border hydrolase, sucrase-isomaltase, and assignment of the gene locus to chromosome 3. Gene. 1987;57(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. S., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., James D. E. Polarized distribution of glucose transporter isoforms in Caco-2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7556–7560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M., Hanafusa H. Analysis of a functional change in membrane in the process of cell transformation by Rous sarcoma virus; alteration in the characteristics of sugar transport. Virology. 1970 Aug;41(4):647–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraki Y., McMorrow I. M., Birnbaum M. J. The regulation of glucose transporter gene expression by cyclic adenosine monophosphate in NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1470–1476. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-9-1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isselbacher K. J. Increased uptake of amino acids and 2-deoxy-D-glucose by virus-transformed cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):585–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laburthe M., Rousset M., Rouyer-Fessard C., Couvineau A., Chantret I., Chevalier G., Zweibaum A. Development of vasoactive intestinal peptide-responsive adenylate cyclase during enterocytic differentiation of Caco-2 cells in culture. Evidence for an increased receptor level. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10180–10184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bivic A., Quaroni A., Nichols B., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Biogenetic pathways of plasma membrane proteins in Caco-2, a human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1351–1361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahraoui L., Rousset M., Dussaulx E., Darmoul D., Zweibaum A., Brot-Laroche E. Expression and localization of GLUT-5 in Caco-2 cells, human small intestine, and colon. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):G312–G318. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.3.G312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Erickson R. H., Gum J. R., Yoshioka M., Gum E., Kim Y. S. Biosynthesis of alkaline phosphatase during differentiation of the human colon cancer cell line Caco-2. Gastroenterology. 1990 May;98(5 Pt 1):1199–1207. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90334-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Brauchbar M., Bucher K., Hauri H. P. Sorting of endogenous plasma membrane proteins occurs from two sites in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M., Chantret I., Darmoul D., Trugnan G., Sapin C., Green F., Swallow D., Zweibaum A. Reversible forskolin-induced impairment of sucrase-isomaltase mRNA levels, biosynthesis, and transport to the brush border membrane in Caco-2 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Dec;141(3):627–635. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M., Laburthe M., Pinto M., Chevalier G., Rouyer-Fessard C., Dussaulx E., Trugnan G., Boige N., Brun J. L., Zweibaum A. Enterocytic differentiation and glucose utilization in the human colon tumor cell line Caco-2: modulation by forskolin. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jun;123(3):377–385. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M., Trugnan G., Brun J. L., Zweibaum A. Inhibition of the post-translational processing of microvillar hydrolases is associated with a specific decreased expression of sucrase-isomaltase and an increased turnover of glucose in Caco-2 cells treated with monensin. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G., Kessler M., Hosang M., Weber J., Schmidt U. Biochemistry of the Na+, D-glucose cotransporter of the small-intestinal brush-border membrane. The state of the art in 1984. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 3;779(3):343–379. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. The J.E. Purkyne lecture: the insertion of stalked proteins of the brush border membranes: the state of the art in 1988. Biochem Int. 1989 Jan;18(1):15–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd P. R., Gould G. W., Colville C. A., McCoid S. C., Gibbs E. M., Kahn B. B. Distribution of GLUT3 glucose transporter protein in human tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B. Facilitated glucose transporters in epithelial cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:591–608. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.003111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon P. H., Beaulieu J. F. Transient mosaic patterns of morphological and functional differentiation in the Caco-2 cell line. Gastroenterology. 1992 Aug;103(2):414–423. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90829-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Donovan J. A., Van Ness B. G., Fellows R. E., Pessin J. E. Glucose-dependent regulation of glucose transport activity, protein, and mRNA in primary cultures of rat brain glial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15594–15601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Ramlal T., Donovan J. A., Doering T. P., Sandra A., Klip A., Pessin J. E. Insulin and glucose-dependent regulation of the glucose transport system in the rat L6 skeletal muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6587–6595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. J. Hexose transport in normal and in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):2978–2983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertheimer E., Sasson S., Cerasi E., Ben-Neriah Y. The ubiquitous glucose transporter GLUT-1 belongs to the glucose-regulated protein family of stress-inducible proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. K., Bramwell M. E., Harris H. Hexose transport in hybrids between malignant and normal cells. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):232–235. doi: 10.1038/294232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wice B. M., Trugnan G., Pinto M., Rousset M., Chevalier G., Dussaulx E., Lacroix B., Zweibaum A. The intracellular accumulation of UDP-N-acetylhexosamines is concomitant with the inability of human colon cancer cells to differentiate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M. The intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:575–589. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Seino Y., Fukumoto H., Koh G., Yano H., Inagaki N., Yamada Y., Inoue K., Manabe T., Imura H. Over-expression of facilitative glucose transporter genes in human cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91263-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]