Abstract
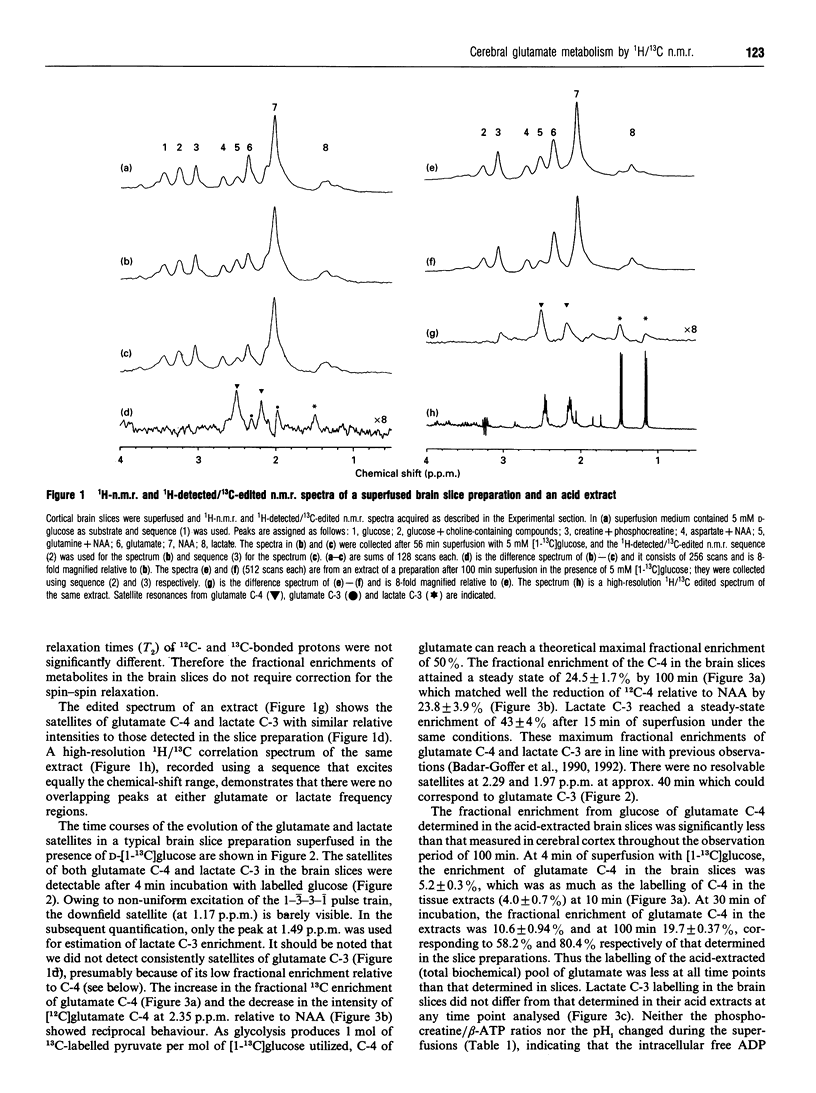
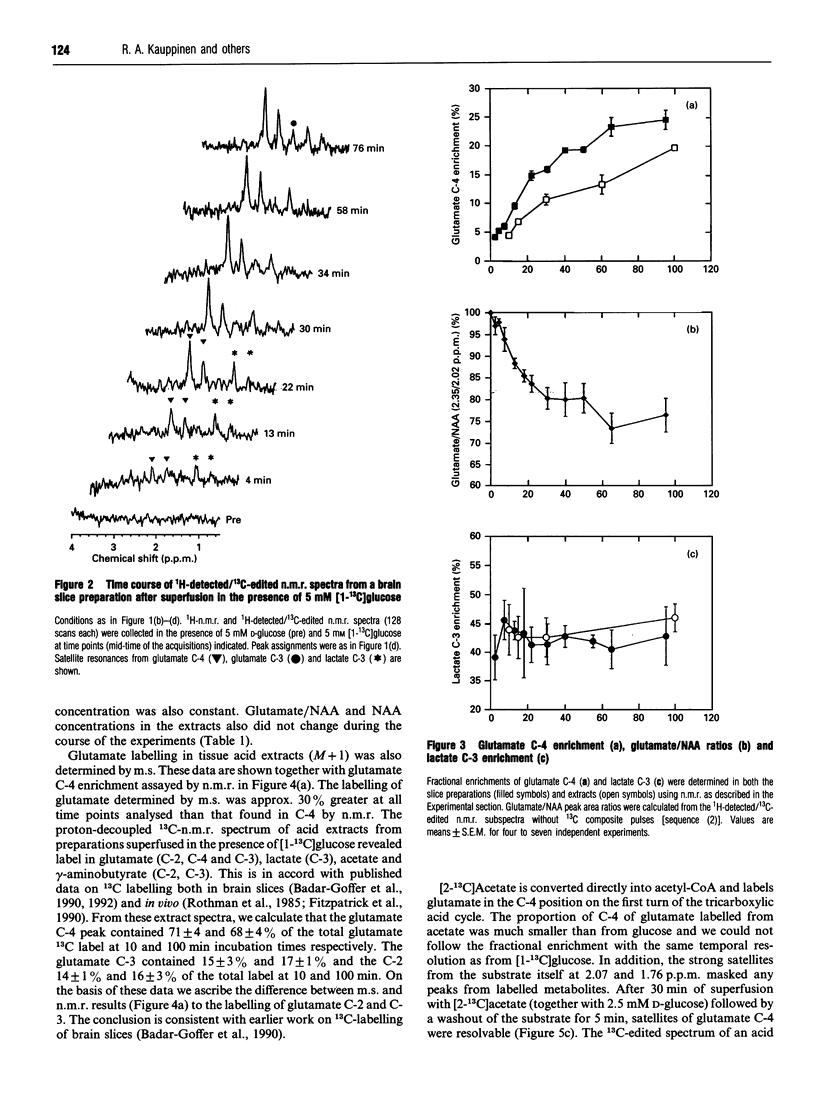
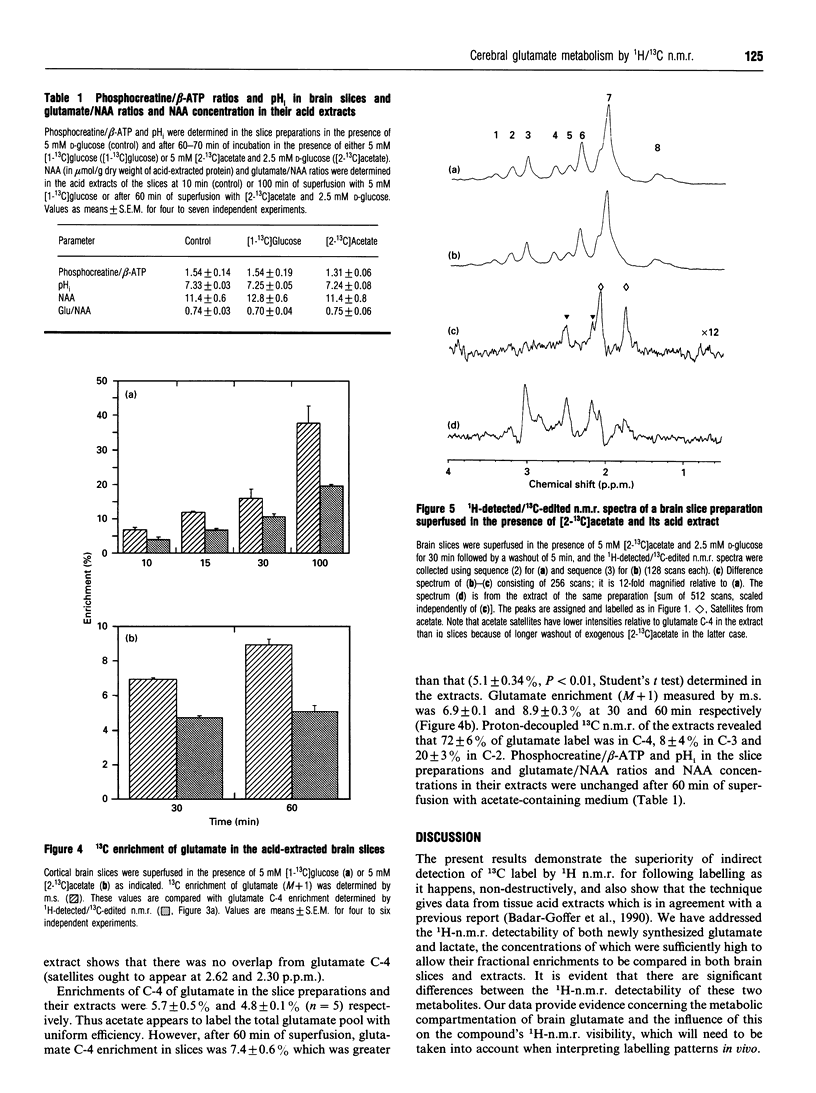
Incorporation of 13C label from either [1-13C]glucose to glutamate C-4 and lactate C-3 or from [2-13C]acetate to glutamate C-4 was monitored in situ in a superfused brain slice preparation by using 1H-detected/13C-edited (1H/13C) n.m.r. spectroscopy. The fractional enrichments of both metabolites were determined by this means in both brain slices and acid extracts of the preparations in order to assess their 1H-n.m.r. detectabilities. The 1H/13C satellite resonances from glutamate C-4 and lactate C-3 in brain tissue were followed from 4 min onwards in the presence of 5 mM [1-13C]glucose. Fractional enrichment of glutamate C-4 in the slice preparations was higher than in their acid extracts throughout the incubation of 100 min; at 30 min the enrichment was 15.9 +/- 0.6% in the slice preparations and 10.6 +/- 0.9% in extracts and at 100 min 24.5 +/- 1.7% compared with 19.7 +/- 0.4%, respectively. In contrast, lactate C-3 reached a steady-state fractional enrichment of approx. 43% by 15 min and there was no difference between the values determined in the slice preparations and the acid extracts. There was a significant difference between the glutamate C-4 fractional enrichments in the brain slices (7.4 +/- 0.6%) and extracts (5.1 +/- 0.3%) after 60 min of incubation with [2-13C]acetate. Thus 13C label from both glucose and exogenous acetate enters a pool of glutamate that is more amenable to 1H n.m.r. detection than total acid-extracted brain biochemical glutamate, whereas lactate is labelled with full 1H n.m.r. visibility. The results are discussed in the light of the biochemical factors that affect glutamate 1H-n.m.r. susceptibility and thus its n.m.r. visibility.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERL S., TAKAGAKI G., CLARKE D. D., WAELSCH H. Carbon dioxide fixation in the brain. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2570–2573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badar-Goffer R. S., Bachelard H. S., Morris P. G. Cerebral metabolism of acetate and glucose studied by 13C-n.m.r. spectroscopy. A technique for investigating metabolic compartmentation in the brain. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):133–139. doi: 10.1042/bj2660133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badar-Goffer R. S., Ben-Yoseph O., Bachelard H. S., Morris P. G. Neuronal-glial metabolism under depolarizing conditions. A 13C-n.m.r. study. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):225–230. doi: 10.1042/bj2820225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar K. L., Ogino T. Assignment of resonance in the 1H spectrum of rat brain by two-dimensional shift correlated and J-resolved NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Feb;17(2):285–303. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl S., Nicklas W. J., Clarke D. D. Compartmentation of citric acid cycle metabolism in brain: labelling of glutamate, glutamine, aspartate and gaba by several radioactive tracer metabolites. J Neurochem. 1970 Jul;17(7):1009–1015. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brainard J. R., Kyner E., Rosenberg G. A. 13C nuclear magnetic resonance evidence for gamma-aminobutyric acid formation via pyruvate carboxylase in rat brain: a metabolic basis for compartmentation. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1285–1292. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle K. M., Brown F. F., Campbell I. D., Grathwohl C., Kuchel P. W. Application of spin-echo nuclear magnetic resonance to whole-cell systems. Membrane transport. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):37–44. doi: 10.1042/bj1800037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdan S., Künnecke B., Seelig J. Cerebral metabolism of [1,2-13C2]acetate as detected by in vivo and in vitro 13C NMR. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12916–12926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Methods for antagonizing glutamate neurotoxicity. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1990 Summer;2(2):105–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Morris P. G., Feeney J., Bachelard H. S. 31P-n.m.r. studies on cerebral energy metabolism under conditions of hypoglycaemia and hypoxia in vitro. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):365–370. doi: 10.1042/bj2120365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick S. M., Hetherington H. P., Behar K. L., Shulman R. G. The flux from glucose to glutamate in the rat brain in vivo as determined by 1H-observed, 13C-edited NMR spectroscopy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990 Mar;10(2):170–179. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1990.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holowenko D., Peeling J., Sutherland G. 1H NMR properties of N-acetylaspartylglutamate in extracts of nervous tissue of the rat. NMR Biomed. 1992 Jan-Feb;5(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940050108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapetanovic I. M., Yonekawa W. D., Kupferberg H. J. Use of stable isotopes and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in the study of different pools of neurotransmitter amino acids in brain slices. J Chromatogr. 1990 Feb 2;500:387–394. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)96080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauppinen R. A., Nissinen T., Kärkkäinen A. M., Pirttilä T. R., Palvimo J., Kokko H., Williams S. R. Detection of thymosin beta 4 in situ in a guinea pig cerebral cortex preparation using 1H NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9905–9910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauppinen R. A., Williams S. R. Nondestructive detection of glutamate by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in cortical brain slices from the guinea pig: evidence for changes in detectability during severe anoxic insults. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1136–1144. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaNoue K. F., Schoolwerth A. C. Metabolite transport in mitochondria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:871–922. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maycox P. R., Hell J. W., Jahn R. Amino acid neurotransmission: spotlight on synaptic vesicles. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Mar;13(3):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90178-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Nicholls D. G. The bioenergetics of neurotransmitter release. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 13;1059(3):243–264. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis T., Merboldt K. D., Bruhn H., Hänicke W., Frahm J. Absolute concentrations of metabolites in the adult human brain in vivo: quantification of localized proton MR spectra. Radiology. 1993 Apr;187(1):219–227. doi: 10.1148/radiology.187.1.8451417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake M., Kakimoto Y., Sorimachi M. A gas chromatographic method for the determination of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid, N-acetyl-alpha-aspartylglutamic acid and beta-citryl-L-glutamic acid and their distributions in the brain and other organs of various species of animals. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):804–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., Ueda T. Adenosine triphosphate-dependent uptake of glutamate into protein I-associated synaptic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):696–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. Release of glutamate, aspartate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid from isolated nerve terminals. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):331–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirttilä T. R., Hakumäki J. M., Kauppinen R. A. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of cerebral glutamate in an ex vivo brain preparation of guinea pig. J Neurochem. 1993 Apr;60(4):1274–1282. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman D. L., Behar K. L., Hetherington H. P., den Hollander J. A., Bendall M. R., Petroff O. A., Shulman R. G. 1H-Observe/13C-decouple spectroscopic measurements of lactate and glutamate in the rat brain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1633–1637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman D. L., Novotny E. J., Shulman G. I., Howseman A. M., Petroff O. A., Mason G., Nixon T., Hanstock C. C., Prichard J. W., Shulman R. G. 1H-[13C] NMR measurements of [4-13C]glutamate turnover in human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9603–9606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank R. P., Bennett G. S., Freytag S. O., Campbell G. L. Pyruvate carboxylase: an astrocyte-specific enzyme implicated in the replenishment of amino acid neurotransmitter pools. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 11;329(1-2):364–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Bore P. J., Styles P., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Bioenergetics of intact human muscle. A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):77–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urenjak J., Williams S. R., Gadian D. G., Noble M. Specific expression of N-acetylaspartate in neurons, oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte progenitors, and immature oligodendrocytes in vitro. J Neurochem. 1992 Jul;59(1):55–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg C. J., Krzalić L., Mela P., Waelsch H. Compartmentation of glutamate metabolism in brain. Evidence for the existence of two different tricarboxylic acid cycles in brain. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):281–290. doi: 10.1042/bj1130281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. R., Proctor E., Allen K., Gadian D. G., Crockard H. A. Quantitative estimation of lactate in the brain by 1H NMR. Magn Reson Med. 1988 Aug;7(4):425–431. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910070405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf A. A., Bovée W. M. Improved quantification of in vivo 1H NMR spectra by optimization of signal acquisition and processing and by incorporation of prior knowledge into the spectral fitting. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Aug;15(2):305–319. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910150212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg C. J., Garfinkel D. A simulation study of brain compartments. Metabolism of glutamate and related substances in mouse brain. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj1230211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


