Abstract
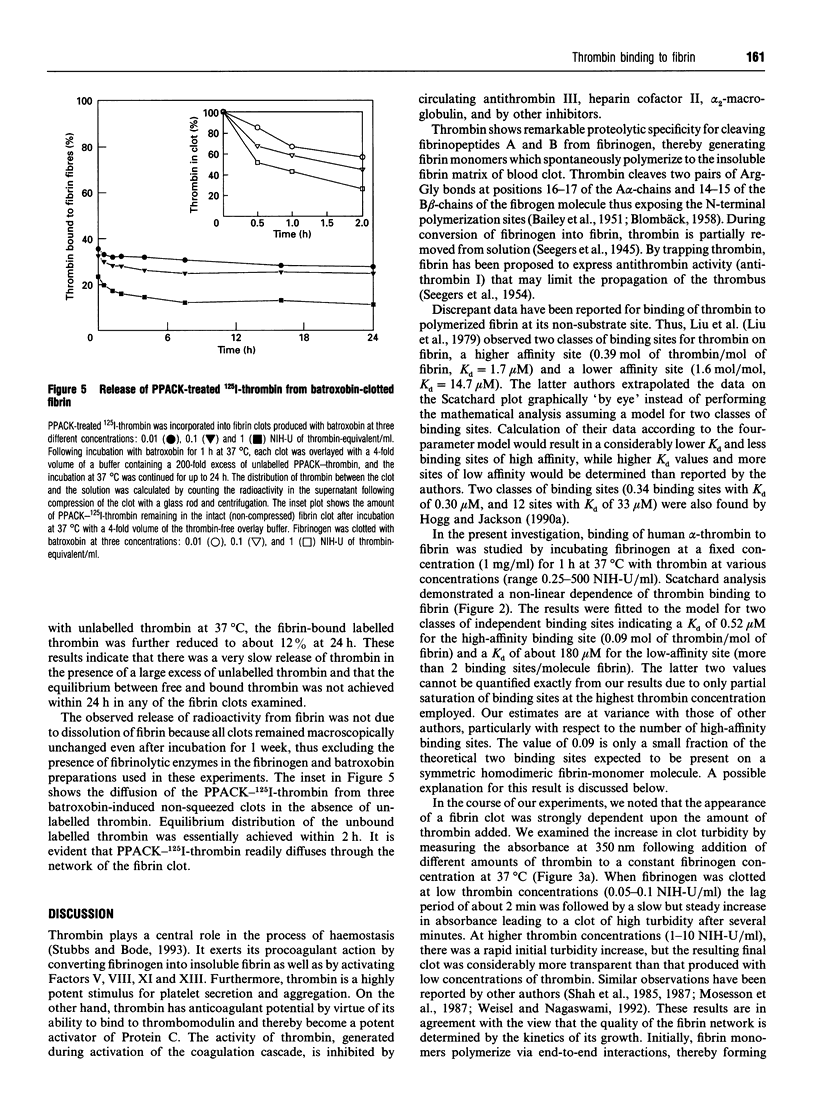
Binding of human alpha-thrombin to fibrin was studied in a purified system at pH 7.35, I 0.08 and 37 degrees C. Binding experiments with active thrombin resulted in fibrin clots of variable quality, depending on the thrombin concentration: opaque gels composed of 'coarse' network were produced at low thrombin concentrations, while increasing concentrations of thrombin led to more translucent 'fine' gels. Scatchard analysis showed a non-linear dependence of thrombin binding to fibrin, suggesting the existence in fibrin(ogen) of multiple classes of binding sites for thrombin. Binding of catalytic-site-inhibited thrombin was investigated in clots of defined quality produced with three different concentrations of a thrombin-like enzyme, batroxobin (EC 3.4.21.29). Straight lines of different slopes were established by Scatchard analysis of binding data at each fixed batroxobin concentration. These results favour a model according to which binding affinity for thrombin depends on the thickness of fibrin bundles. Labelled active-site-inactivated thrombin incorporated in batroxobin-induced clots was only sparingly released during incubation for 24 h in the presence of a 200-fold excess of unlabelled thrombin, indicating that thrombin binding to fibrin is not reversible and that Scatchard analysis is not appropriate for quantification of binding parameters. Irreversible binding of thrombin appears to reflect trapping of thrombin molecules within fibrin fibres. The amount of trapped thrombin depends on the quality of the fibrin fibres, which in turn is determined by the concentration of the clotting enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAILEY K., BETTELHEIM F. R., LORAND L., MIDDLEBROOK W. R. Action of thrombin in the clotting of fibrinogen. Nature. 1951 Feb 10;167(4241):233–234. doi: 10.1038/167233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner L. J., Sugawara Y., Fenton J. W., 2nd Human alpha-thrombin binding to nonpolymerized fibrin-Sepharose: evidence for an anionic binding region. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):7005–7009. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. E. Fibrin formed in plasma is composed of fibers more massive than those formed from purified fibrinogen. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Jun 16;59(3):535–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. E., Jr, Hermans J. Size and density of fibrin fibers from turbidity. Macromolecules. 1978 Jan-Feb;11(1):46–50. doi: 10.1021/ma60061a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. E., Jr, Shen L. L., Hermans J. Mass-length ratio of fibrin fibers from gel permeation and light scattering. Biopolymers. 1977 Jan;16(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J., Stackrow A. B. Human thrombins. Production, evaluation, and properties of alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3587–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Olson T. A., Zabinski M. P., Wilner G. D. Anion-binding exosite of human alpha-thrombin and fibrin(ogen) recognition. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7106–7112. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Rupp C., Beck E. A., Svendsen L. Effect of calcium and synthetic peptides on fibrin polymerization. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Apr 30;47(2):118–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis D. K., Lane B. P., Simon S. R. Albumin modulates lateral assembly of fibrin polymers: evidence of enhanced fine fibril formation and of unique synergism with fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2389–2400. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg P. J., Jackson C. M. Fibrin monomer protects thrombin from inactivation by heparin-antithrombin III: implications for heparin efficacy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3619–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg P. J., Jackson C. M. Formation of a ternary complex between thrombin, fibrin monomer, and heparin influences the action of thrombin on its substrates. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):248–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg P. J., Jackson C. M. Heparin promotes the binding of thrombin to fibrin polymer. Quantitative characterization of a thrombin-fibrin polymer-heparin ternary complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):241–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleman W. H., Weiss L. J. The thrombin-like enzyme from Bothrops atrox snake venom. Properties of the enzyme purified by affinity chromatography on p-aminobenzamidine-substituted agarose. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1663–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Ferry J. D. Gel formation by fibrin oligomers without addition of monomers. Biopolymers. 1986 Jul;25(7):1337–1344. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski M., McDonagh J. Studies on the mechanism of thrombin. Interaction with fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10530–10535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. D-Phe-Pro-ArgCH2C1-A selective affinity label for thrombin. Thromb Res. 1979;14(6):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman J., Haverkate F., Lord S. T., Grimbergen J., Mannucci P. M. Molecular basis of fibrinogen Naples associated with defective thrombin binding and thrombophilia. Homozygous substitution of B beta 68 Ala----Thr. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):238–244. doi: 10.1172/JCI115841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. Y., Nossel H. L., Kaplan K. L. The binding of thrombin by fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10421–10425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R., Carroll W. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. I. Physicochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2111–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., DiOrio J. P., Müller M. F., Shainoff J. R., Siebenlist K. R., Amrani D. L., Homandberg G. A., Soria J., Soria C., Samama M. Studies on the ultrastructure of fibrin lacking fibrinopeptide B (beta-fibrin). Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1073–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W. Fibrin polymerization and its regulatory role in hemostasis. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Jul;116(1):8–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair C. H., Dhall D. P. Studies on fibrin network structure: the effect of some plasma proteins. Thromb Res. 1991 Feb 1;61(3):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90109-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair C. H., Shah G. A., Dhall D. P. Effect of temperature, pH and ionic strength and composition on fibrin network structure and its development. Thromb Res. 1986 Jun 15;42(6):809–816. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEEGERS W. H., JOHNSON J. F., FELL C. An antithrombin reaction to prothrombin activation. Am J Physiol. 1954 Jan;176(1):97–103. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.176.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers W. H., Nieft M., Loomis E. C. NOTE ON THE ADSORPTION OF THROMBIN ON FIBRIN. Science. 1945 May 18;101(2629):520–521. doi: 10.1126/science.101.2629.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah G. A., Ferguson I. A., Dhall T. Z., Dhall D. P. Polydispersion in the diameter of fibers in fibrin networks: consequences on the measurement of mass-length ratio by permeability and turbidity. Biopolymers. 1982 Jun;21(6):1037–1047. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah G. A., Nair C. H., Dhall D. P. Comparison of fibrin networks in plasma and fibrinogen solution. Thromb Res. 1987 Feb 1;45(3):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah G. A., Nair C. H., Dhall D. P. Physiological studies on fibrin network structure. Thromb Res. 1985 Oct 15;40(2):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist K. R., DiOrio J. P., Budzynski A. Z., Mosesson M. W. The polymerization and thrombin-binding properties of des-(B beta 1-42)-fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18650–18655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker K., Barlow G. H. The coagulant enzyme from Bothrops atrox venom (batroxobin). Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:214–223. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M. T., Bode W. A player of many parts: the spotlight falls on thrombin's structure. Thromb Res. 1993 Jan 1;69(1):1–58. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(93)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vali Z., Scheraga H. A. Localization of the binding site on fibrin for the secondary binding site of thrombin. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1956–1963. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisel J. W. Fibrin assembly. Lateral aggregation and the role of the two pairs of fibrinopeptides. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1079–1093. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83552-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisel J. W., Nagaswami C. Computer modeling of fibrin polymerization kinetics correlated with electron microscope and turbidity observations: clot structure and assembly are kinetically controlled. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):111–128. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81594-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz J. I., Hudoba M., Massel D., Maraganore J., Hirsh J. Clot-bound thrombin is protected from inhibition by heparin-antithrombin III but is susceptible to inactivation by antithrombin III-independent inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):385–391. doi: 10.1172/JCI114723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Danitz M. P., Mudd M. S., Hsieh K. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd Selective immobilization of alpha-thrombin by surface-bound fibrin. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Mar;97(3):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



