Abstract
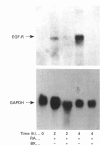
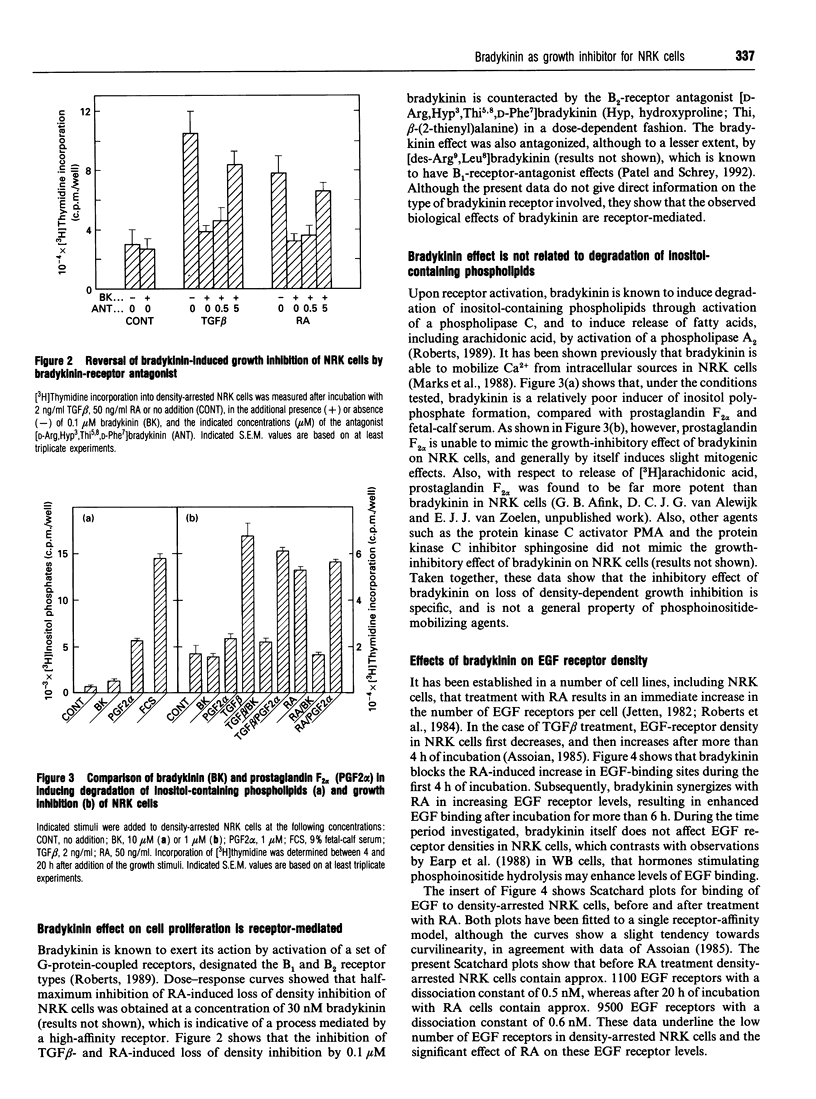
Normal rat kidney fibroblasts, grown to density arrest in the presence of epidermal growth factor (EGF), can be induced to undergo phenotypic transformation by treatment with transforming growth factor beta or retinoic acid. Here we show that bradykinin blocks this growth-stimulus-induced loss of density-dependent growth arrest by a specific receptor-mediated mechanism. The effects of bradykinin are specific, and are not mimicked by other phosphoinositide-mobilizing agents such as prostaglandin F2 alpha. Northern-blot analysis and receptor-binding studies demonstrate that bradykinin also inhibits the retinoic acid-induced increase in EGF receptor levels in these cells. These studies provide additional evidence that EGF receptor levels modulate EGF-induced expression of the transformed phenotype in these cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoian R. K. Biphasic effects of type beta transforming growth factor on epidermal growth factor receptors in NRK fibroblasts. Functional consequences for epidermal growth factor-stimulated mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9613–9617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Frolik C. A., Roberts A. B., Miller D. M., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta controls receptor levels for epidermal growth factor in NRK fibroblasts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binggeli R., Weinstein R. C. Deficits in elevating membrane potential of rat fibrosarcoma cells after cell contact. Cancer Res. 1985 Jan;45(1):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Ishii S., Richert N., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Epidermal growth factor regulates the expression of its own receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8374–8378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earp H. S., Hepler J. R., Petch L. A., Miller A., Berry A. R., Harris J., Raymond V. W., McCune B. K., Lee L. W., Grisham J. W. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and hormones stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and increase EGF receptor protein synthesis and mRNA levels in rat liver epithelial cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13868–13874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Pol J. A., Klos D. J., Hamilton P. D. Modulation of transforming growth factor alpha-dependent expression of epidermal growth factor receptor gene by transforming growth factor beta, triiodothyronine, and retinoic acid. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Nov;41(3):159–170. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240410306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Regulation of receptor expression by agonists: transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Jun;14(6):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90124-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamanaka R., Ono M., Kuratomi Y., Mizoguchi H., Hirai R., Kohno K., Kuwano M. Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-nonresponsive variants of normal rat kidney cell line: response to EGF and transforming growth factor-beta. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Jan;186(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90213-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel L., Blat C., Chatelain G. Regulation of cell proliferation inhibitory and stimulatory factors diffused by 3T3 cultured cells. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Apr;123(1):139–143. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Armour R., Baldwin J. H., Brown K. D., Yeh Y. C. Density-dependent regulation of growth of BSC-1 cells in cell culture: control of growth by serum factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. G., Santon J. B., Gill G. N. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Feb;3(2):400–408. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-2-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M. Effects of retinoic acid on the binding and mitogenic activity of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Mar;110(3):235–240. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast R., Fürstenberger G., Marks F. Activation of a keratinocyte phospholipase A2 by bradykinin and 4 beta-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Evidence for a receptor-GTP-binding protein versus a protein-kinase-C mediated mechanism. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):941–950. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusuhara M., Yamaguchi K., Kuranami M., Suzaki A., Ishikawa S., Moon H., Adachi I., Hori S., Handa S. Stimulation of anchorage-independent cell growth by endothelin in NRK 49F cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 1;52(11):3011–3014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Song X. H. Bradykinin and bombesin rapidly stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation of a 120-kDa group of proteins in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7746–7749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication and the control of growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 4;560(1):1–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. W., Kruskal B. A., Maxfield F. R. Simultaneous addition of EGF prolongs the increase in cytosolic free calcium seen in response to bradykinin in NRK-49F cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Sep;136(3):519–525. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. L., Hyldahl L., Larsson O., Engström W., Rees A. R. Bradykinin blocks the action of EGF, but not PDGF, on fibroblast division. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81459-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg K. C., Carpenter G. Dexamethasone and retinoic acid regulate the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor mRNA by distinct mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Nov;149(2):244–251. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041490210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E., Villereal M. L. Lys-bradykinin stimulates Na+ influx and DNA synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):979–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallen C. J., Tong P. H. Elevation of membrane tyrosine phosphatase activity in density-dependent growth-arrested fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6996–7000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. V., Schrey M. P. Inhibition of DNA synthesis and growth in human breast stromal cells by bradykinin: evidence for independent roles of B1 and B2 receptors in the respective control of cell growth and phospholipid hydrolysis. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 15;52(2):334–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijksen G., Völler M. C., Van Zoelen E. J. Orthovanadate both mimics and antagonizes the transforming growth factor beta action on normal rat kidney cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Feb;154(2):393–401. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijksen G., Völler M. C., van Zoelen E. J. The role of protein tyrosine phosphatases in density-dependent growth control of normal rat kidney cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 May 3;322(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81117-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A., Kazakoff P., Nebelsick J. Density-induced down regulation of epidermal growth factor receptors. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1990 May;26(5):537–542. doi: 10.1007/BF02624098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A., Kazakoff P., Ruff E., Kuszynski C., Nebelsick J. Regulatory effects of cell density on the binding of transforming growth factor beta, epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 1;48(15):4266–4271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Lamb L. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B. Antagonistic actions of retinoic acid and dexamethasone on anchorage-independent growth and epidermal growth factor binding of normal rat kidney cells. Cancer Res. 1984 Apr;44(4):1635–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. A. Bradykinin receptors: characterization, distribution and mechanisms of signal transduction. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(4):237–252. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. A., Gullick W. J. Bradykinin receptor number and sensitivity to ligand stimulation of mitogenesis is increased by expression of a mutant ras oncogene. J Cell Sci. 1989 Nov;94(Pt 3):527–535. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero M., Srivastava S. K., Fleming T. P., Ron D., Eva A. NIH3T3 fibroblasts transformed by the dbl oncogene show altered expression of bradykinin receptors: effect on inositol lipid turnover. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):767–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. L., Assoian R., Rosner M. R. Transforming growth factor-beta increases transcription of the genes encoding the epidermal growth factor receptor and fibronectin in normal rat kidney fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19519–19524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. L., Rosner M. R. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression by retinoic acid and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3230–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., van Paridon P. A., Verlaan I., Wirtz K. W., de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Inositol phosphate metabolism in bradykinin-stimulated human A431 carcinoma cells. Relationship to calcium signalling. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):129–135. doi: 10.1042/bj2440129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Eijnden-Van Raaij A. J., Koornneef I., Van Oostwaard T. M., Feyen A., Kruijer W., De Laat S. W., Van Zoelen E. J. Purification of a growth factor related to platelet-derived growth factor and a type beta transforming growth factor secreted by mouse neuroblastoma cells. A general strategy for the purification of basic polypeptide growth factors. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2570375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark B. Local starvation for epidermal growth factor cannot explain density-dependent inhibition of normal human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1619–1621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieser R. J., Schütz S., Tschank G., Thomas H., Dienes H. P., Oesch F. Isolation and characterization of a 60-70-kD plasma membrane glycoprotein involved in the contact-dependent inhibition of growth. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2681–2692. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Blitterswijk W. J., Hilkmann H., de Widt J., van der Bend R. L. Phospholipid metabolism in bradykinin-stimulated human fibroblasts. I. Biphasic formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine, controlled by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10337–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Blitterswijk W. J., Hilkmann H., de Widt J., van der Bend R. L. Phospholipid metabolism in bradykinin-stimulated human fibroblasts. II. Phosphatidylcholine breakdown by phospholipases C and D; involvement of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10344–10350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J. Phenotypic transformation of normal rat kidney cells: a model for studying cellular alterations in oncogenesis. Crit Rev Oncog. 1991;2(4):311–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J. Receptor-ligand interaction: a new method for determining binding parameters without a priori assumptions on non-specific binding. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):549–556. doi: 10.1042/bj2620549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J., Tertoolen L. G. Transforming growth factor-beta enhances the extent of intercellular communication between normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12075–12081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J., van Oostwaard T. M., de Laat S. W. The role of polypeptide growth factors in phenotypic transformation of normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):64–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J., van Rotterdam W., Ward-Van Oostwaard T. M., Feijen A. Phenotypic transformation of normal rat kidney cells by transforming growth factor beta is not paralleled by enhanced production of a platelet-derived growth factor. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 1;209(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Eijnden-van Raaij A. J., Koornneef I., van Zoelen E. J. A new method for high yield purification of type beta transforming growth factor from human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):16–23. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]