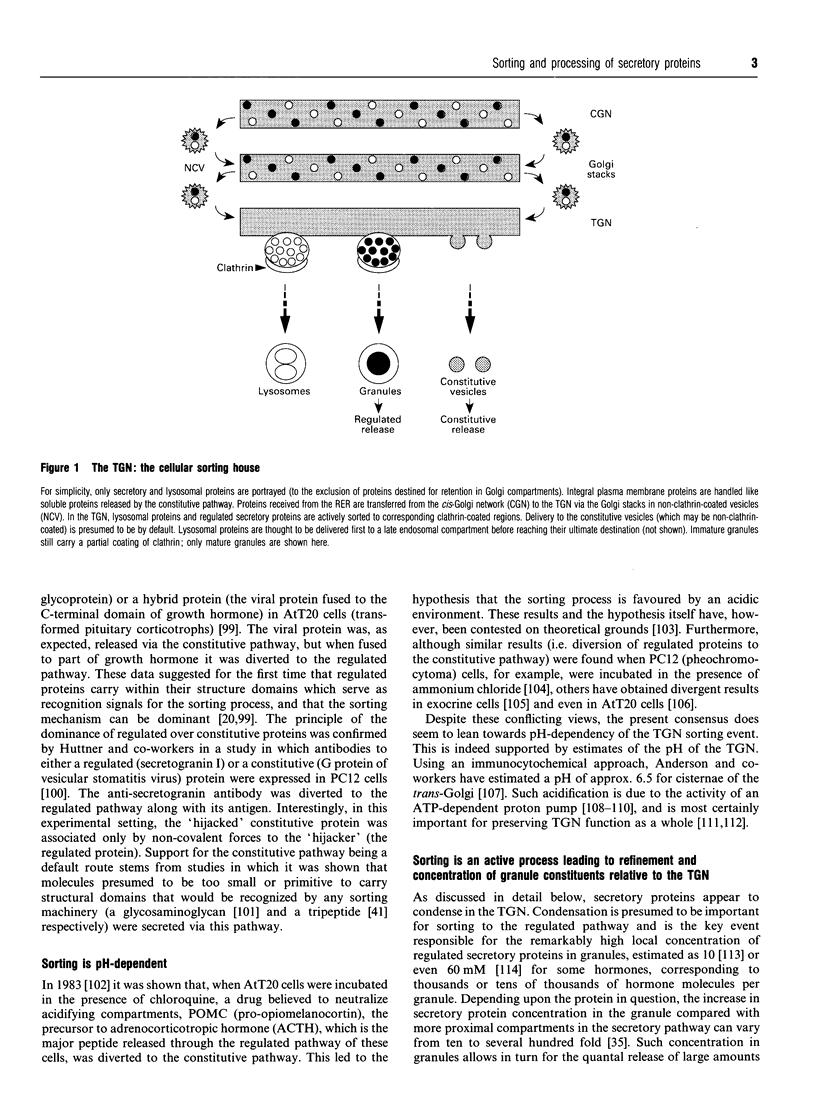
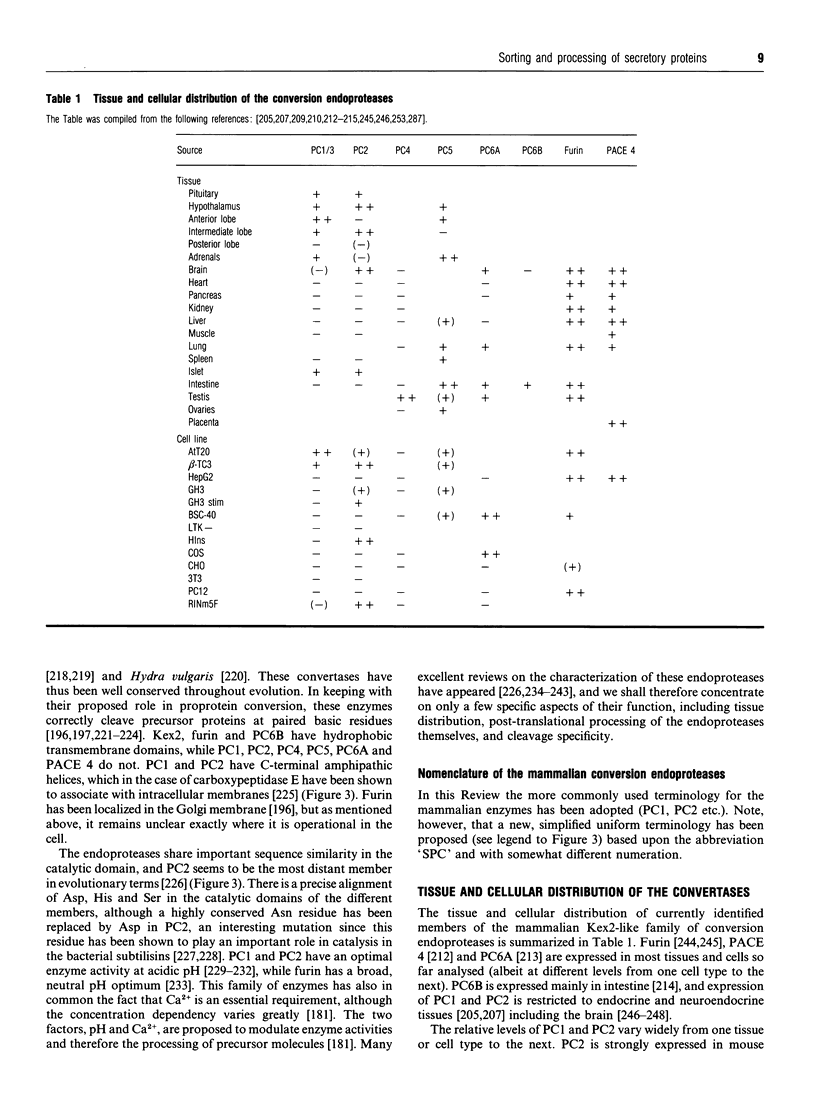
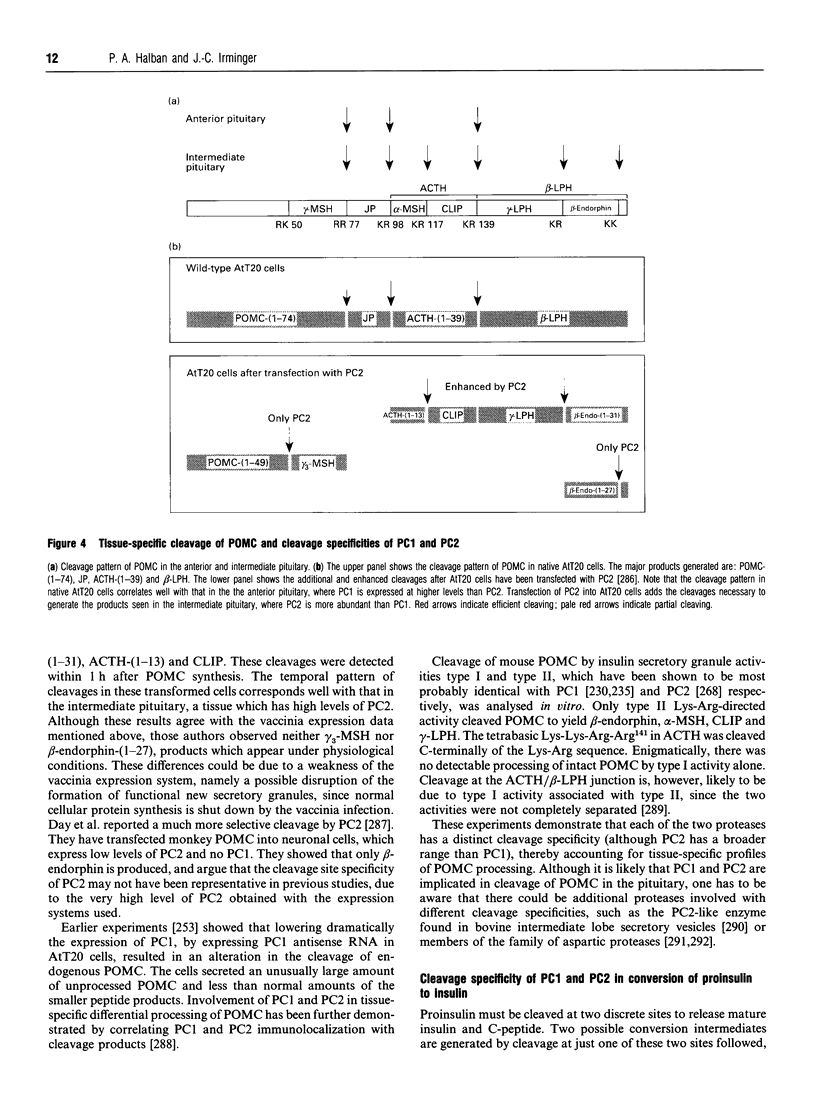
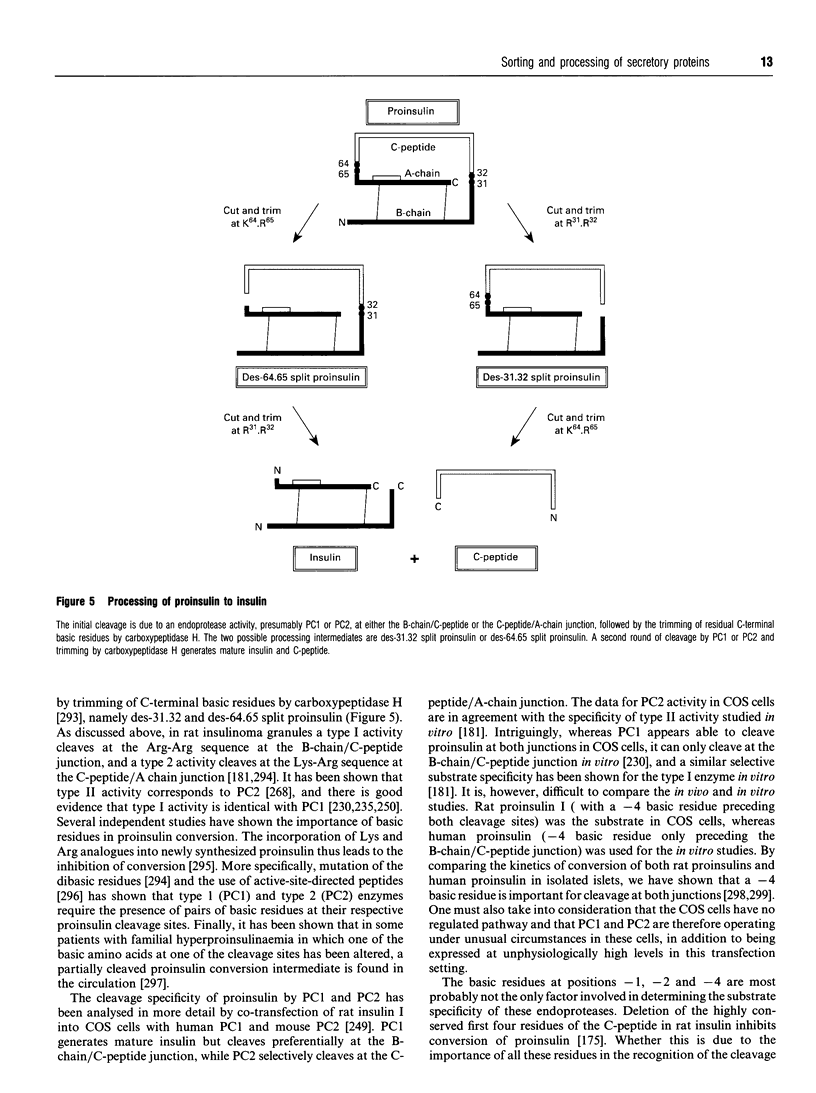
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acton S. L., Brodsky F. M. Predominance of clathrin light chain LCb correlates with the presence of a regulated secretory pathway. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1419–1426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Awqati Q. Proton-translocating ATPases. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:179–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón C., Lincoln B., Rhodes C. J. The biosynthesis of the subtilisin-related proprotein convertase PC3, but no that of the PC2 convertase, is regulated by glucose in parallel to proinsulin biosynthesis in rat pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4276–4280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Orci L. A view of acidic intracellular compartments. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):539–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Pathak R. K. Vesicles and cisternae in the trans Golgi apparatus of human fibroblasts are acidic compartments. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvan P., Castle D. Protein sorting and secretion granule formation in regulated secretory cells. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90181-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvan P., Castle J. D. Phasic release of newly synthesized secretory proteins in the unstimulated rat exocrine pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):243–252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvan P., Chang A. Constitutive protein secretion from the exocrine pancreas of fetal rats. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3886–3890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvan P., Kuliawat R., Prabakaran D., Zavacki A. M., Elahi D., Wang S., Pilkey D. Protein discharge from immature secretory granules displays both regulated and constitutive characteristics. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14171–14174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azaryan A. V., Wong M., Friedman T. C., Cawley N. X., Estivariz F. E., Chen H. C., Loh Y. P. Purification and characterization of a paired basic residue-specific yeast aspartic protease encoded by the YAP3 gene. Similarity to the mammalian pro-opiomelanocortin-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11968–11975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailyes E. M., Bennett D. L., Hutton J. C. Proprotein-processing endopeptidases of the insulin secretory granule. Enzyme. 1991;45(5-6):301–313. doi: 10.1159/000468903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailyes E. M., Shennan K. I., Seal A. J., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Hutton J. C., Docherty K. A member of the eukaryotic subtilisin family (PC3) has the enzymic properties of the type 1 proinsulin-converting endopeptidase. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 15;285(Pt 2):391–394. doi: 10.1042/bj2850391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E. Sequential intermediates in the pathway of intercompartmental transport in a cell-free system. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr P. J. Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90129-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr P. J., Mason O. B., Landsberg K. E., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J. cDNA and gene structure for a human subtilisin-like protease with cleavage specificity for paired basic amino acid residues. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;10(5):319–328. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckers C. J., Keller D. S., Balch W. E. Semi-intact cells permeable to macromolecules: use in reconstitution of protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckers C. J., Plutner H., Davidson H. W., Balch W. E. Sequential intermediates in the transport of protein between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18298–18310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjannet S., Reudelhuber T., Mercure C., Rondeau N., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. Proprotein conversion is determined by a multiplicity of factors including convertase processing, substrate specificity, and intracellular environment. Cell type-specific processing of human prorenin by the convertase PC1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11417–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjannet S., Rondeau N., Day R., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. PC1 and PC2 are proprotein convertases capable of cleaving proopiomelanocortin at distinct pairs of basic residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3564–3568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjannet S., Rondeau N., Paquet L., Boudreault A., Lazure C., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. Comparative biosynthesis, covalent post-translational modifications and efficiency of prosegment cleavage of the prohormone convertases PC1 and PC2: glycosylation, sulphation and identification of the intracellular site of prosegment cleavage of PC1 and PC2. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 15;294(Pt 3):735–743. doi: 10.1042/bj2940735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjannet S., Rondeau N., Paquet L., Boudreault A., Lazure C., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. Comparative biosynthesis, covalent post-translational modifications and efficiency of prosegment cleavage of the prohormone convertases PC1 and PC2: glycosylation, sulphation and identification of the intracellular site of prosegment cleavage of PC1 and PC2. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 15;294(Pt 3):735–743. doi: 10.1042/bj2940735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. L., Bailyes E. M., Nielsen E., Guest P. C., Rutherford N. G., Arden S. D., Hutton J. C. Identification of the type 2 proinsulin processing endopeptidase as PC2, a member of the eukaryote subtilisin family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15229–15236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. K., Rees D. J., Rizza C., Brownlee G. G. Defective propeptide processing of blood clotting factor IX caused by mutation of arginine to glutamine at position -4. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Eipper B. A., Mains R. E. Prohormone-converting enzymes: regulation and evaluation of function using antisense RNA. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2014–2024. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Degradation of proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):592–600. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90028-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbonnais Y., Germain D., Latchinian-Sadek L., Boileau G., Thomas D. Y. Prohormone processing by yeast proteases. Enzyme. 1991;45(5-6):244–256. doi: 10.1159/000468899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brakch N., Rholam M., Boussetta H., Cohen P. Role of beta-turn in proteolytic processing of peptide hormone precursors at dibasic sites. Biochemistry. 1993 May 11;32(18):4925–4930. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braks J. A., Guldemond K. C., van Riel M. C., Coenen A. J., Martens G. J. Structure and expression of Xenopus prohormone convertase PC2. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 22;305(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80652-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan S. O. Propeptide cleavage: evidence from human proalbumins. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Feb;6(1):87–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan P. A., Leduc R., Thomas L., Thorner J., Gibson H. L., Brake A. J., Barr P. J., Thomas G. Human fur gene encodes a yeast KEX2-like endoprotease that cleaves pro-beta-NGF in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2851–2859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brion C., Miller S. G., Moore H. P. Regulated and constitutive secretion. Differential effects of protein synthesis arrest on transport of glycosaminoglycan chains to the two secretory pathways. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M. Living with clathrin: its role in intracellular membrane traffic. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1396–1402. doi: 10.1126/science.2904698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändli A. W. Mammalian glycosylation mutants as tools for the analysis and reconstitution of protein transport. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj2760001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Craik C. S., Kelly R. B. The exocrine protein trypsinogen is targeted into the secretory granules of an endocrine cell line: studies by gene transfer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):639–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Kelly R. B. Constitutive and regulated secretion of proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:243–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Kelly R. B. Sorting and secretion of adrenocorticotropin in a pituitary tumor cell line after perturbation of the level of a secretory granule-specific proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2223–2230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A. Regulated exocytosis. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):305–316. doi: 10.1042/bj2930305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron R. S., Cameron P. L., Castle J. D. A common spectrum of polypeptides occurs in secretion granule membranes of different exocrine glands. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1299–1313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle J. D. Sorting and secretory pathways in exocrine cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;2(2):119–126. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Oliva A. A., Jr, LaMendola J., Grens A., Bode H., Steiner D. F. Conservation of the prohormone convertase gene family in metazoa: analysis of cDNAs encoding a PC3-like protein from hydra. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6678–6682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanat E., Huttner W. B. Milieu-induced, selective aggregation of regulated secretory proteins in the trans-Golgi network. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1505–1519. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanat E., Pimplikar S. W., Stinchcombe J. C., Huttner W. B. What the granins tell us about the formation of secretory granules in neuroendocrine cells. Cell Biophys. 1991 Oct-Dec;19(1-3):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF02989882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanat E., Weiss U., Huttner W. B., Tooze S. A. Reduction of the disulfide bond of chromogranin B (secretogranin I) in the trans-Golgi network causes its missorting to the constitutive secretory pathways. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2159–2168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappell T. G., Welch W. J., Schlossman D. M., Palter K. B., Schlesinger M. J., Rothman J. E. Uncoating ATPase is a member of the 70 kilodalton family of stress proteins. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Batchelor D. C., Palmer D. J. Identification of kex2-related proteases in chromaffin granules by partial amino acid sequence analysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15679–15683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Liston D., Martin M., Rosen H., Herbert E. Expression of the human proenkephalin gene in mouse pituitary cells: accurate and efficient mRNA production and proteolytic processing. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3115–3122. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Barondes S. H. Evidence for export of a muscle lectin from cytosol to extracellular matrix and for a novel secretory mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1681–1691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creemers J. W., Siezen R. J., Roebroek A. J., Ayoubi T. A., Huylebroeck D., Van de Ven W. J. Modulation of furin-mediated proprotein processing activity by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21826–21834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullinan W. E., Day N. C., Schäfer M. K., Day R., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Akil H., Watson S. J. Neuroanatomical and functional studies of peptide precursor-processing enzymes. Enzyme. 1991;45(5-6):285–300. doi: 10.1159/000468902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahms N. M., Lobel P., Kornfeld S. Mannose 6-phosphate receptors and lysosomal enzyme targeting. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12115–12118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Hutton J. C. The insulin-secretory-granule carboxypeptidase H. Purification and demonstration of involvement in proinsulin processing. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):575–582. doi: 10.1042/bj2450575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Peshavaria M., Hutton J. C. Proteolytic conversion of proinsulin into insulin. Identification of a Ca2+-dependent acidic endopeptidase in isolated insulin-secretory granules. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):279–286. doi: 10.1042/bj2460279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Rhodes C. J., Hutton J. C. Intraorganellar calcium and pH control proinsulin cleavage in the pancreatic beta cell via two distinct site-specific endopeptidases. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):93–96. doi: 10.1038/333093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day N. C., Lin H., Ueda Y., Meador-Woodruff J. H., Akil H. Characterization of pro-opiomelanocortin processing in heterologous neuronal cells that express PC2 mRNA. Neuropeptides. 1993 May;24(5):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(93)90013-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R., Schafer M. K., Watson S. J., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. Distribution and regulation of the prohormone convertases PC1 and PC2 in the rat pituitary. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;6(3):485–497. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1316544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Jahn R. Pathways to regulated exocytosis in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:625–645. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T. Amines and secretory pathways. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):73–74. doi: 10.1038/305073c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi L. Consensus sequence for processing of peptide precursors at monobasic sites. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 25;280(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80290-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson I. M., Dixon J. E., Mains R. E. Transfected human neuropeptide Y cDNA expression in mouse pituitary cells. Inducible high expression, peptide characterization, and secretion. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13646–13653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disdier M., Morrissey J. H., Fugate R. D., Bainton D. F., McEver R. P. Cytoplasmic domain of P-selectin (CD62) contains the signal for sorting into the regulated secretory pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Mar;3(3):309–321. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Rhodes C. J., Taylor N. A., Shennan K. I., Hutton J. C. Proinsulin endopeptidase substrate specificities defined by site-directed mutagenesis of proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18335–18339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Civelli O., Herbert E. Polyprotein gene expression: generation of diversity of neuroendocrine peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:665–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eder J., Rheinnecker M., Fersht A. R. Folding of subtilisin BPN': role of the pro-sequence. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 20;233(2):293–304. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards K., Fleischer B., Dryburgh H., Fleischer S., Schreiber G. The distribution of albumin precursor protein and albumin in liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):310–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90995-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipper B. A., Stoffers D. A., Mains R. E. The biosynthesis of neuropeptides: peptide alpha-amidation. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992;15:57–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.15.030192.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estivariz F. E., Friedman T. C., Chikuma T., Loh Y. P. Processing of adrenocorticotropin by two proteases in bovine intermediate lobe secretory vesicle membranes. A distinct acidic, tetrabasic residue-specific calcium-activated serine protease and a PC2-like enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7456–7463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. M., Scheller R. H. Prohormone processing and the secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16515–16518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Das B., Angeletti R. H. Identification of the pH-dependent membrane anchor of carboxypeptidase E (EC 3.4.17.10). J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2476–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:345–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanopoulou A. S., Kent G., Rabbani S. N., Seidah N. G., Patel Y. C. Heterologous processing of prosomatostatin in constitutive and regulated secretory pathways. Putative role of the endoproteases furin, PC1, and PC2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):6041–6049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H. Using recombinant DNA techniques to study protein targeting in the eucaryotic cell. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:403–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J. Polypeptide secondary structure may direct the specificity of prohormone conversion. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes H. H., Rosa P., Phillips E., Baeuerle P. A., Frank R., Argos P., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of human secretogranin II, a widespread tyrosine-sulfated secretory granule protein that exhibits low pH- and calcium-induced aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):12009–12015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goda Y., Pfeffer S. R. Cell-free systems to study vesicular transport along the secretory and endocytic pathways. FASEB J. 1989 Nov;3(13):2488–2495. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.13.2680705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorr S. U., Dean W. L., Radley T. L., Cohn D. V. Calcium-binding and aggregation properties of parathyroid secretory protein-I (chromogranin A). Bone Miner. 1988 Apr;4(1):17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorr S. U., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Regulated, but not constitutive, secretory proteins bind porcine chymotrypsinogen. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21595–21600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorr S. U., Shioi J., Cohn D. V. Interaction of calcium with porcine adrenal chromogranin A (secretory protein-I) and chromogranin B (secretogranin I). Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):E247–E254. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.2.E247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh B., Ohnishi Y., Inocencio N. M., Esaki E., Nakayama K., Barr P. J., Thomas G., Nagai Y. Mammalian subtilisin-related proteinases in cleavage activation of the paramyxovirus fusion glycoprotein: superiority of furin/PACE to PC2 or PC1/PC3. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6391–6397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6391-6397.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravotta D., Adesnik M., Sabatini D. D. Transport of influenza HA from the trans-Golgi network to the apical surface of MDCK cells permeabilized in their basolateral plasma membranes: energy dependence and involvement of GTP-binding proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2893–2908. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi K. A., Hutton J. C., Siddle K. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to insulin secretory granule membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):557–566. doi: 10.1042/bj2450557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes M., Kelly R. B. Intermediates in the constitutive and regulated secretory pathways released in vitro from semi-intact cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):539–549. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. J., Villa-Komaroff L., Kahn C. R., Weir G. C., Halban P. A. Deletion of a highly conserved tetrapeptide sequence of the proinsulin connecting peptide (C-peptide) inhibits proinsulin to insulin conversion by transfected pituitary corticotroph (AtT20) cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21486–21490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest P. C., Arden S. D., Bennett D. L., Clark A., Rutherford N. G., Hutton J. C. The post-translational processing and intracellular sorting of PC2 in the islets of Langerhans. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22401–22406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest P. C., Bailyes E. M., Rutherford N. G., Hutton J. C. Insulin secretory granule biogenesis. Co-ordinate regulation of the biosynthesis of the majority of constituent proteins. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):73–78. doi: 10.1042/bj2740073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B., Kelly R. B. Two distinct intracellular pathways transport secretory and membrane glycoproteins to the surface of pituitary tumor cells. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90374-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakes D. J., Birch N. P., Mezey A., Dixon J. E. Isolation of two complementary deoxyribonucleic acid clones from a rat insulinoma cell line based on similarities to Kex2 and furin sequences and the specific localization of each transcript to endocrine and neuroendocrine tissues in rats. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3053–3063. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A. Inhibition of proinsulin to insulin conversion in rat islets using arginine and lysine analogs. Lack of effect on rate of release of modified products. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13177–13180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A. Structural domains and molecular lifestyles of insulin and its precursors in the pancreatic beta cell. Diabetologia. 1991 Nov;34(11):767–778. doi: 10.1007/BF00408349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Hosaka M., Nakagawa T., Nagase M., Shoda A., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Structure and expression of mouse furin, a yeast Kex2-related protease. Lack of processing of coexpressed prorenin in GH4C1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22075–22078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Nagahama M., Takahashi S., Takada K., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Purification and characterization of furin, a Kex2-like processing endoprotease, produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16094–16099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marquardt T., Braakman I. The endoplasmic reticulum as a protein-folding compartment. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;2(8):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90309-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerman J. G., Cone R. C., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A., Mulligan R. C., Kronenberg H. M. Secretion of human parathyroid hormone from rat pituitary cells infected with a recombinant retrovirus encoding preproparathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5340–5344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Kowal R. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Proteolytic processing of the 600 kd low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) occurs in a trans-Golgi compartment. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1769–1776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Benedum U. M. Chromogranin A and pancreastatin. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):305–305. doi: 10.1038/325305b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Gerdes H. H., Rosa P. The granin (chromogranin/secretogranin) family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jan;16(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90012-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Tooze S. A. Biosynthetic protein transport in the secretory pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;1(4):648–654. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B. Tyrosine sulfation and the secretory pathway. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:363–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C. Secretory granules. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1091–1098. doi: 10.1007/BF01971456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C. Subtilisin-like proteinases involved in the activation of proproteins of the eukaryotic secretory pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;2(6):1131–1142. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90167-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C. The internal pH and membrane potential of the insulin-secretory granule. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj2040171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara Y., Oda K., Kato K. Conversion of proalbumin into serum albumin in the secretory vesicles of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90996-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean F., Basak A., Rondeau N., Benjannet S., Hendy G. N., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Lazure C. Enzymic characterization of murine and human prohormone convertase-1 (mPC1 and hPC1) expressed in mammalian GH4C1 cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 15;292(Pt 3):891–900. doi: 10.1042/bj2920891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judah J. D., Gamble M., Steadman J. H. Biosynthesis of serum albumin in rat liver. Evidence for the existence of 'proalbumin'. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1083–1091. doi: 10.1042/bj1341083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judah J. D., Quinn P. S. Calcium ion-dependent vesicle fusion in the conversion of proalbumin to albumin. Nature. 1978 Jan 26;271(5643):384–385. doi: 10.1038/271384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrenbauer A., Jeckel D., Just W., Birk R., Schmidt R. R., Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. The rate of bulk flow from the Golgi to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90159-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H. Clathrin and associated assembly and disassembly proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:415–438. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley W. L., Georgopoulos C. Chaperones and protein folding. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):984–991. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Pathways of protein secretion in eukaryotes. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):25–32. doi: 10.1126/science.2994224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Secretory granule and synaptic vesicle formation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):654–660. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90037-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Storage and release of neurotransmitters. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):43–53. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmler W., Steiner D. F., Borg J. Studies on the conversion of proinsulin to insulin. 3. Studies in vitro with a crude secretion granule fraction isolated from rat islets of Langerhans. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4544–4551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Tucker J. E., Joh R., Landsberg K. E., Saltman D., Barr P. J. Identification of a second human subtilisin-like protease gene in the fes/fps region of chromosome 15. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;10(10):757–769. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchmair R., Egger C., Gee P., Hogue-Angeletti R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Laslop A., Winkler H. Differential subcellular distribution of PC1, PC2 and furin in bovine adrenal medulla and secretion of PC1 and PC2 from this tissue. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Aug 31;143(1-2):143–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchmair R., Gee P., Hogue-Angeletti R., Laslop A., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Immunological characterization of the endoproteases PC1 and PC2 in adrenal chromaffin granules and in the pituitary gland. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 10;297(3):302–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80560-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizer J. S., Tropsha A. A motif found in propeptides and prohormones that may target them to secretory vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):586–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91457-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D. Sorting and traffic in the central vacuolar system. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):703–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90783-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner J., Chun J., Harter D., Axel R. Isolation and functional expression of a mammalian prohormone processing enzyme, murine prohormone convertase 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6834–6838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S., Mellman I. The biogenesis of lysosomes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:483–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. Structure and function of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulinlike growth factor II receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:307–330. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Thorner J. Membrane translocation of proteins without hydrophobic signal peptides. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;2(4):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90102-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Thorner J. Secretion of peptides and proteins lacking hydrophobic signal sequences: the role of adenosine triphosphate-driven membrane translocators. Endocr Rev. 1992 Aug;13(3):499–514. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-3-499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuliawat R., Arvan P. Protein targeting via the "constitutive-like" secretory pathway in isolated pancreatic islets: passive sorting in the immature granule compartment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):521–529. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry S. J., Gierasch L. M. Recognition of nascent polypeptides for targeting and folding. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Apr;16(4):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond F. A., Viau G., Lainé J., Lebel D. Reconstitution in vitro of the pH-dependent aggregation of pancreatic zymogens en route to the secretory granule: implication of GP-2. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):289–296. doi: 10.1042/bj2910289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc R., Molloy S. S., Thorne B. A., Thomas G. Activation of human furin precursor processing endoprotease occurs by an intramolecular autoproteolytic cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14304–14308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg I. The new eukaryotic precursor processing proteinases. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1361–1365. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstedt R., Apodaca G., Barondes S. H., Mostov K. E., Leffler H. Apical secretion of a cytosolic protein by Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Evidence for polarized release of an endogenous lectin by a nonclassical secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11750–11757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R. Intracellular traffic of newly synthesized proteins. Current understanding and future prospects. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):739–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI113952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R. More than just a channel: provocative new features of protein traffic across the ER membrane. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):527–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bonifacino J. S., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Degradation from the endoplasmic reticulum: disposing of newly synthesized proteins. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh Y. P., Andreasson K. I., Birch N. P. Intracellular trafficking and processing of pro-opiomelanocortin. Cell Biophys. 1991 Oct-Dec;19(1-3):73–83. doi: 10.1007/BF02989881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi T., Montesano R., Wohlwend A., Amherdt M., Vassalli J. D., Orci L. Evidence for polarization of plasma membrane domains in pancreatic endocrine cells. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):694–696. doi: 10.1038/313694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusson J., Vieau D., Hamelin J., Day R., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. cDNA structure of the mouse and rat subtilisin/kexin-like PC5: a candidate proprotein convertase expressed in endocrine and nonendocrine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6691–6695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E. Golgi retention signals: do membranes hold the key? Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90001-P. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Cullen E. I., May V., Eipper B. A. The role of secretory granules in peptide biosynthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:278–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A. Coordinate, equimolar secretion of smaller peptide products derived from pro-ACTH/endorphin by mouse pituitary tumor cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;89(1):21–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A. Secretion and regulation of two biosynthetic enzyme activities, peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase and a carboxypeptidase, by mouse pituitary corticotropic tumor cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):1683–1690. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-1683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., May V. The role of a low pH intracellular compartment in the processing, storage, and secretion of ACTH and endorphin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7887–7894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkiewicz M., Day R., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M. Ontogeny of the prohormone convertases PC1 and PC2 in the mouse hypophysis and their colocalization with corticotropin and alpha-melanotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):4922–4926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.4922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Franzusoff A., Howell K. E. Vesicle budding: insights from cell-free assays. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Simons K. The Golgi complex: in vitro veritas? Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90027-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I. The importance of being acid: the role of acidification in intracellular membrane traffic. J Exp Biol. 1992 Nov;172:39–45. doi: 10.1242/jeb.172.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I. Protein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum: a light at the end of the tunnel. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Moore H. P. Reconstitution of constitutive secretion using semi-intact cells: regulation by GTP but not calcium. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):39–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Moore H. P. Regulated secretion. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;2(4):642–647. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90105-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Oda K., Fujiwara T., Takami N., Tashiro K., Ikehara Y. Functional expression of furin demonstrating its intracellular localization and endoprotease activity for processing of proalbumin and complement pro-C3. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16954–16959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Inocencio N. M., Robertson B. J., Moehring T. J. Expression of mouse furin in a Chinese hamster cell resistant to Pseudomonas exotoxin A and viruses complements the genetic lesion. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2590–2594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy S. S., Bresnahan P. A., Leppla S. H., Klimpel K. R., Thomas G. Human furin is a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease that recognizes the sequence Arg-X-X-Arg and efficiently cleaves anthrax toxin protective antigen. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16396–16402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. H., Kelly R. B. Re-routing of a secretory protein by fusion with human growth hormone sequences. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):443–446. doi: 10.1038/321443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Gumbiner B., Kelly R. B. Chloroquine diverts ACTH from a regulated to a constitutive secretory pathway in AtT-20 cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):434–436. doi: 10.1038/302434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Kelly R. B. Secretory protein targeting in a pituitary cell line: differential transport of foreign secretory proteins to distinct secretory pathways. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1773–1781. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Walker M. D., Lee F., Kelly R. B. Expressing a human proinsulin cDNA in a mouse ACTH-secreting cell. Intracellular storage, proteolytic processing, and secretion on stimulation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mroz E. A., Lechene C. Pancreatic zymogen granules differ markedly in protein composition. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):871–873. doi: 10.1126/science.2422756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesch A., Hartmann E., Rohde K., Rubartelli A., Sitia R., Rapoport T. A. A novel pathway for secretory proteins? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):86–88. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90186-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Hosaka M., Torii S., Watanabe T., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Identification and functional expression of a new member of the mammalian Kex2-like processing endoprotease family: its striking structural similarity to PACE4. J Biochem. 1993 Feb;113(2):132–135. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Identification of an isoform with an extremely large Cys-rich region of PC6, a Kex2-like processing endoprotease. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 26;327(2):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80163-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Hosaka M., Hatsuzawa K., Murakami K. Cloning and functional expression of a novel endoprotease involved in prohormone processing at dibasic sites. J Biochem. 1991 Jun;109(6):803–806. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Kim W. S., Torii S., Hosaka M., Nakagawa T., Ikemizu J., Baba T., Murakami K. Identification of the fourth member of the mammalian endoprotease family homologous to the yeast Kex2 protease. Its testis-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5897–5900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neerman-Arbez M., Halban P. A. Novel, non-crinophagic, degradation of connecting peptide in transformed pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16248–16252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H. Proteolytic processing and physiological regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Jul;14(7):268–271. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H. Proteolytic processing and regulation. Enzyme. 1991;45(5-6):239–243. doi: 10.1159/000468898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Morris J. F. Method for quantitating the molecular content of a subcellular organelle: hormone and neurophysin content of newly formed and aged neurosecretory granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):180–184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Ikeda M., Tsuji E., Sohda M., Takami N., Misumi Y., Ikehara Y. Sequence requirements for proteolytic cleavage of precursors with paired basic amino acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1181–1186. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91696-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Ikehara Y. Monensin inhibits the conversion of proalbumin to serum albumin in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):766–772. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91500-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Hojo H., Aimoto S., Kobayashi T., Zhu X., Jordan F., Inouye M. Pro-peptide as an intramolecular chaperone: renaturation of denatured subtilisin E with a synthetic pro-peptide [corrected]. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1507–1510. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Halban P., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Vassalli J. D., Perrelet A. A clathrin-coated, Golgi-related compartment of the insulin secreting cell accumulates proinsulin in the presence of monensin. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Halban P., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Vassalli J. D., Perrelet A. Nonconverted, amino acid analog-modified proinsulin stays in a Golgi-derived clathrin-coated membrane compartment. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2187–2192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. Macro- and micro-domains in the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):538–565. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malhotra V., Amherdt M., Serafini T., Rothman J. E. Dissection of a single round of vesicular transport: sequential intermediates for intercisternal movement in the Golgi stack. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Louvard D., Perrelet A. Clathrin-immunoreactive sites in the Golgi apparatus are concentrated at the trans pole in polypeptide hormone-secreting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5385–5389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Madsen O., Perrelet A., Vassalli J. D., Anderson R. G. Conversion of proinsulin to insulin occurs coordinately with acidification of maturing secretory vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2273–2281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Madsen O., Vassalli J. D., Perrelet A. Direct identification of prohormone conversion site in insulin-secreting cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):671–681. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Powell S. K., Quinn D. L., Moore H. P. The trans-most cisternae of the Golgi complex: a compartment for sorting of secretory and plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Anderson R. G. The condensing vacuole of exocrine cells is more acidic than the mature secretory vesicle. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):77–79. doi: 10.1038/326077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Perrelet A. (Pro)insulin associates with Golgi membranes of pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6743–6746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Storch M. J., Anderson R. G., Vassalli J. D., Perrelet A. Proteolytic maturation of insulin is a post-Golgi event which occurs in acidifying clathrin-coated secretory vesicles. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):865–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90624-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. The insulin factory: a tour of the plant surroundings and a visit to the assembly line. The Minkowski lecture 1973 revisited. Diabetologia. 1985 Aug;28(8):528–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00281987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. J., Christie D. L. Identification of molecular aggregates containing glycoproteins III, J, K (carboxypeptidase H), and H (Kex2-related proteases) in the soluble and membrane fractions of adrenal medullary chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19806–19812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolillo L., Simonetti M., Brakch N., D'Auria G., Saviano M., Dettin M., Rholam M., Scatturin A., Di Bello C., Cohen P. Evidence for the presence of a secondary structure at the dibasic processing site of prohormone: the pro-ocytocin model. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2399–2405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05304.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Schekman R. Clathrin: a role in the intracellular retention of a Golgi membrane protein. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2675311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Bretscher M. S. Membrane recycling by coated vesicles. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:85–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M. Clathrin and coated vesicles. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2507–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M. Coated vesicles from pig brain: purification and biochemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 5;97(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Crowther R. A. Structure and assembly of coated vesicles. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:49–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. Mannose 6-phosphate receptors and their role in targeting proteins to lysosomes. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(1):7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF01871928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Rothman J. E. Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:829–852. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimplikar S. W., Huttner W. B. Chromogranin B (secretogranin I), a secretory protein of the regulated pathway, is also present in a tightly membrane-associated form in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4110–4118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. K., Orci L., Craik C. S., Moore H. P. Efficient targeting to storage granules of human proinsulins with altered propeptide domain. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1843–1851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryer N. K., Wuestehube L. J., Schekman R. Vesicle-mediated protein sorting. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:471–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport T. A. Transport of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):931–936. doi: 10.1126/science.1332192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M., Perrelet A., Roth J., Orci L. Insulin immunoreactive sites demonstrated in the Golgi apparatus of pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5661–5664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Banerjee D., Manning C., Huang C. Y., Green K. In vivo effect of colchicine on hepatic protein synthesis and on the conversion of proalbumin to serum albumin. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):400–416. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes C. J., Lucas C. A., Mutkoski R. L., Orci L., Halban P. A. Stimulation by ATP of proinsulin to insulin conversion in isolated rat pancreatic islet secretory granules. Association with the ATP-dependent proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10712–10717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes C. J., Thorne B. A., Lincoln B., Nielsen E., Hutton J. C., Thomas G. Processing of proopiomelanocortin by insulin secretory granule proinsulin processing endopeptidases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4267–4275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes C. J., Zumbrunn A., Bailyes E. M., Shaw E., Hutton J. C. The inhibition of proinsulin-processing endopeptidase activities by active-site-directed peptides. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):305–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2580305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rholam M., Nicolas P., Cohen P. Precursors for peptide hormones share common secondary structures forming features at the proteolytic processing sites. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. J., Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Defective processing of the insulin receptor in an endoprotease-deficient Chinese hamster cell strain is corrected by expression of mouse furin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24274–24277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertus J. D., Kraut J., Alden R. A., Birktoft J. J. Subtilisin; a stereochemical mechanism involving transition-state stabilization. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4293–4303. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. S. Adaptins. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;2(10):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Powell S. K. Polarity of epithelial and neuronal cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:395–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Creemers J. W., Pauli I. G., Kurzik-Dumke U., Rentrop M., Gateff E. A., Leunissen J. A., Van de Ven W. J. Cloning and functional expression of Dfurin2, a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme of Drosophila melanogaster with multiple repeats of a cysteine motif. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17208–17215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Pauli I. G., Zhang Y., van de Ven W. J. cDNA sequence of a Drosophila melanogaster gene, Dfur1, encoding a protein structurally related to the subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme furin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 9;289(2):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81052-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Leunissen J. A., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Evolutionary conserved close linkage of the c-fes/fps proto-oncogene and genetic sequences encoding a receptor-like protein. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2197–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Weiss U., Pepperkok R., Ansorge W., Niehrs C., Stelzer E. H., Huttner W. B. An antibody against secretogranin I (chromogranin B) is packaged into secretory granules. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):17–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rufaut N. W., Brennan S. O., Hakes D. J., Dixon J. E., Birch N. P. Purification and characterization of the candidate prohormone-processing enzyme SPC3 produced in a mouse L cell line. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20291–20298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalken J. A., Roebroek A. J., Oomen P. P., Wagenaar S. S., Debruyne F. M., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. fur gene expression as a discriminating marker for small cell and nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1545–1549. doi: 10.1172/JCI113240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlossman D. M., Schmid S. L., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. An enzyme that removes clathrin coats: purification of an uncoating ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):723–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel E., Mains R. E., Farquhar M. G. Proteolytic processing of pro-ACTH/endorphin begins in the Golgi complex of pituitary corticotropes and AtT-20 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1223–1235. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W. The processing of peptide precursors. 'Proline-directed arginyl cleavage' and other monobasic processing mechanisms. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 5;200(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80500-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer M. K., Day R., Cullinan W. E., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G., Watson S. J. Gene expression of prohormone and proprotein convertases in the rat CNS: a comparative in situ hybridization analysis. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):1258–1279. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-01258.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Day R., Hamelin J., Gaspar A., Collard M. W., Chrétien M. Testicular expression of PC4 in the rat: molecular diversity of a novel germ cell-specific Kex2/subtilisin-like proprotein convertase. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;6(10):1559–1570. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.10.1448111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Day R., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Chrétien M. Mammalian neural and endocrine pro-protein and pro-hormone convertases belonging to the subtilisin family of serine proteinases. Enzyme. 1991;45(5-6):271–284. doi: 10.1159/000468901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Day R., Marcinkiewicz M., Chrétien M. Mammalian paired basic amino acid convertases of prohormones and proproteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 May 31;680:135–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb19680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Gaspar L., Mion P., Marcinkiewicz M., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. cDNA sequence of two distinct pituitary proteins homologous to Kex2 and furin gene products: tissue-specific mRNAs encoding candidates for pro-hormone processing proteinases. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(6):415–424. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Gaspar L., Beaubien G., Mattei M. G., Lazure C., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, Furin, and Kex2: distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevarino K. A., Felix R., Banks C. M., Low M. J., Montminy M. R., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Cell-specific processing of preprosomatostatin in cultured neuroendocrine cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):4987–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevarino K. A., Stork P. Multiple preprosomatostatin sorting signals mediate secretion via discrete cAMP- and tetradecanoylphorbolacetate-responsive pathways. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18507–18513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevarino K. A., Stork P., Ventimiglia R., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Amino-terminal sequences of prosomatostatin direct intracellular targeting but not processing specificity. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevarino K. A., Ventimiglia R., Stork P. Processing and intracellular sorting of anglerfish and rat preprosomatostatins in mammalian endocrine cells. Metabolism. 1990 Sep;39(9 Suppl 2):26–29. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90203-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen F. S., Seidah N. G., Lindberg I. Biosynthesis of the prohormone convertase PC2 in Chinese hamster ovary cells and in rat insulinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24910–24915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shennan K. I., Seal A. J., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Docherty K. Site-directed mutagenesis and expression of PC2 in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24011–24017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shennan K. I., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Docherty K. Characterization of PC2, a mammalian Kex2 homologue, following expression of the cDNA in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80703-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizonenko S. V., Halban P. A. Differential rates of conversion of rat proinsulins I and II. Evidence for slow cleavage at the B-chain/C-peptide junction of proinsulin II. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):621–625. doi: 10.1042/bj2780621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizonenko S., Irminger J. C., Buhler L., Deng S., Morel P., Halban P. A. Kinetics of proinsulin conversion in human islets. Diabetes. 1993 Jun;42(6):933–936. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Avruch A. S., LaMendola J., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of a cDNA encoding a second putative prohormone convertase related to PC2 in AtT20 cells and islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):340–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. The biosynthesis and processing of neuroendocrine peptides: identification of proprotein convertases involved in intravesicular processing. Prog Brain Res. 1992;92:235–246. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Montag A. G., Thomas G., Albiges-Rizo C., Carroll R., Benig M., Phillips L. A., Martin S., Ohagi S., Gardner P. Proinsulin processing by the subtilisin-related proprotein convertases furin, PC2, and PC3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8822–8826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F. Identification of a human insulinoma cDNA encoding a novel mammalian protein structurally related to the yeast dibasic processing protease Kex2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2997–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit A. B., Spijker S., Geraerts W. P. Molluscan putative prohormone convertases: structural diversity in the central nervous system of Lymnaea stagnalis. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 9;312(2-3):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80938-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Cunningham D., Spigelman L., Aten B. Insulin biosynthesis: evidence for a precursor. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):697–700. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., James D. E. Cellular and molecular biology of the beta cell. Diabetologia. 1992 Dec;35 (Suppl 2):S41–S48. doi: 10.1007/BF00586278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Kemmler W., Tager H. S., Peterson J. D. Proteolytic processing in the biosynthesis of insulin and other proteins. Fed Proc. 1974 Oct;33(10):2105–2115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Michael J., Houghten R., Mathieu M., Gardner P. R., Ravazzola M., Orci L. Use of a synthetic peptide antigen to generate antisera reactive with a proteolytic processing site in native human proinsulin: demonstration of cleavage within clathrin-coated (pro)secretory vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6184–6188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Oyer P. E. The biosynthesis of insulin and a probable precursor of insulin by a human islet cell adenoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):473–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Tager H. S., Chan S. J., Nanjo K., Sanke T., Rubenstein A. H. Lessons learned from molecular biology of insulin-gene mutations. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):600–609. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieneke-Gröber A., Vey M., Angliker H., Shaw E., Thomas G., Roberts C., Klenk H. D., Garten W. Influenza virus hemagglutinin with multibasic cleavage site is activated by furin, a subtilisin-like endoprotease. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2407–2414. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoller T. J., Shields D. Retrovirus-mediated expression of preprosomatostatin: posttranslational processing, intracellular storage, and secretion in GH3 pituitary cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2087–2095. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoller T. J., Shields D. The propeptide of preprosomatostatin mediates intracellular transport and secretion of alpha-globin from mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1647–1655. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoller T. J., Shields D. The role of paired basic amino acids in mediating proteolytic cleavage of prosomatostatin. Analysis using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6922–6928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausberg S., Alexander P., Wang L., Schwarz F., Bryan P. Catalysis of a protein folding reaction: thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of subtilisin BPN' interactions with its propeptide fragment. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 17;32(32):8112–8119. doi: 10.1021/bi00083a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Willemsen R., van Kerkhof P., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Lodish H. F. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein, albumin, and transferrin are transported to the cell surface via the same Golgi vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Nomizu M., Kurosumi K. Intracellular sites of proteolytic processing of pro-opiomelanocortin in melanotrophs and corticotrophs in rat pituitary. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Jun;39(6):809–821. doi: 10.1177/39.6.1851777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A., Vassalli P., Détraz M. Comparative studies of intracellular transport of secretory proteins. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):694–707. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Leduc R., Thorne B. A., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Thomas G. Kex2-like endoproteases PC2 and PC3 accurately cleave a model prohormone in mammalian cells: evidence for a common core of neuroendocrine processing enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5297–5301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Hollinshead M., Frank R., Burke B. An antibody specific for an endoproteolytic cleavage site provides evidence that pro-opiomelanocortin is packaged into secretory granules in AtT20 cells before its cleavage. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):155–162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Kern H. F., Fuller S. D., Howell K. E. Condensation-sorting events in the rough endoplasmic reticulum of exocrine pancreatic cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):35–50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Tooze S. A. Clathrin-coated vesicular transport of secretory proteins during the formation of ACTH-containing secretory granules in AtT20 cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):839–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Tooze S. A., Fuller S. D. Sorting of progeny coronavirus from condensed secretory proteins at the exit from the trans-Golgi network of AtT20 cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1215–1226. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze S. A. Biogenesis of secretory granules. Implications arising from the immature secretory granule in the regulated pathway of secretion. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):220–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80805-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze S. A., Huttner W. B. Cell-free protein sorting to the regulated and constitutive secretory pathways. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):837–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90097-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze S. A., Weiss U., Huttner W. B. Requirement for GTP hydrolysis in the formation of secretory vesicles. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):207–208. doi: 10.1038/347207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungewickell E., Branton D. Assembly units of clathrin coats. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):420–422. doi: 10.1038/289420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Ven W. J., Creemers J. W., Roebroek A. J. Furin: the prototype mammalian subtilisin-like proprotein-processing enzyme. Endoproteolytic cleavage at paired basic residues of proproteins of the eukaryotic secretory pathway. Enzyme. 1991;45(5-6):257–270. doi: 10.1159/000468900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Ven W. J., Roebroek A. J., Van Duijnhoven H. L. Structure and function of eukaryotic proprotein processing enzymes of the subtilisin family of serine proteases. Crit Rev Oncog. 1993;4(2):115–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidricaire G., Denault J. B., Leduc R. Characterization of a secreted form of human furin endoprotease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 15;195(2):1011–1018. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vindrola O., Lindberg I. Biosynthesis of the prohormone convertase mPC1 in AtT-20 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jul;6(7):1088–1094. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.7.1508222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider F., Irminger J. C., Gross D. J., Villa-Komaroff L., Halban P. A. Processing of proinsulin by transfected hepatoma (FAO) cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14629–14636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Saffaripour S., Bonfanti R., Sadler J. E., Cramer E. M., Chapman B., Mayadas T. N. Induction of specific storage organelles by von Willebrand factor propolypeptide. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90648-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Positional and additive effects of basic amino acids on processing of precursor proteins within the constitutive secretory pathway. FEBS Lett. 1993 Apr 12;320(3):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80589-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Frank B. H., Khait I., Pekar A., Heiney R., Shoelson S. E., Neuringer L. J. NMR and photo-CIDNP studies of human proinsulin and prohormone processing intermediates with application to endopeptidase recognition. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8389–8401. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F. T., Gleason M. L., Serafini T. A., Rothman J. E. The rate of bulk flow from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Barr P. J., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J., Kaufman R. J. Expression of a human proprotein processing enzyme: correct cleavage of the von Willebrand factor precursor at a paired basic amino acid site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9378–9382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. H., Ignatius M. J., Parosky G., Parham P., Trojanowski J. Q., Brodsky F. M. Neuron-specific expression of high-molecular-weight clathrin light chain. J Neurosci. 1990 Sep;10(9):3025–3031. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-09-03025.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Schneider D. L. The bioenergetics of Golgi apparatus function: evidence for an ATP-dependent proton pump. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):620–625. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90825-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y., Lindberg I. Purification and characterization of the prohormone convertase PC1(PC3). J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5615–5623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. L., Ohta Y., Jordan F., Inouye M. Pro-sequence of subtilisin can guide the refolding of denatured subtilisin in an intermolecular process. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):483–484. doi: 10.1038/339483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Camilli P., Navone F. Regulated secretory pathways of neurons and their relation to the regulated secretory pathway of endocrine cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:461–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Ven W. J., Voorberg J., Fontijn R., Pannekoek H., van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Roebroek A. J., Siezen R. J. Furin is a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme in higher eukaryotes. Mol Biol Rep. 1990 Nov;14(4):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00429896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K., Hasilik A. Lysosomal enzymes and their receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:167–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K. Molecular recognition and targeting of lysosomal proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):642–646. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90035-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Zastrow M., Castle A. M., Castle J. D. Ammonium chloride alters secretory protein sorting within the maturing exocrine storage compartment. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6566–6571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Zastrow M., Castle J. D. Protein sorting among two distinct export pathways occurs from the content of maturing exocrine storage granules. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2675–2684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]