Abstract
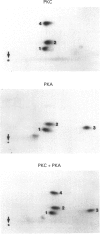
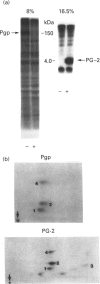
Specific sites in the linker region of human P-glycoprotein phosphorylated by protein kinase C (PKC) were identified by means of a synthetic peptide substrate, PG-2, corresponding to residues 656-689 from this region of the molecule. As PG-2 has several sequences of the type recognized by the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), PG-2 was also tested as a substrate for PKA. PG-2 was phosphorylated by purified PKC in a Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent manner, with a Km of 1.3 microM, and to a maximum stoichiometry of 2.9 +/- 0.1 mol of phosphate/mol of peptide. Sequence analysis of tryptic fragments of PG-2 phosphorylated by PKC identified Ser-661, Ser-667 and Ser-671 as the three sites of phosphorylation. PG-2 was also found to be phosphorylated by purified PKA in a cyclic AMP-dependent manner, with a Km of 21 microM, and to a maximum stoichiometry of 2.6 +/- 0.2 mol of phosphate/mol of peptide. Ser-667, Ser-671 and Ser-683 were phosphorylated by PKA. Truncated peptides of PG-2 were utilized to confirm that Ser-661 was PKC-specific and Ser-683 was PKA-specific. Further studies showed that PG-2 acted as a competitive substrate for the P-glycoprotein kinase present in membranes from multidrug-resistant human KB cells. The membrane kinase phosphorylated PG-2 mainly on Ser-661, Ser-667 and Ser-671. These results show that human P-glycoprotein can be phosphorylated by at least two protein kinases, stimulated by different second-messenger systems, which exhibit both overlapping and unique specificities for phosphorylation of multiple sites in the linker region of the molecule.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambudkar S. V., Lelong I. H., Zhang J., Cardarelli C. O., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Partial purification and reconstitution of the human multidrug-resistance pump: characterization of the drug-stimulatable ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8472–8476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates S. E., Currier S. J., Alvarez M., Fojo A. T. Modulation of P-glycoprotein phosphorylation and drug transport by sodium butyrate. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 21;31(28):6366–6372. doi: 10.1021/bi00143a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel P. J., Beavo J. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of catalytic subunit of skeletal muscle adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2691–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boscoboinik D., Debanne M. T., Stafford A. R., Jung C. Y., Gupta R. S., Epand R. M. Dimerization of the P-glycoprotein in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 7;1027(3):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90311-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. C., Chalikonda I., Eilon G. Correlation of protein kinase C translocation, P-glycoprotein phosphorylation and reduced drug accumulation in multidrug resistant human KB cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 31;169(1):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91461-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. C., McAvoy E. M., Jacobs J. W., Eilon G. Protein kinase C phosphorylates P-glycoprotein in multidrug resistant human KB carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7679–7686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. C., Pohl J., Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. Identification of specific sites in human P-glycoprotein phosphorylated by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4592–4595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. C., Zheng B., Kuo J. F. Regulation by phorbol ester and protein kinase C inhibitors, and by a protein phosphatase inhibitor (okadaic acid), of P-glycoprotein phosphorylation and relationship to drug accumulation in multidrug-resistant human KB cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;41(6):1008–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang X. B., Tabcharani J. A., Hou Y. X., Jensen T. J., Kartner N., Alon N., Hanrahan J. W., Riordan J. R. Protein kinase A (PKA) still activates CFTR chloride channel after mutagenesis of all 10 PKA consensus phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11304–11311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. J., Chin J. E., Ueda K., Clark D. P., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M., Roninson I. B. Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90595-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Gros P. Two members of the mouse mdr gene family confer multidrug resistance with overlapping but distinct drug specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1652–1663. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine S. E., Hussain A., Davide J. P., Melera P. W. Full length and alternatively spliced pgp1 transcripts in multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster lung cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4545–4555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. A., Ling V. The biochemistry of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:137–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. L., Patel J., Chabner B. A. Phorbol esters induce multidrug resistance in human breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):582–586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard P. R., Mazzei G. J., Kuo J. F. Immunological quantitation of phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent protein kinase and its fragments. Tissue levels, subcellular distribution, and ontogenetic changes in brain and heart. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Croop J., Housman D. Mammalian multidrug resistance gene: complete cDNA sequence indicates strong homology to bacterial transport proteins. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Hagiwara K., Nakajima T., Tsuruo T. Phosphorylation of the Mr 170,000 to 180,000 glycoprotein specific to multidrug-resistant tumor cells: effects of verapamil, trifluoperazine, and phorbol esters. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 1;47(11):2860–2865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde S. C., Emsley P., Hartshorn M. J., Mimmack M. M., Gileadi U., Pearce S. R., Gallagher M. P., Gill D. R., Hubbard R. E., Higgins C. F. Structural model of ATP-binding proteins associated with cystic fibrosis, multidrug resistance and bacterial transport. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):362–365. doi: 10.1038/346362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Design and use of peptide substrates for protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:121–134. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00134-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma L. D., Marquardt D., Takemoto L., Center M. S. Analysis of P-glycoprotein phosphorylation in HL60 cells isolated for resistance to vincristine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5593–5599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado W., Horwitz S. B. Phosphorylation of the multidrug resistance associated glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6900–6904. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Petzold G. L., Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Dissociation and activation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases by cyclic nucleotides and by substrate proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):179–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noland T. A., Jr, Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. Identification of sites phosphorylated in bovine cardiac troponin I and troponin T by protein kinase C and comparative substrate activity of synthetic peptides containing the phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20778–20785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Med. 1991;42:277–286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.42.020191.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S. N., Horwitz S. B. A phosphoglycoprotein associated with taxol resistance in J774.2 cells. Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;45(8):3856–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr E., Raymond M., Bell J. C., Gros P. Characterization of the multidrug resistance protein expressed in cell clones stably transfected with the mouse mdr1 cDNA. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2729–2733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Pohl J., Onunka V. C., Bangalore N., Travis J. Human lysosomal cathepsin G and granzyme B share a functionally conserved broad spectrum antibacterial peptide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):112–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skach W. R., Calayag M. C., Lingappa V. R. Evidence for an alternate model of human P-glycoprotein structure and biogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):6903–6908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staats J., Marquardt D., Center M. S. Characterization of a membrane-associated protein kinase of multidrug-resistant HL60 cells which phosphorylates P-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4084–4090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G., Ahmad S., Aquino A., Fairchild C. R., Trepel J. B., Ohno S., Suzuki K., Tsuruo T., Cowan K. H., Glazer R. I. Transfection with protein kinase C alpha confers increased multidrug resistance to MCF-7 cells expressing P-glycoprotein. Cancer Commun. 1991 Jun;3(6):181–189. doi: 10.3727/095535491820873263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. T., Ling V. Study of membrane orientation and glycosylated extracellular loops of mouse P-glycoprotein by in vitro translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18224–18232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]