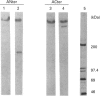
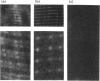
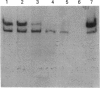
Abstract
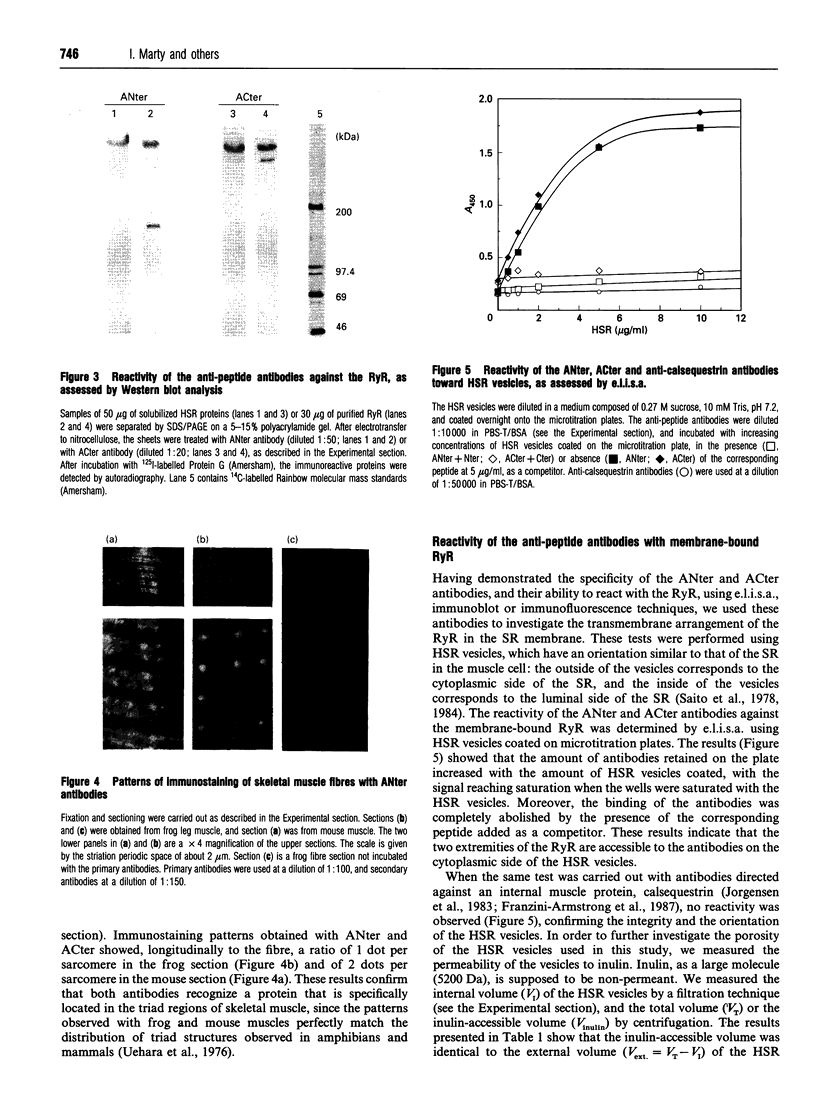
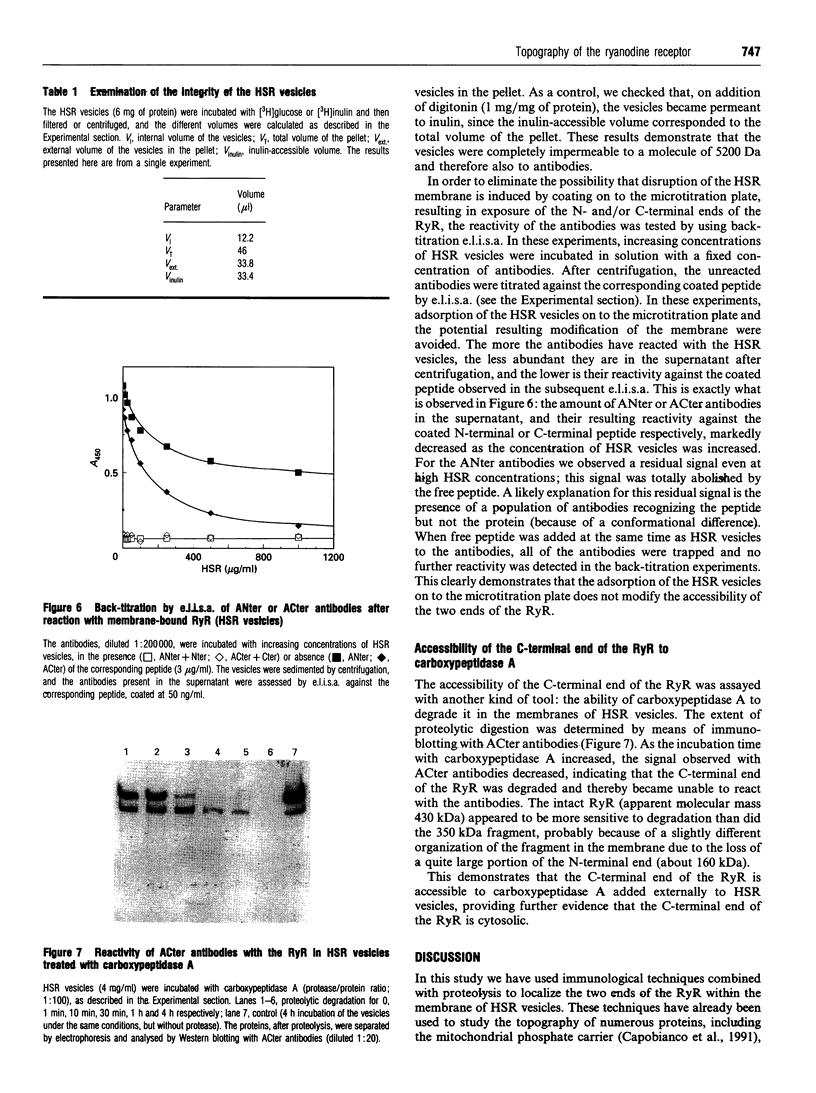
Antibodies were raised against synthetic peptides corresponding to the N-terminal (residues 2-15) and the C-terminal (residues 5027-5037) parts of the rabbit skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. The specificity of the antibodies generated was tested by e.l.i.s.a., Western blotting and immunofluorescence. All these tests demonstrated the specificity of the antibodies and their ability to react with both the native and the denaturated ryanodine receptor. Both the anti-N-terminus and the anti-C-terminus antibodies bound to sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles, indicating that each end of the membrane-embedded ryanodine receptor is exposed to the cytoplasmic side of the vesicles. These immunological data were complemented with proteolysis experiments using carboxypeptidase A. Carboxypeptidase A induced degradation of the C-terminal end of the ryanodine receptor in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles and a concomitant loss of reactivity of the anti-C-terminus antibodies in Western blots, providing extra evidence for the cytoplasmic localization of the C-terminal end of the ryanodine receptor.
Full text
PDF

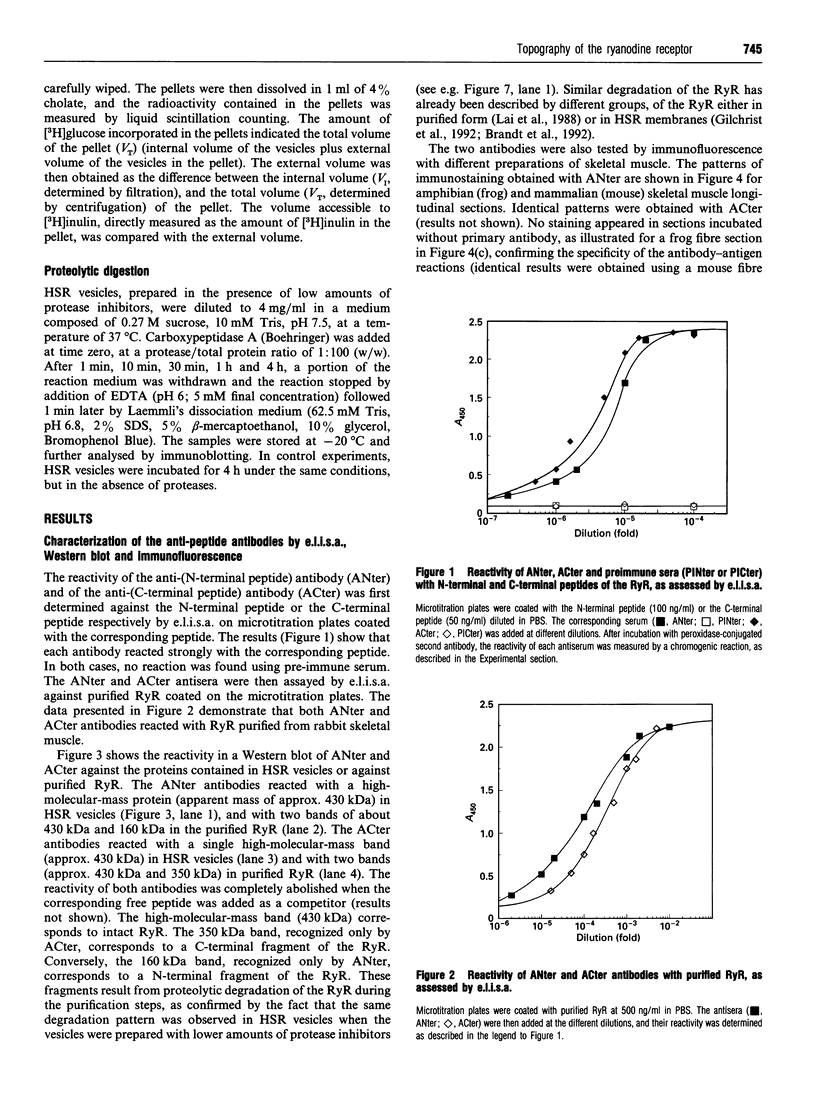


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block B. A., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C. Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2587–2600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandolin G., Boulay F., Dalbon P., Vignais P. V. Orientation of the N-terminal region of the membrane-bound ADP/ATP carrier protein explored by antipeptide antibodies and an arginine-specific endoprotease. Evidence that the accessibility of the N-terminal residues depends on the conformational state of the carrier. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1093–1100. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt N. R., Caswell A. H., Brandt T., Brew K., Mellgren R. L. Mapping of the calpain proteolysis products of the junctional foot protein of the skeletal muscle triad junction. J Membr Biol. 1992 Apr;127(1):35–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00232756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco L., Brandolin G., Palmieri F. Transmembrane topography of the mitochondrial phosphate carrier explored by peptide-specific antibodies and enzymatic digestion. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):4963–4969. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. R., Zhang L., MacLennan D. H. Characterization of a Ca2+ binding and regulatory site in the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23318–23326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu A., Sumbilla C., Scales D., Piazza A., Inesi G. Trypsin digestion of junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2827–2833. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Meeran K., Cairns M. T., Baldwin S. A. Peptide-specific antibodies as probes of the orientation of the glucose transporter in the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9347–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C., Kenney L. J., Varriano-Marston E. The structure of calsequestrin in triads of vertebrate skeletal muscle: a deep-etch study. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):49–56. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist J. S., Wang K. K., Katz S., Belcastro A. N. Calcium-activated neutral protease effects upon skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum protein structure and calcium release. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20857–20865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L. Topography of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:999–1027. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.005031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. O., Shen A. C., Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H. Ultrastructural localization of calsequestrin in rat skeletal muscle by immunoferritin labeling of ultrathin frozen sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1573–1581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. H., Ohnishi S. T., Ikemoto N. Kinetic studies of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9662–9668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kometani T., Kasai M. Ionic permeability of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles measured by light scattering method. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jul 18;41(4):295–308. doi: 10.1007/BF01871994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H., Block B. A., Meissner G. Evidence for a junctional feet-ryanodine receptor complex from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):704–709. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91411-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Misra M., Xu L., Smith H. A., Meissner G. The ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Evidence for a cooperatively coupled, negatively charged homotetramer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16776–16785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandala S. M., Slayman C. W. The amino and carboxyl termini of the Neurospora plasma membrane H+-ATPase are cytoplasmically located. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16276–16281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks A. R., Fleischer S., Tempst P. Surface topography analysis of the ryanodine receptor/junctional channel complex based on proteolysis sensitivity mapping. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13143–13149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty I., Brandolin G., Gagnon J., Brasseur R., Vignais P. V. Topography of the membrane-bound ADP/ATP carrier assessed by enzymatic proteolysis. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):4058–4065. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews I., Colyer J., Mata A. M., Green N. M., Sharma R. P., Lee A. G., East J. M. Evidence for the cytoplasmic location of the N- and C-terminal segments of sarcoplasmic reticulum (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):683–688. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92653-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Rousseau E., Lai F. A. Structural and functional correlation of the trypsin-digested Ca2+ release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1715–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radermacher M., Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Inui M., Chadwick C., Fleischer S. Cryo-EM of the native structure of the calcium release channel/ryanodine receptor from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):936–940. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81900-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam M., Nguyen D. L., Rivier J., Sargent P. B., Lindstrom J. Transmembrane topography of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: immunochemical tests contradict theoretical predictions based on hydrophobicity profiles. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2633–2643. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Seiler S., Chu A., Fleischer S. Preparation and morphology of sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):875–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Wang C. T., Fleischer S. Membrane asymmetry and enhanced ultrastructural detail of sarcoplasmic reticulum revealed with use of tannic acid. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):601–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoshan-Barmatz V., Zarka A. Trypsin destruction of the high affinity ryanodine binding sites of the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16772–16779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Bauer H. Monoclonal antibody against the carboxy terminal peptide of pp60src of Rous sarcoma virus reacts with native pp60src. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1479–1485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01343.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thielens N. M., Van Dorsselaer A., Gagnon J., Arlaud G. J. Chemical and functional characterization of a fragment of C1-s containing the epidermal growth factor homology region. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 10;29(14):3570–3578. doi: 10.1021/bi00466a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Saito A., Inui M., Fleischer S. Three-dimensional architecture of the calcium channel/foot structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):167–170. doi: 10.1038/338167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., Kuwazuru Y., Sumizawa T., Ichikawa M., Ikeda S., Uda T., Akiyama S. Cytoplasmic orientation and two-domain structure of the multidrug transporter, P-glycoprotein, demonstrated with sequence-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16282–16291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Fujii J., Otsu K., Phillips M., Green N. M., Lai F. A., Meissner G., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2244–2256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]