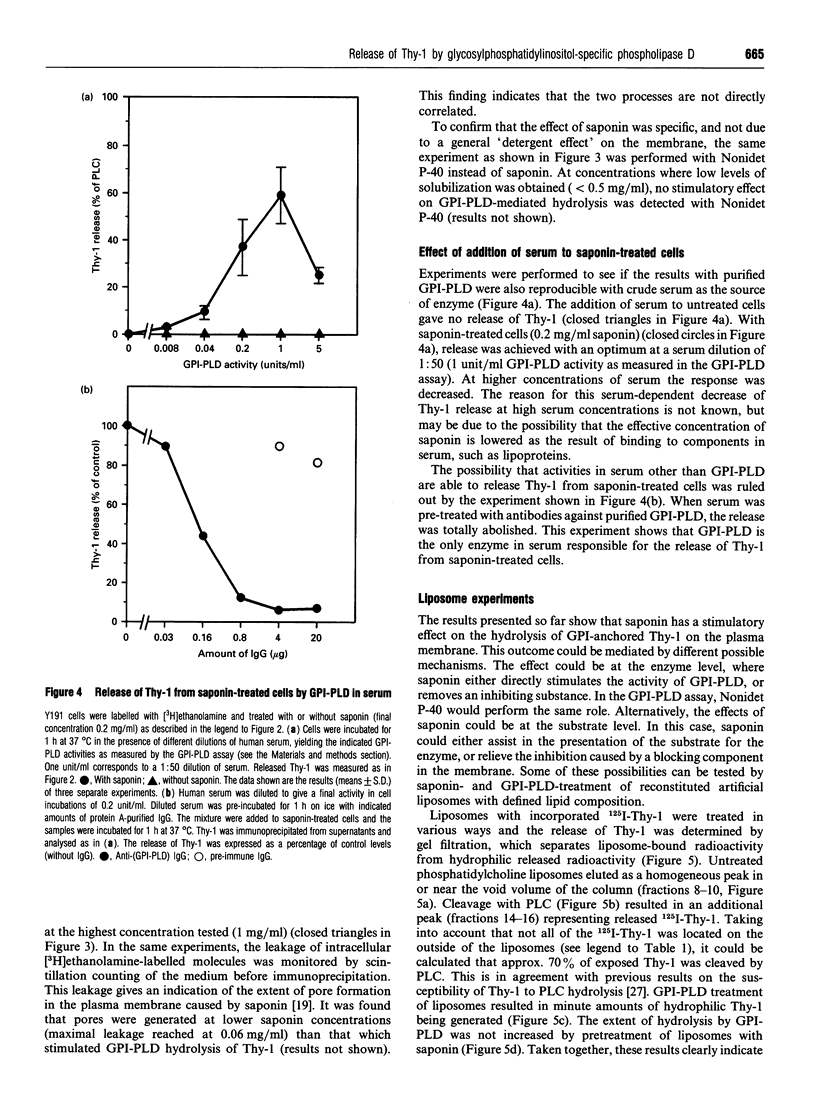
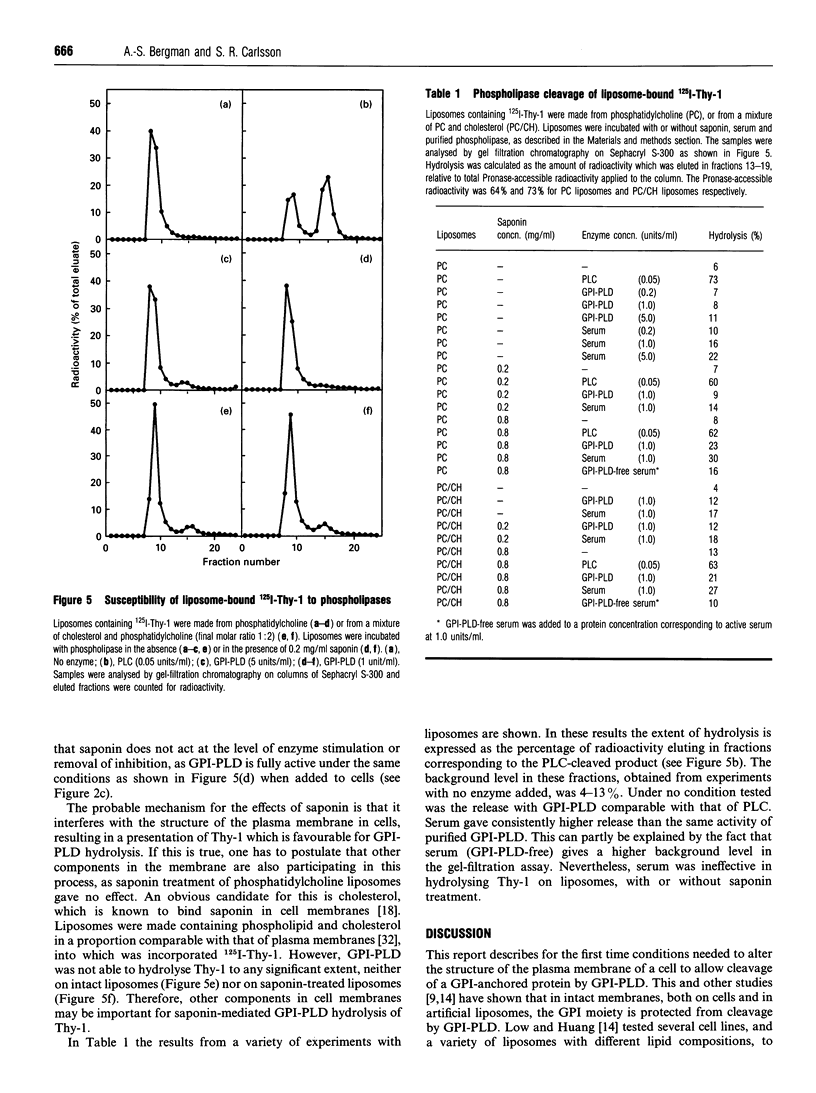
Abstract
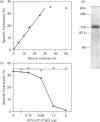
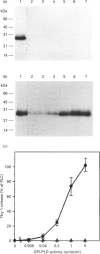
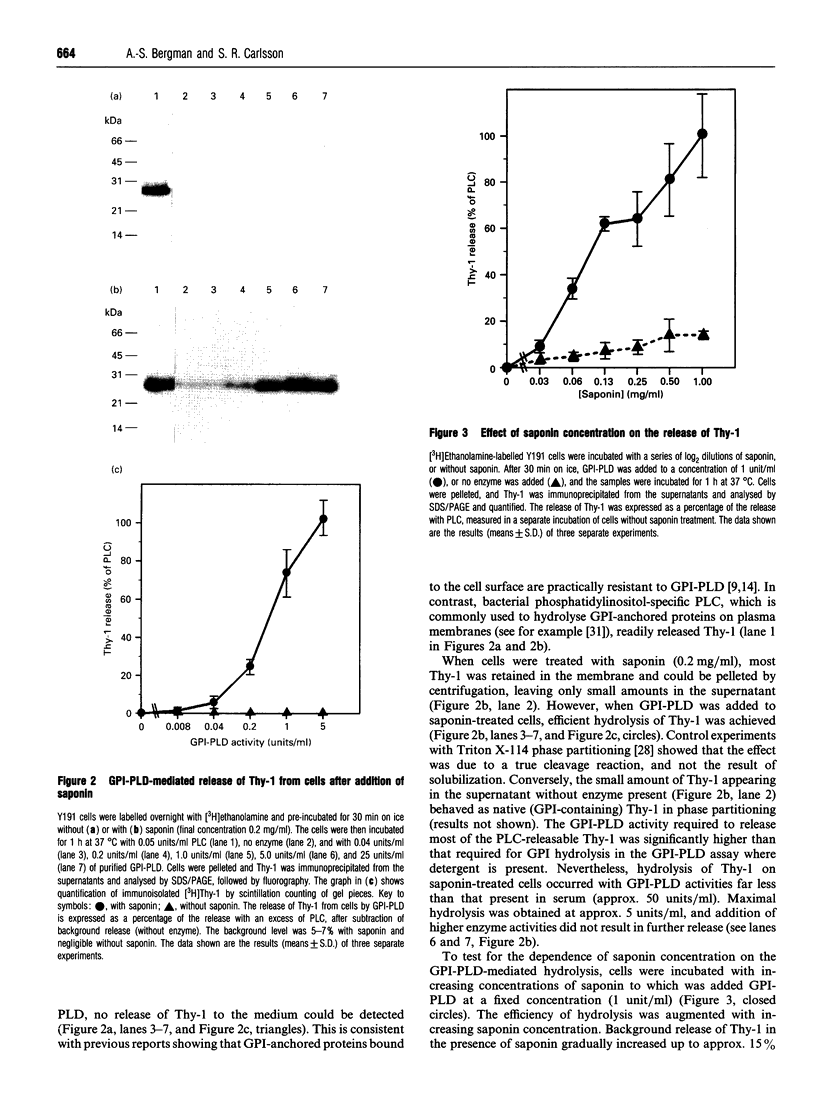
A glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D (GPI-PLD) was purified from human serum and used for studies on the release of GPI-anchored Thy-1 glycoprotein from mouse T lymphoma cells Y191. Previous studies have shown that whereas GPI-PLD is highly active against detergent-solubilized GPI-anchored proteins, it is normally unable to release GPI-containing proteins anchored in a lipid bilayer. Confirming these findings, the addition of GPI-PLD to intact Y191 cells did not result in cleavage of Thy-1. However, pretreatment of cells with saponin, a cholesterol-sequestering agent, rendered Thy-1 susceptible to hydrolysis. Very little solubilization of GPI-containing Thy-1 occurred under these conditions. From experiments with reconstituted liposomes it was inferred that the effect of saponin on cells was to aid in the presentation of Thy-1 to GPI-PLD. Furthermore, it was concluded that cholesterol-saponin complexes formed in the membrane were not alone responsible for the effect. Rather, additional molecules in the plasma membrane are possibly involved in the presentation of Thy-1 on saponin-treated cells. This finding may have implications for a physiological role of circulating GPI-PLD in the regulation of GPI-anchored proteins on cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almqvist P., Carlsson S. R. Characterization of a hydrophilic form of Thy-1 purified from human cerebrospinal fluid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12709–12715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almqvist P., Carlsson S. Identification of a neodeterminant in complexes of human brain Thy-1. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Aug;14(8):734–738. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., HORNE R. W., GLAUERT A. M., DINGLE J. T., LUCY J. A. Action of saponin on biological cell membranes. Nature. 1962 Dec 8;196:952–955. doi: 10.1038/196952a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A. Interactions between GPI-anchored proteins and membrane lipids. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):338–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner J., Skrabal P., Hauser H. Single bilayer vesicles prepared without sonication. Physico-chemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):322–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzozowski A. M., Derewenda U., Derewenda Z. S., Dodson G. G., Lawson D. M., Turkenburg J. P., Bjorkling F., Huge-Jensen B., Patkar S. A., Thim L. A model for interfacial activation in lipases from the structure of a fungal lipase-inhibitor complex. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):491–494. doi: 10.1038/351491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S. R., Fukuda M. The lysosomal membrane glycoprotein lamp-1 is transported to lysosomes by two alternative pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Aug 1;296(2):630–639. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90619-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S. R., Stigbrand T. I. Alterations in expression and glycosylation pattern of the Thy-1 glycoprotein during maturation and transformation of mouse T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1837–1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S. R., Stigbrand T. I. Purification and characterization of the mouse thymocyte Thy-1 glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):641–647. doi: 10.1042/bj2110641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerneus D. P., Ueffing E., Posthuma G., Strous G. J., van der Ende A. Detergent insolubility of alkaline phosphatase during biosynthetic transport and endocytosis. Role of cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3150–3155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Spiazzi A., Hyman R., Bron C. Anchoring of membrane proteins via phosphatidylinositol is deficient in two classes of Thy-1 negative mutant lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3291–3296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04642.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Hereld D., Shak S., Krakow J., Englund P. T., Nussenzweig V. A glycan-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D in human serum. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.2443973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Hom J., Schenkman S. Purification of a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13760–13764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A. Colworth Medal Lecture. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors: the tale of a tail. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):243–256. doi: 10.1042/bst0200243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gögelein H., Hüby A. Interaction of saponin and digitonin with black lipid membranes and lipid monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):32–38. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90547-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoener M. C., Brodbeck U. Phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase D is an amphiphilic glycoprotein that in serum is associated with high-density lipoproteins. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):747–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoener M. C., Stieger S., Brodbeck U. Isolation and characterization of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-anchor-specific phospholipase D from bovine brain. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):593–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M. More than just a membrane anchor. Curr Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):617–619. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90183-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Li S., Fung W. J., Hulmes J. D., Reik L., Pan Y. C., Low M. G. Purification and characterization of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17738–17745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Saltiel A. R. Emerging functional roles for the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchor. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jul;117(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01871561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Huang K. S. Factors affecting the ability of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D to degrade the membrane anchors of cell surface proteins. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 15;279(Pt 2):483–493. doi: 10.1042/bj2790483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Prasad A. R. A phospholipase D specific for the phosphatidylinositol anchor of cell-surface proteins is abundant in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. The glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):427–454. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg K. G., Ying Y. S., Kamen B. A., Anderson R. G. Cholesterol controls the clustering of the glycophospholipid-anchored membrane receptor for 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2931–2938. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scallon B. J., Fung W. J., Tsang T. C., Li S., Kado-Fong H., Huang K. S., Kochan J. P. Primary structure and functional activity of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase D. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):446–448. doi: 10.1126/science.2017684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., White S. P., Otwinowski Z., Yuan W., Gelb M. H., Sigler P. B. Interfacial catalysis: the mechanism of phospholipase A2. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1541–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2274785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Structure, biosynthesis, and function of glycosylphosphatidylinositols. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5413–5422. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschesche V. R., Wulff G. Chemie und Biologie der Saponine. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 1973;30:461–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassler M., Jonasson I., Persson R., Fries E. Differential permeabilization of membranes by saponin treatment of isolated rat hepatocytes. Release of secretory proteins. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):407–415. doi: 10.1042/bj2470407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G. Lipid traffic in animal cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:247–275. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]