Abstract
The phosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) to inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (InsP4) is catalysed by InsP3 3-kinase. A method is presented for a rapid purification of the enzyme from human platelets. The purified enzyme was identified as a polypeptide of M(r) 69,000-70,000 after SDS/PAGE. It had a specific activity of 1.45 +/- 0.1 mumol/min per mg, and the degree of stimulation by Ca2+/calmodulin was 17-fold at saturating calmodulin and 10 microM free Ca2+. The Km for InsP3 and for ATP was 2.0 microM and 2.5 mM respectively. Human platelet InsP3 3-kinase was not recognized by immunodetection with anti-(InsP3 3-kinase A) or anti-(InsP3 3-kinase B) antibodies. These data provide the first biochemical evidence for the existence of a novel InsP3 3-kinase isoenzyme in human platelets, which is distinct from previously reported InsP3 3-kinase A and InsP3 3-kinase B.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Altin J. G., Karjalainen A., Bygrave F. L. Stimulation of hepatic inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate kinase activity by Ca2+-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):697–701. doi: 10.1042/bj2560697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. Y., Kim H. K., Lee S. Y., Moon K. H., Sim S. S., Kim J. W., Chung H. K., Rhee S. G. Molecular cloning and expression of a complementary DNA for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.2157285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conigrave A., Patwardhan A., Broomhead L., Roufogalis B. A purification strategy for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from rat liver based upon heparin interaction chromatography. Cell Signal. 1992 May;4(3):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(92)90070-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Dangelmaier C. A., Smith J. B. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in human platelets. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):109–114. doi: 10.1042/bj2460109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erneux C., Van Sande J., Miot F., Cochaux P., Decoster C., Dumont J. E. A mechanism in the control of intracellular cAMP level: the activation of a calmodulin-sensitive phosphodiesterase by a rise of intracellular free calcium. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Dec;43(2-3):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Pattison G. Regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate kinase activity after stimulation of human T cell antigen receptor. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1538–1541. doi: 10.1172/JCI112986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. Is inositol tetrakisphosphate the second messenger that controls Ca2+ entry into cells? Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;26:161–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. G., Rittenhouse S. E. Inhibition of protein kinase C by staurosporine promotes elevated accumulations of inositol trisphosphates and tetrakisphosphate in human platelets exposed to thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6070–6074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Sim S. S., Kim J. W., Moon K. H., Kim J. H., Rhee S. G. Purification and properties of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from rat brain. Susceptibility to calpain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9434–9440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. N., Barnes S., Wallace R. W. Phosphorylation by protein kinase C inactivates an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase purified from human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 16;170(3):1371–1376. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90546-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Wallace R. W., Barnes S. Purification and properties of a human platelet inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jun;303(2):412–420. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphee C. H., Reifsnyder D. H., Moore T. A., Lerea K. M., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation results in activation of a cAMP phosphodiesterase in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10353–10358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
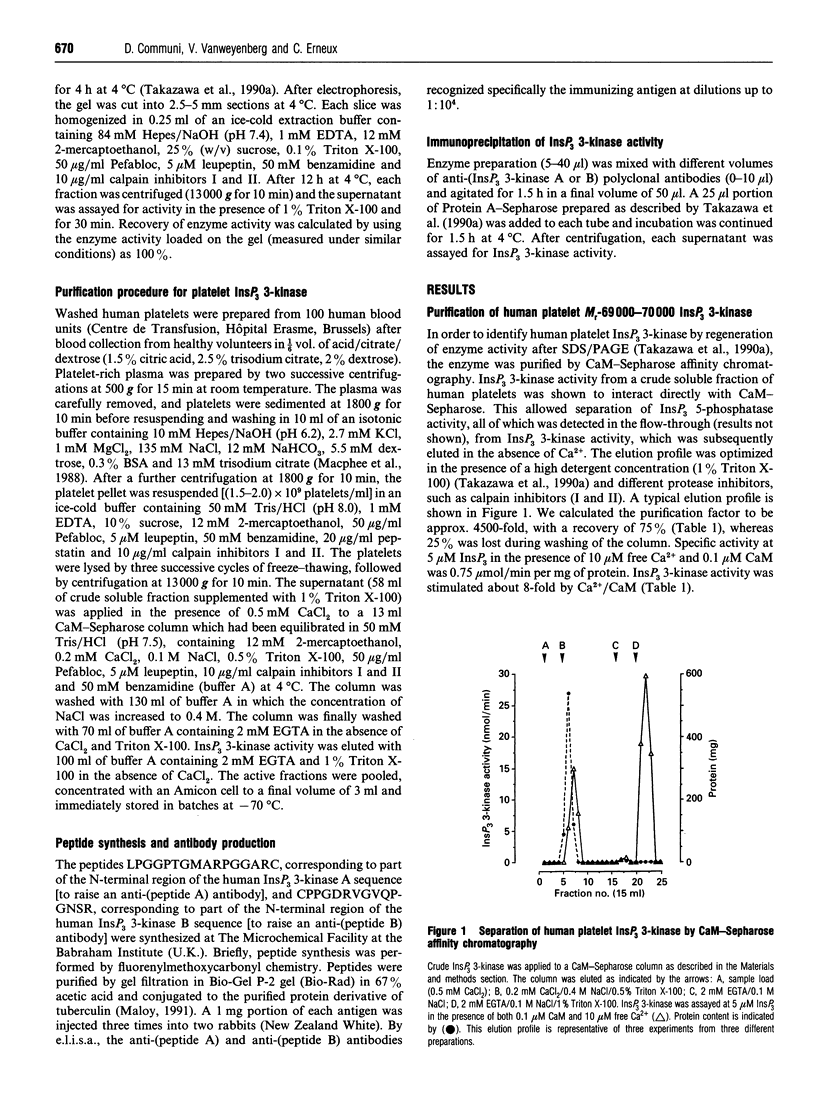
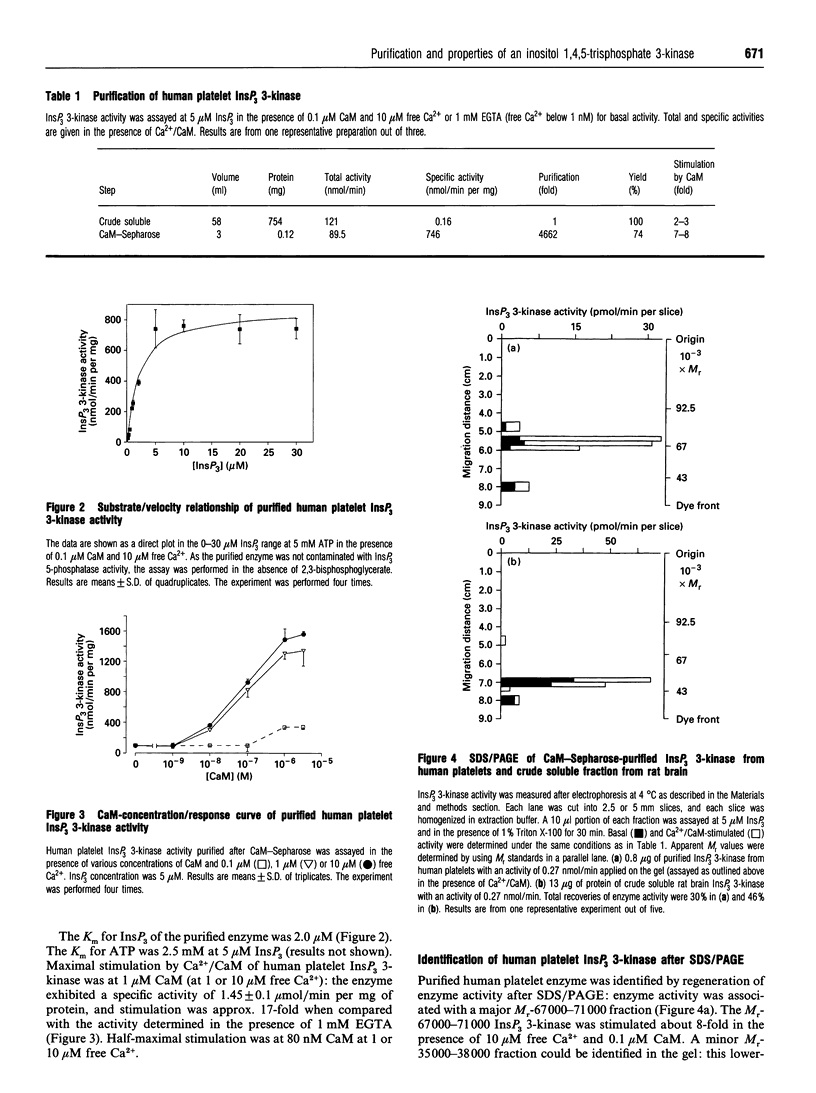
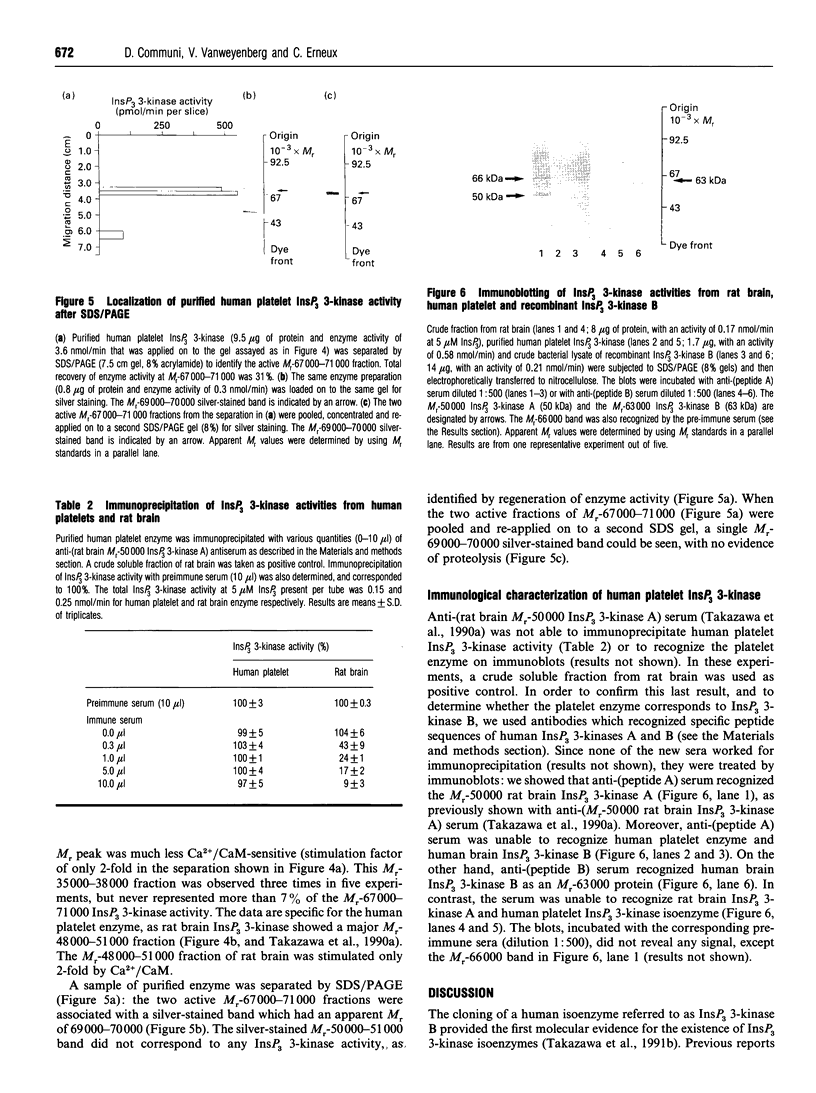
- Takazawa K., Lemos M., Delvaux A., Lejeune C., Dumont J. E., Erneux C. Rat brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Ca2(+)-sensitivity, purification and antibody production. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):213–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2680213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazawa K., Perret J., Dumont J. E., Erneux C. Molecular cloning and expression of a human brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):529–535. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91449-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazawa K., Perret J., Dumont J. E., Erneux C. Molecular cloning and expression of a new putative inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase isoenzyme. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):883–886. doi: 10.1042/bj2780883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazawa K., Vandekerckhove J., Dumont J. E., Erneux C. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a rat brain cDNA encoding a Ca2+/calmodulin-sensitive inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 15;272(1):107–112. doi: 10.1042/bj2720107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truglia J. A., Stracher A. Purification and characterization of a calcium dependent sulfhydryl protease from human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):814–822. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujinaka T., Sakon M., Kambayashi J., Kosaki G. Cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins by two forms of Ca2+ activated neutral proteases in human platelets. Thromb Res. 1982 Oct 15;28(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90257-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Hirata M., Kuriyama H. Purification and characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from pig aortic smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):129–134. doi: 10.1042/bj2510129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]