Abstract
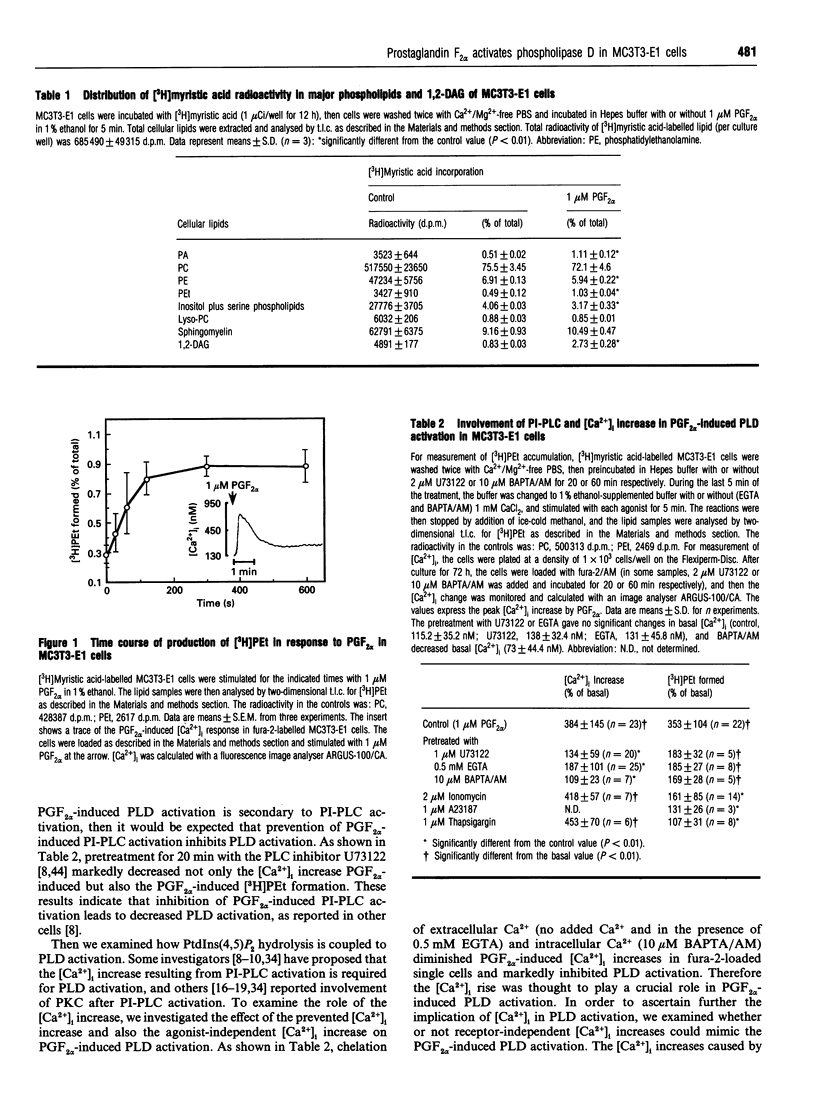
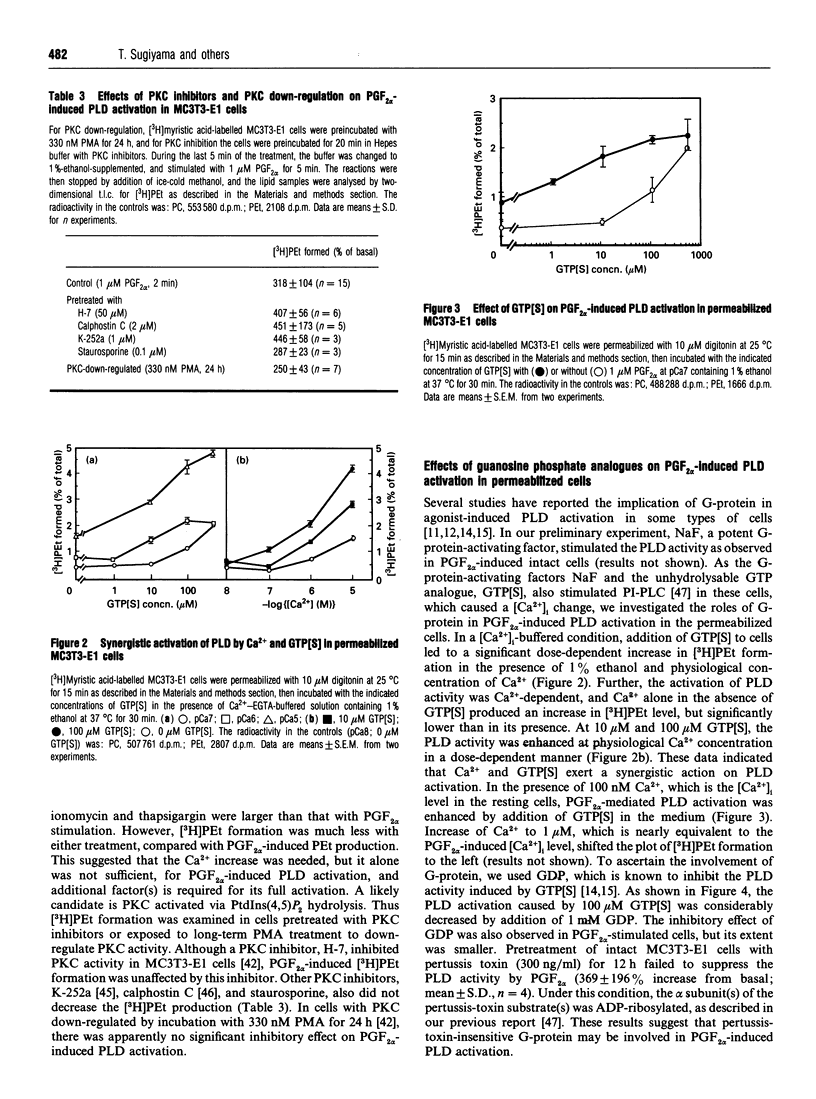
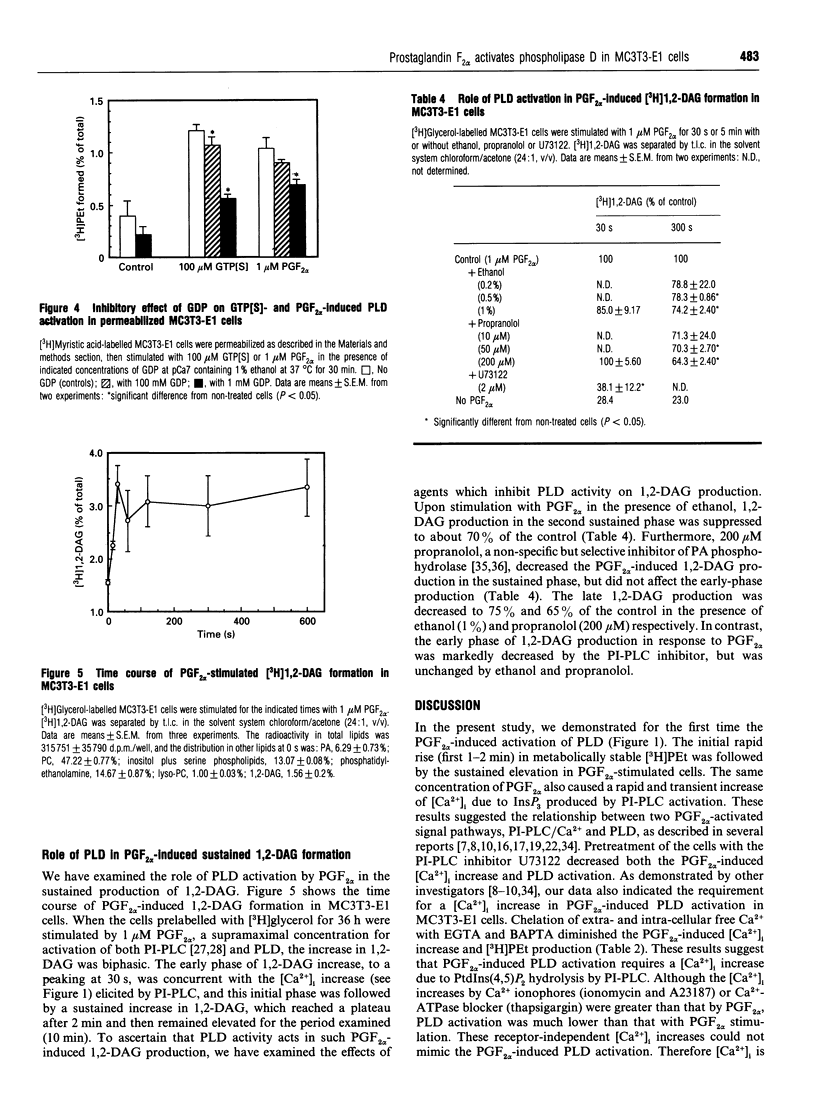
In [3H]myristic acid-labelled osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells, prostaglandin F2 alpha (PGF2 alpha)-induced PLD activity was assessed by measuring the [3H]phosphatidylethanol (PEt) formation in the presence of ethanol. Inhibition of the increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) by U73122, an inhibitor of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC), or chelation of extracellular Ca2+ with EGTA or of intracellular Ca2+ with BAPTA, suppressed PGF2 alpha-induced phospholipase D (PLD) activation. Neither protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors nor PKC down-regulation with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate affected PGF2 alpha-induced [3H]PEt formation. In permeabilized cells, guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate enhanced PGF2 alpha 's potency in [3H]PEt formation in the presence of Ca2+. The pretreatment of intact cells with pertussis toxin failed to inhibit PGF2 alpha-induced [3H]PEt formation. PGF2 alpha caused a biphasic production of [3H]1,2-diacylglycerol ([3H]1,2-DAG) in [3H]glycerol-labelled cells. The initial transient phase was decreased by U73122, whereas the late sustained phase was decreased by ethanol and the phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase inhibitor, propranolol. From these results, it was suggested that PGF2 alpha-induced PLD activation was mediated by the dual control of the [Ca2+]i increase due to PI-PLC activation and activation of pertussis-toxin-insensitive G-protein, but not mediated by PKC, and also that PLD activation was involved in the late sustained 1,2-DAG generation in MC3T3-E1 cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthes J. C., Eckel S., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D in homogenates from HL-60 granulocytes: implications of calcium and G protein control. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):657–664. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banno Y., Sakai T., Kumada T., Nozawa Y. Potentiation by cholera toxin of bradykinin-induced inositol phosphate production in the osteoblast-like cell line MC3T3-E1. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 1;292(Pt 2):401–408. doi: 10.1042/bj2920401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Anthes J. C. The regulation and cellular functions of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):281–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2690281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot M. C., McPhail L. C., Wykle R. L., Kennerly D. A., McCall C. E. Comparison of diglyceride production from choline-containing phosphoglycerides in human neutrophils stimulated with N-formylmethionyl-leucylphenylalanine, ionophore A23187 or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):693–699. doi: 10.1042/bj2860693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Briscoe C. P., Wakelam M. J. The regulation of phospholipase D activity and its role in sn-1,2-diradylglycerol formation in bombesin- and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 1;280(Pt 2):431–438. doi: 10.1042/bj2800431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich J. W., Goodson J. M., Raisz L. G. Stimulation of bone resorption by various prostaglandins in organ culture. Prostaglandins. 1975 Aug;10(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinh T. T., Kennerly D. A. Assessment of receptor-dependent activation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by both phospholipase D and phospholipase C. Cell Regul. 1991 Apr;2(4):299–309. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.4.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Watanabe H., Yamamoto H., Tanaka S., Hashimoto M. Prostaglandin F2 alpha- and phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate-stimulated progesterone production by cultured human luteal cells in the mid-luteal phase: prostaglandin F2 alpha increases cytosolic Ca2+ and inositol phosphates. J Endocrinol. 1992 Jun;133(3):451–458. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1330451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T., Okano Y., Nozawa Y. Differential pathways (phospholipase C and phospholipase D) of bradykinin-induced biphasic 1,2-diacylglycerol formation in non-transformed and K-ras-transformed NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Involvement of intracellular Ca2+ oscillations in phosphatidylcholine breakdown. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):347–354. doi: 10.1042/bj2830347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami K., Takenawa T. Quantitative changes in polyphosphoinositides 1,2-diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate by platelet-derived growth factor and prostaglandin F2 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14985–14989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geny B., Cockcroft S. Synergistic activation of phospholipase D by protein kinase C- and G-protein-mediated pathways in streptolysin O-permeabilized HL60 cells. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):531–538. doi: 10.1042/bj2840531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goin M., Jimenez de Asua L. Stimulation of protein kinase C (PKC) activity in resting Swiss 3T3 cells by prostaglandin F2 alpha. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 3;297(1-2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80354-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakeda Y., Harada S., Matsumoto T., Tezuka K., Higashino K., Kodama H., Hashimoto-Goto T., Ogata E., Kumegawa M. Prostaglandin F2 alpha stimulates proliferation of clonal osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells by up-regulation of insulin-like growth factor I receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21044–21050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakeda Y., Hotta T., Kurihara N., Ikeda E., Maeda N., Yagyu Y., Kumegawa M. Prostaglandin E1 and F2 alpha stimulate differentiation and proliferation, respectively, of clonal osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells by different second messengers in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987 Dec;121(6):1966–1974. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-6-1966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakeda Y., Yoshino T., Natakani Y., Kurihara N., Maeda N., Kumegawa M. Prostaglandin E2 stimulates DNA synthesis by a cyclic AMP-independent pathway in osteoblastic clone MC3T3-E1 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Aug;128(2):155–161. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Rehm A. G. Evidence for the calcium-dependent activation of phospholipase D in thrombin-stimulated human erythroleukaemia cells. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):479–483. doi: 10.1042/bj2670479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. F., Cabot M. C. Phorbol diesters stimulate the accumulation of phosphatidate, phosphatidylethanol, and diacylglycerol in three cell types. Evidence for the indirect formation of phosphatidylcholine-derived diacylglycerol by a phospholipase D pathway and direct formation of diacylglycerol by a phospholipase C pathway. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14858–14863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. F., Cabot M. C. Vasopressin-induced polyphosphoinositide and phosphatidylcholine degradation in fibroblasts. Temporal relationship for formation of phospholipase C and phospholipase D hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17468–17473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst K. M., Hughes B. P., Barritt G. J. The roles of phospholipase D and a GTP-binding protein in guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-stimulated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine in rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):749–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2720749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh H., Kanaho Y., Nozawa Y. Pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein mediates carbachol activation of phospholipase D in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1786–1794. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kase H., Iwahashi K., Nakanishi S., Matsuda Y., Yamada K., Takahashi M., Murakata C., Sato A., Kaneko M. K-252 compounds, novel and potent inhibitors of protein kinase C and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):436–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kester M., Simonson M. S., McDermott R. G., Baldi E., Dunn M. J. Endothelin stimulates phosphatidic acid formation in cultured rat mesangial cells: role of a protein kinase C-regulated phospholipase D. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):578–585. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Kanfer J. N. Phosphatidylethanol formation via transphosphatidylation by rat brain synaptosomal phospholipase D. J Neurochem. 1987 May;48(5):1597–1603. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P., Gilfillan A. M. The role of calcium and protein kinase C in the IgE-dependent activation of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase D in a rat mast (RBL 2H3) cell line. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 1;207(1):163–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Geisbuhler B., Jones A. W. Activation of multiple mechanisms including phospholipase D by endothelin-1 in rat aorta. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C941–C949. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llahi S., Fain J. N. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase D in rat cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3679–3685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffelholz K. Receptor regulation of choline phospholipid hydrolysis. A novel source of diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1543–1549. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNulty E. E., Plevin R., Wakelam M. J. Stimulation of the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylcholine by endothelin, a complete mitogen for Rat-1 fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):761–766. doi: 10.1042/bj2720761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki T., Williams J. A. Multiple sources of 1,2-diacylglycerol in isolated rat pancreatic acini stimulated by cholecystokinin. Involvement of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate and phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14729–14734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Activation of phospholipase D by chemotactic peptide in HL-60 granulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppers S. C., Holz R. W. Catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated PC12 cells. Effects of Ca2+, ATP, and protein kinase C activators. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14665–14669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. D., Morris J. D., Hall A. Stimulation of phosphatidylcholine breakdown and diacylglycerol production by growth factors in Swiss-3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):509–515. doi: 10.1042/bj2640509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkiss J. R., Boarder M. R. Stimulation of phosphatidate synthesis in endothelial cells in response to P2-receptor activation. Evidence for phospholipase C and phospholipase D involvement, phosphatidate and diacylglycerol interconversion and the role of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 1;287(Pt 1):31–36. doi: 10.1042/bj2870031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Z., Drewes L. R. Cross-talk between receptor-regulated phospholipase D and phospholipase C in brain. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):315–319. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.2001791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisz L. G., Alander C. B., Fall P. M., Simmons H. A. Effects of prostaglandin F2 alpha on bone formation and resorption in cultured neonatal mouse calvariae: role of prostaglandin E2 production. Endocrinology. 1990 Feb;126(2):1076–1079. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-2-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Okano Y., Nozawa Y., Oka N. Different protein kinase C isozymes could modulate bradykinin-induced extracellular calcium-dependent and -independent increases in osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells. Cell Calcium. 1992 May;13(5):329–340. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smallridge R. C., Kiang J. G., Gist I. D., Fein H. G., Galloway R. J. U-73122, an aminosteroid phospholipase C antagonist, noncompetitively inhibits thyrotropin-releasing hormone effects in GH3 rat pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Oct;131(4):1883–1888. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.4.1396332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H., James-Kracke M. R., Halenda S. P. Direct relationship between intracellular calcium mobilization and phospholipase D activation in prostaglandin E-stimulated human erythroleukemia cells. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3370–3377. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Kanaho Y., Miura K., Nozawa Y. Antigen-induced phospholipase D activation in rat mast cells is independent of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Hahn T. J., Beeker T. G., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Relationship of cAMP and calcium messenger systems in prostaglandin-stimulated UMR-106 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10745–10753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. F., Freer S., Benson A. A. Transphosphatidylation by phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


