Abstract
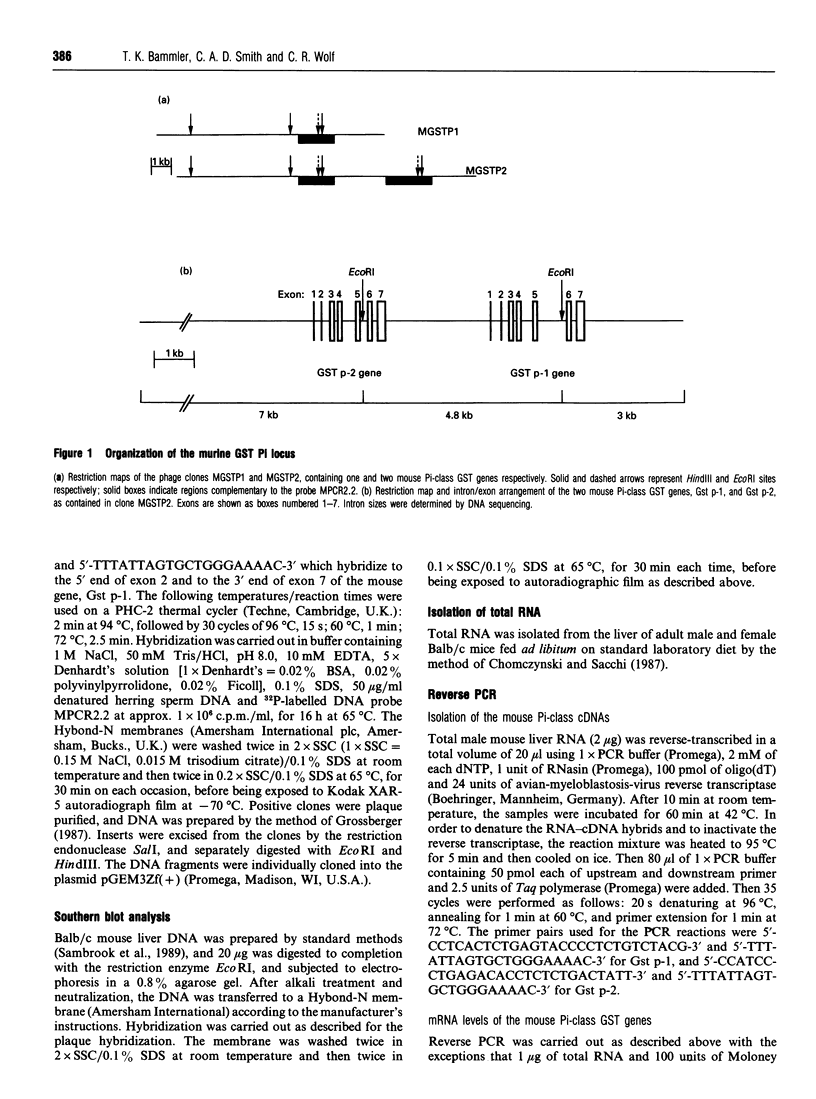
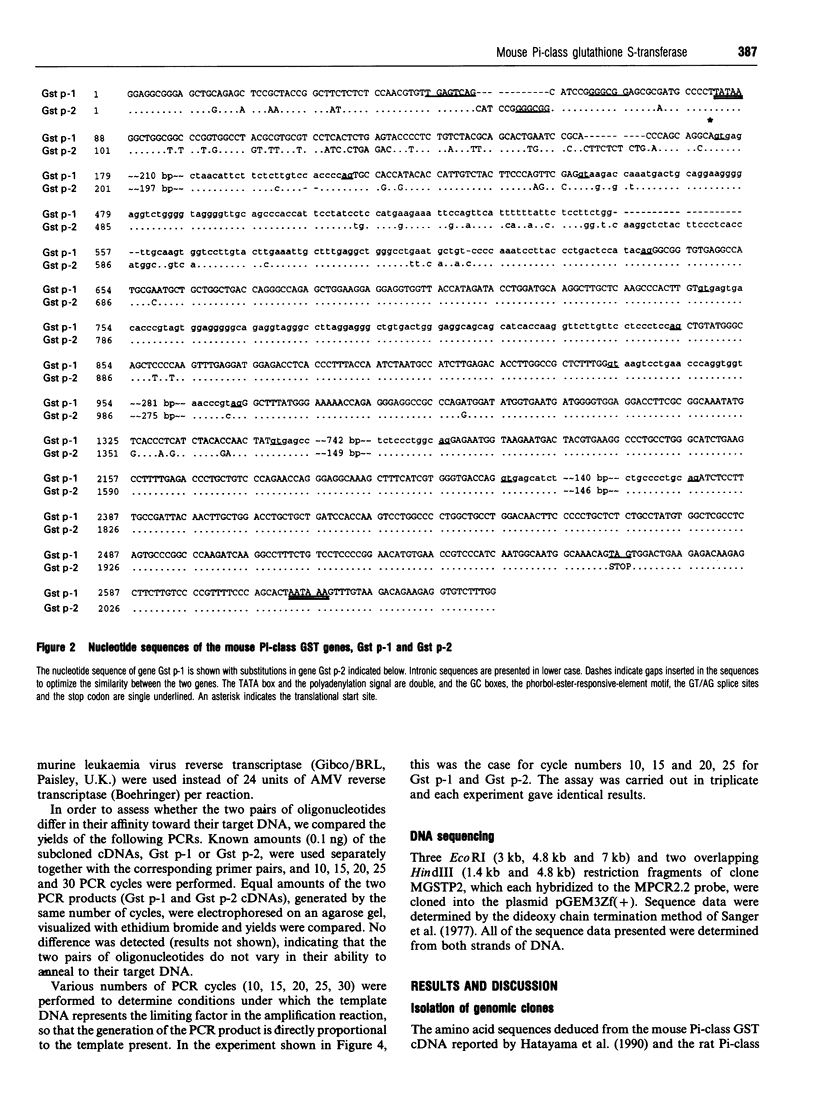
Pi-class glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) play an important role in the detoxification of chemical toxins and mutagens and are implicated in neoplastic development and drug resistance. In all species characterized to date, only one functional Pi-class GST gene has been described. In this report we have identified two actively transcribed murine Pi-class GST genes, Gst p-1 and Gst p-2. The coding regions of Gst p-1 and the mouse Pi-class GST cDNA (GST-II) reported by Hatayama, Satoh and Satoh (1990) (Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 4606) are identical, whereas Gst p-2 encodes a protein that has not been described previously. The two genes are approximately 3 kb long and contain seven exons interrupted by six introns. In addition to a TATA box and a sequence motif matching the phorbol-ester-responsive element, the promoters of Gst p-1 and Gst p-2 exhibit one and two G+C boxes (GGGCGG) respectively. The cDNAs of the two genes were isolated from total liver RNA using reverse PCR. The peptide sequence deduced from the cDNAs share 97% identity and differ in six amino acids. Both genes are transcribed at significantly higher levels in male mouse liver than in female, and Gst p-1 mRNA is more abundant in both sexes than Gst p-2.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. M., Wolf C. R. The role of glutathione-dependent enzymes in drug resistance. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;51(1):139–154. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90044-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld O. O., Adamany A. M., Kikuchi M., Sabo B., McCreary J. Membrane glycophorins in Sta blood group erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5544–5552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles B., Ketterer B. The role of glutathione and glutathione transferases in chemical carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(1):47–70. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. H., Batist G., Tulpule A., Sinha B. K., Myers C. E. Similar biochemical changes associated with multidrug resistance in human breast cancer cells and carcinogen-induced resistance to xenobiotics in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9328–9332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell I. G., Dixon K. H., Pemble S. E., Ketterer B., Taylor J. B. The structure of the human glutathione S-transferase pi gene. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):79–83. doi: 10.1042/bj2550079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirr H. W., Mann K., Huber R., Ladenstein R., Reinemer P. Class pi glutathione S-transferase from pig lung. Purification, biochemical characterization, primary structure and crystallization. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 28;196(3):693–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossberger D. Minipreps of DNA from bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6737–6737. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatayama I., Satoh K., Sato K. A cDNA sequence coding a class pi glutathione S-transferase of mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4606–4606. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatayama I., Satoh K., Sato K. Developmental and hormonal regulation of the major form of hepatic glutathione S-transferase in male mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 30;140(2):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90771-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes P. C., May L., Hayes J. D., Harrison D. J. Glutathione S-transferases in human liver cancer. Gut. 1991 Dec;32(12):1546–1549. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.12.1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata S., Odajima T., Kohama G., Ishigaki S., Niitsu Y. Significance of glutathione S-transferase-pi as a tumor marker in patients with oral cancer. Cancer. 1992 Nov 15;70(10):2381–2387. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19921115)70:10<2381::aid-cncr2820701002>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie A. F., Forrester L. M., Glancey M. J., Schlager J. J., Powis G., Beckett G. J., Hayes J. D., Wolf C. R. Glutathione S-transferase and glutathione peroxidase expression in normal and tumour human tissues. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Mar;11(3):451–458. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano T., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Structure and expression of a human class pi glutathione S-transferase messenger RNA. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5626–5630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Alin P., Guthenberg C., Jensson H., Tahir M. K., Warholm M., Jörnvall H. Identification of three classes of cytosolic glutathione transferase common to several mammalian species: correlation between structural data and enzymatic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7202–7206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Awasthi Y. C., Board P. G., Hayes J. D., Di Ilio C., Ketterer B., Listowsky I., Morgenstern R., Muramatsu M., Pearson W. R. Nomenclature for human glutathione transferases. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):305–306. doi: 10.1042/bj2820305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan L. I., Hayes J. D. Differential induction of class alpha glutathione S-transferases in mouse liver by the anticarcinogenic antioxidant butylated hydroxyanisole. Purification and characterization of glutathione S-transferase Ya1Ya1. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):393–402. doi: 10.1042/bj2630393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Coles B., Pemble S. E., Gilmore K. S., Fraser G. M., Ketterer B. Theta, a new class of glutathione transferases purified from rat and man. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj2740409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Miyazawa S., Yasunaga T. Two types of amino acid substitutions in protein evolution. J Mol Evol. 1979 Mar 15;12(3):219–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01732340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. S., Cowan K. H., Goldsmith M. E. Structure of the human genomic glutathione S-transferase-pi gene. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90377-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. The structure of the rat glutathione S-transferase P gene and related pseudogenes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. F., Mantle T. J. Inactivation of mouse liver glutathione S-transferase YfYf (Pi class) by ethacrynic acid and 5,5'-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid). Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294(Pt 1):57–62. doi: 10.1042/bj2940057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinemer P., Dirr H. W., Ladenstein R., Schäffer J., Gallay O., Huber R. The three-dimensional structure of class pi glutathione S-transferase in complex with glutathione sulfonate at 2.3 A resolution. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1997–2005. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K. Glutathione transferases as markers of preneoplasia and neoplasia. Adv Cancer Res. 1989;52:205–255. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Kitahara A., Satoh K., Ishikawa T., Tatematsu M., Ito N. The placental form of glutathione S-transferase as a new marker protein for preneoplasia in rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Gan. 1984 Mar;75(3):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawaki M., Enomoto K., Takahashi H., Nakajima Y., Mori M. Phenotype of preneoplastic and neoplastic liver lesions during spontaneous liver carcinogenesis of LEC rats. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Oct;11(10):1857–1861. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.10.1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volm M., Mattern J., Samsel B. Overexpression of P-glycoprotein and glutathione S-transferase-pi in resistant non-small cell lung carcinomas of smokers. Br J Cancer. 1991 Oct;64(4):700–704. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]