Abstract
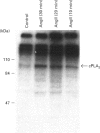
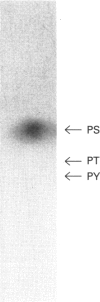
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) may be one of the major components involved in cell signalling and proliferation, as suggested by recent studies. In this paper we show that the potent vasoconstrictor and hypertrophic agent angiotensin II (AngII) activates cytosolic PLA2 (cPLA2) in vascular smooth-muscle cells. AngII induced a rapid time-dependent release of [3H]arachidonic acid from prelabelled cells that was inhibited by mepacrine, a PLA2 inhibitor. AngII treatment of intact cells also activated a cPLA2, as measured in cell-free extracts by the release of radiolabelled arachidonic acid from exogenously added 1-stearoyl-2-[1-14C]arachidonoyl phosphatidylcholine. This AngII-stimulated cPLA2 activity was also significantly inhibited by mepacrine. AngII induced a rapid and time-dependent increase in cPLA2 phosphorylation. Protein kinase C (PKC) depletion inhibited both AngII-induced [3H]arachidonic acid release and cPLA2 phosphorylation. Together, these results suggest strongly that (1) AngII phosphorylates and activates cPLA2 in a PKC-dependent manner, and that (2) cPLA2 mediates the AngII-induced [3H]arachidonic acid release in vascular smooth-muscle cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander R. W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Stimulation of prostaglandin E synthesis in cultured human umbilical vein smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1617–1620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod J., Burch R. M., Jelsema C. L. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 via GTP-binding proteins: arachidonic acid and its metabolites as second messengers. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Mar;11(3):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C activities of platelets. Differential substrate specificity, Ca2+ requirement, pH dependence, and cellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10227–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Gronich J. H., Nemenoff R. A. Epidermal growth factor enhances glomerular mesangial cell soluble phospholipase A2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4934–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. C., Pritchard E. T., Gerrard J. M., Man R. Y., Choy P. C. Biphasic modulation of platelet phospholipase A2 activity and platelet aggregation by mepacrine (quinacrine). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 14;713(1):170–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Milona N., Knopf J. L. Purification of a 110-kilodalton cytosolic phospholipase A2 from the human monocytic cell line U937. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7708–7712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Dennis E. A. Evolutionary relationships and implications for the regulation of phospholipase A2 from snake venom to human secreted forms. J Mol Evol. 1990 Sep;31(3):228–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02109500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diez E., Mong S. Purification of a phospholipase A2 from human monocytic leukemic U937 cells. Calcium-dependent activation and membrane association. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14654–14661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. The importance of phospholipase-A2 in prostaglandin biosynthesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Feb 1;25(3):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Force T., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Bonventre J. V. Endothelin, vasopressin, and angiotensin II enhance tyrosine phosphorylation by protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways in glomerular mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6650–6656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronich J. H., Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. A. Identification and characterization of a hormonally regulated form of phospholipase A2 in rat renal mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16645–16651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronich J. H., Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. A. Purification of a high-molecular-mass form of phospholipase A2 from rat kidney activated at physiological calcium concentrations. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 1;271(1):37–43. doi: 10.1042/bj2710037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J. Platelet activating factor: a biologically active phosphoglyceride. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:483–509. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. A., Danilowicz R. M., Eling T. E. Mitogenic signaling by epidermal growth factor (EGF), but not platelet-derived growth factor, requires arachidonic acid metabolism in BALB/c 3T3 cells. Modulation of EGF-dependent c-myc expression by prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3669–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Homma T., Jacobson H. R., Capdevila J. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids activate Na+/H+ exchange and are mitogenic in cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Sep;144(3):429–437. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt E., Fried V. A. Phosphoamino acid analysis of protein immobilized on polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. Anal Biochem. 1989 Mar;177(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Manetta J., Putnam J. E. The Ca2(+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 is a 100-kDa protein in human monoblast U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5268–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassègue B., Alexander R. W., Clark M., Akers M., Griendling K. K. Phosphatidylcholine is a major source of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 1;292(Pt 2):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj2920509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassègue B., Alexander R. W., Clark M., Griendling K. K. Angiotensin II-induced phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis in cultured vascular smooth-muscle cells. Regulation and localization. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):19–25. doi: 10.1042/bj2760019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is coupled to hormonally regulated release of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., Davis R. J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A., Gross R. W. Identification and purification of sheep platelet phospholipase A2 isoforms. Activation by physiologic concentrations of calcium ion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10467–10470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina E. J., Weiner R., Kaley G. Inhibition of bradykinin vasodilation and potentiation of norepinephrine and angiotensin vasoconstriction by inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis in skeletal muscle of the rat. Circ Res. 1975 Oct;37(4):430–437. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.4.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina J. L., Standaert M. L., Ishizuka T., Weinstock R. S., Farese R. V. Role of protein kinase C in insulin's regulation of c-fos transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9223–9228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Winitz S., Qian N. X., Van Putten V., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. Phosphorylation and activation of a high molecular weight form of phospholipase A2 by p42 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1960–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on DNA synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 1):C584–C588. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.4.C584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmberg L., Claesson H. E., Thyberg J. Leukotrienes stimulate initiation of DNA synthesis in cultured arterial smooth muscle cells. J Cell Sci. 1987 Sep;88(Pt 2):151–159. doi: 10.1242/jcs.88.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Pignat W., Märki F., Wiesenberg I. Release of phospholipase A2 activity from rat vascular smooth muscle cells mediated by cAMP. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 15;181(1):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk C. G., Märki F., Van den Bosch H. Studies on the acyl-chain selectivity of cellular phospholipases A2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 1;1044(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90229-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., White S. P., Otwinowski Z., Yuan W., Gelb M. H., Sigler P. B. Interfacial catalysis: the mechanism of phospholipase A2. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1541–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2274785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellmayer A., Uedelhoven W. M., Weber P. C., Bonventre J. V. Endogenous non-cyclooxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid modulate growth and mRNA levels of immediate-early response genes in rat mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3800–3807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimakura S., Boland C. R. Eicosanoid production by the human gastric cancer cell line AGS and its relation to cell growth. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1744–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka S. R., Insel P. A. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis and prostaglandin E2 formation in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Possible parallel activation of phospholipase C and phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4200–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L. The eicosanoids and their biochemical mechanisms of action. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):315–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2590315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern N., Golub M., Nozawa K., Berger M., Knoll E., Yanagawa N., Natarajan R., Nadler J. L., Tuck M. L. Selective inhibition of angiotensin II-mediated vasoconstriction by lipoxygenase blockade. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 2):H434–H443. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.2.H434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suga K., Kawasaki T., Blank M. L., Snyder F. An arachidonoyl (polyenoic)-specific phospholipase A2 activity regulates the synthesis of platelet-activating factor in granulocytic HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12363–12371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. B., Berk B. C., Izumo S., Tsuda T., Alexander R. W., Nadal-Ginard B. Angiotensin II induces c-fos mRNA in aortic smooth muscle. Role of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):526–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo H., Ono T., Kuramitsu S., Kagamiyama H., Okamoto M. A phospholipase A2 in the supernatant fraction of rat spleen. Its similarity to rat pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5724–5731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travo P., Barrett G., Burnstock G. Differences in proliferation of primary cultures of vascular smooth muscle cells taken from male and female rats. Blood Vessels. 1980;17(2):110–116. doi: 10.1159/000158240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Kawahara Y., Ishida Y., Koide M., Shii K., Yokoyama M. Angiotensin II stimulates two myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1992 Sep;71(3):620–630. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.3.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Watanabe Y., Sano M., Lister M. D., Deems R. A., Dennis E. A. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of a membrane-bound phospholipase A2 from the P388D1 macrophage-like cell line. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3079–3085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M. Approaches to the study of mammalian cellular phospholipases. J Lipid Res. 1985 Dec;26(12):1379–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing M., Mattera R. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of phospholipase A2 by G-proteins and Ca2+ in HL60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25966–25975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong J. G., Amesz H., Aarsman A. J., Lenting H. B., van den Bosch H. Monoclonal antibodies against an intracellular phospholipase A2 from rat liver and their cross-reactivity with other phospholipases A2. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 1;164(1):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]