Abstract
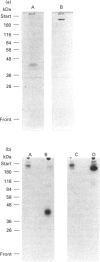
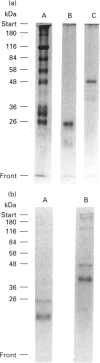
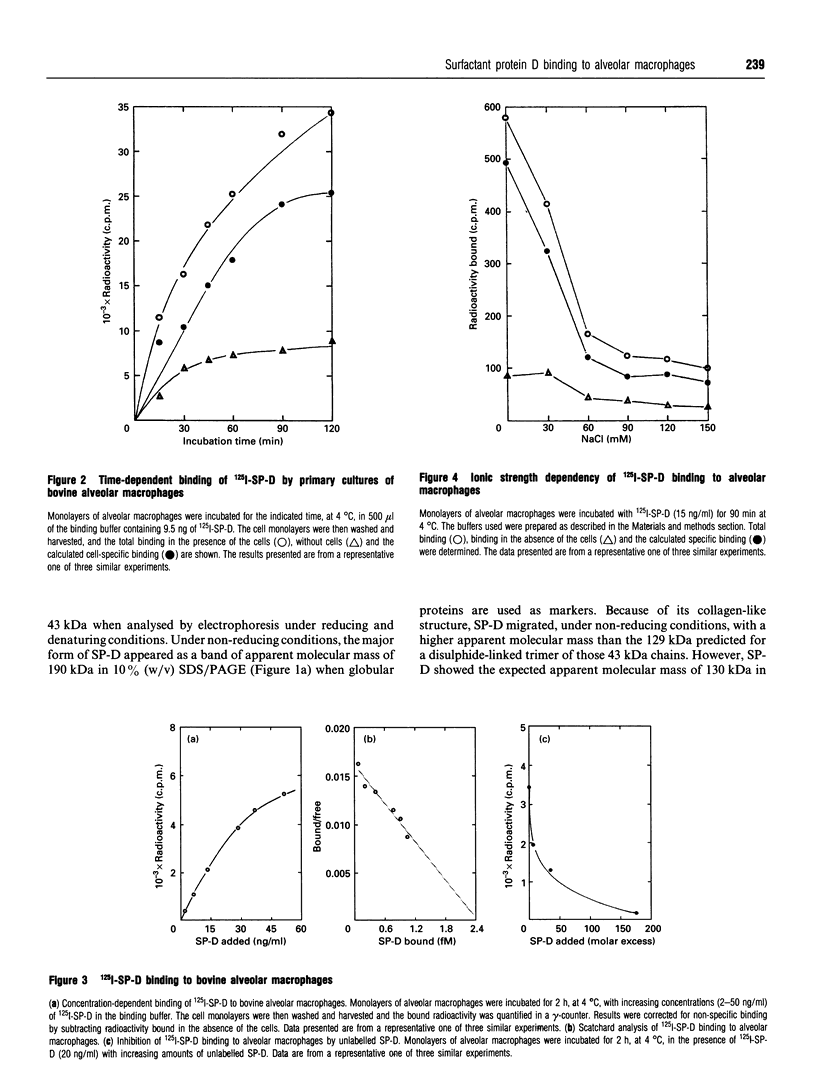
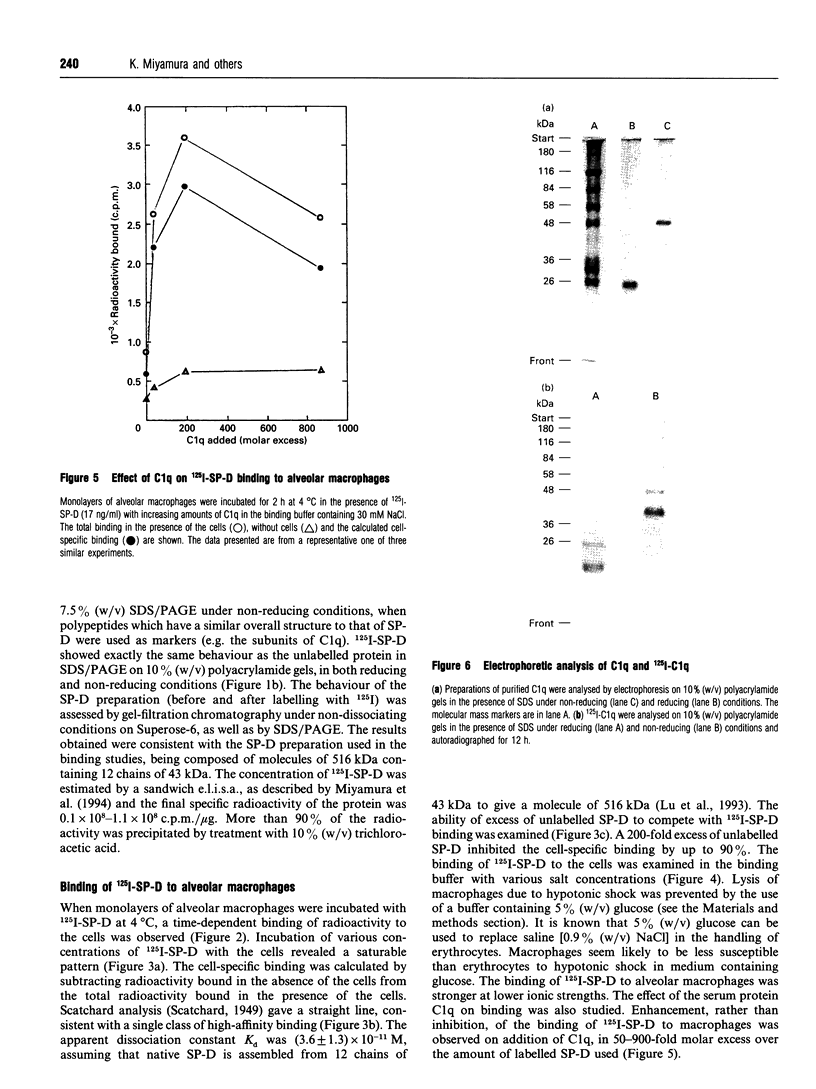
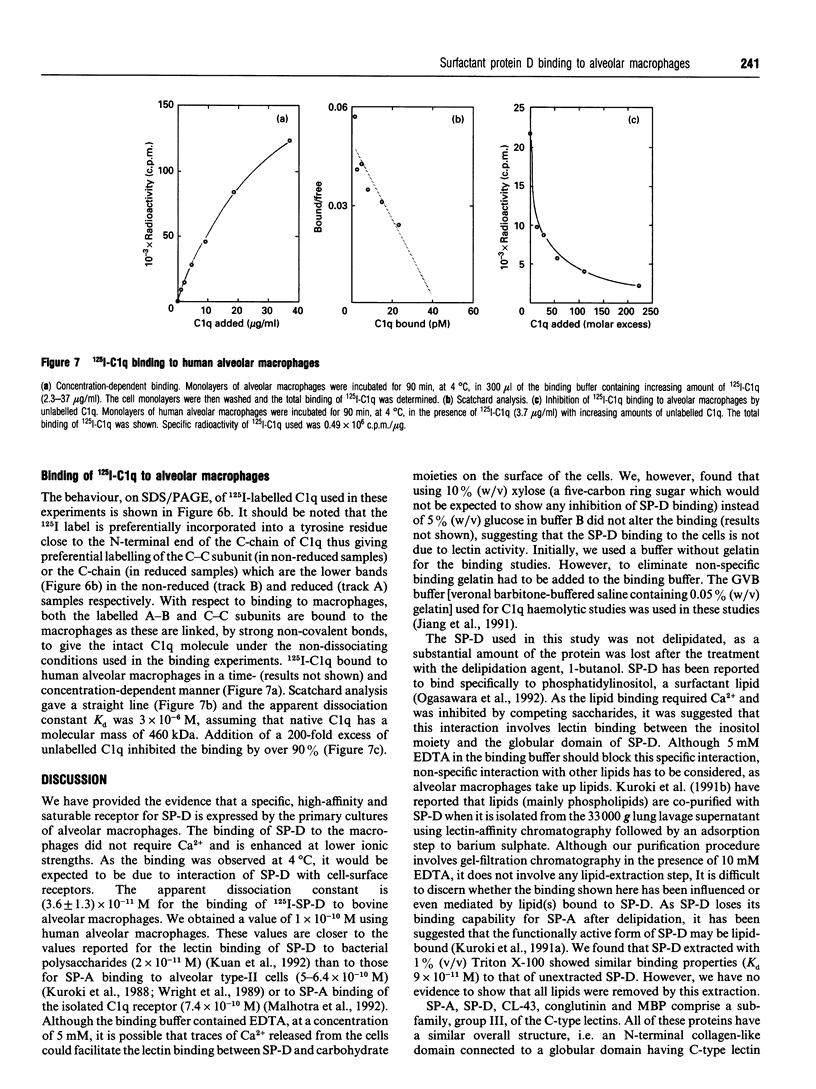
Surfactant protein D (SP-D) is a lung-specific protein, synthesized and secreted by lung epithelial cells. It belongs to group III of the family of C-type lectins; each member of this group has an unusual overall structure consisting of multiple globular 'head' regions (which contain the C-type lectin domains) linked by triple-helical, collagen-like, strands. This group includes the surfactant protein A (SP-A) and the serum proteins mannan-binding protein, conglutinin and collectin-43, all of which have been shown to bind to the C1q receptor found on a wide variety of cells, including macrophages. Both SP-D and SP-A have been shown to enhance oxygen radical production by alveolar macrophages. Although this strongly suggests a direct interaction between SP-D and a specific receptor on alveolar macrophages, it is still unclear whether SP-D binds to the same receptor used by SP-A and/or C1q. Human SP-D was isolated from amniotic fluid and was radiolabelled using 125I. Alveolar macrophages were isolated from human bronchioalveolar lavage fluid, and also from bovine lung washings, by differential adhesion to 24-well tissue-culture plates. The study was carried out using EDTA-containing buffers, to eliminate Ca(2+)-dependent C-type lectin binding, and was also carried out at 4 degrees C to eliminate possible internalization by the cells. 125I-SP-D showed specific binding to alveolar macrophages in both a time- and concentration-saturable manner. The binding was inhibited, by approx. 90%, on addition of a 200-fold excess of unlabelled SP-D. The apparent dissociation constant (Kd) was (3.6 +/- 1.3) x 10(-11) M, based on the assumption that native SP-D is assembled as a dodecamer of 12 identical polypeptides of 43 kDa to yield a protein of 516 kDa. C1q was also shown to bind alveolar macrophages (Kd 3 x 10(-6) M), but addition of C1q did not show inhibition of the binding of 125I-SP-D to the macrophages. We conclude that SP-D binds specifically to alveolar macrophages and the receptor involved is different from that utilized by C1q.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drickamer K. Two distinct classes of carbohydrate-recognition domains in animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9557–9560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B. C1q receptor. Methods Enzymol. 1987;150:558–578. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)50108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmskov U., Teisner B., Willis A. C., Reid K. B., Jensenius J. C. Purification and characterization of a bovine serum lectin (CL-43) with structural homology to conglutinin and SP-D and carbohydrate specificity similar to mannan-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10120–10125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H. X., Siegel J. N., Gewurz H. Binding and complement activation by C-reactive protein via the collagen-like region of C1q and inhibition of these reactions by monoclonal antibodies to C-reactive protein and C1q. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2324–2330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuan S. F., Rust K., Crouch E. Interactions of surfactant protein D with bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Surfactant protein D is an Escherichia coli-binding protein in bronchoalveolar lavage. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):97–106. doi: 10.1172/JCI115861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Alveolar type II cells express a high-affinity receptor for pulmonary surfactant protein A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5566–5570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Shiratori M., Murata Y., Akino T. Surfactant protein D (SP-D) counteracts the inhibitory effect of surfactant protein A (SP-A) on phospholipid secretion by alveolar type II cells. Interaction of native SP-D with SP-A. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):115–119. doi: 10.1042/bj2790115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Shiratori M., Ogasawara Y., Tsuzuki A., Akino T. Characterization of pulmonary surfactant protein D: its copurification with lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 5;1086(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Wiedemann H., Holmskov U., Thiel S., Timpl R., Reid K. B. Structural similarity between lung surfactant protein D and conglutinin. Two distinct, C-type lectins containing collagen-like sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):793–799. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Willis A. C., Reid K. B. Purification, characterization and cDNA cloning of human lung surfactant protein D. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 15;284(Pt 3):795–802. doi: 10.1042/bj2840795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra R., Haurum J., Thiel S., Sim R. B. Interaction of C1q receptor with lung surfactant protein A. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1437–1445. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra R., Laursen S. B., Willis A. C., Sim R. B. Localization of the receptor-binding site in the collectin family of proteins. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 1;293(Pt 1):15–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2930015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra R., Thiel S., Reid K. B., Sim R. B. Human leukocyte C1q receptor binds other soluble proteins with collagen domains. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):955–959. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura K., Malhotra R., Hoppe H. J., Reid K. B., Phizackerley P. J., Macpherson P., López Bernal A. Surfactant proteins A (SP-A) and D (SP-D): levels in human amniotic fluid and localization in the fetal membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jan 20;1210(3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(94)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata Y., Kuroki Y., Akino T. Role of the C-terminal domain of pulmonary surfactant protein A in binding to alveolar type II cells and regulation of phospholipid secretion. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):71–76. doi: 10.1042/bj2910071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara Y., Kuroki Y., Akino T. Pulmonary surfactant protein D specifically binds to phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21244–21249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Chang D., Crouch E. Surfactant protein D is a divalent cation-dependent carbohydrate-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5755–5760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Chang D., Rust K., Moxley M., Longmore W., Crouch E. Purification and biochemical characterization of CP4 (SP-D), a collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6361–6367. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Rust K., Chang D., Moxley M., Longmore W., Crouch E. CP4: a pneumocyte-derived collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Evidence for heterogeneity of collagenous surfactant proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8576–8584. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Chemistry and molecular genetics of C1q. Behring Inst Mitt. 1989 Jul;(84):8–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. Subunit composition and structure of subcomponent C1q of the first component of human complement. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):19–23. doi: 10.1042/bj1550019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rust K., Grosso L., Zhang V., Chang D., Persson A., Longmore W., Cai G. Z., Crouch E. Human surfactant protein D: SP-D contains a C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Oct;290(1):116–126. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90597-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Reid K. B. C1: molecular interactions with activating systems. Immunol Today. 1991 Sep;12(9):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90004-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J. M., Gigli I., Pearlstein E. The effect of fibronectin on the processing of C1q- and C3b/bi-coated immune complexes by peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1023–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Robinson S. L., Borchelt J., Wright J. R. Human pulmonary surfactant protein (SP-A), a protein structurally homologous to C1q, can enhance FcR- and CR1-mediated phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13923–13928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel S., Reid K. B. Structures and functions associated with the group of mammalian lectins containing collagen-like sequences. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 19;250(1):78–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80689-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss T., Melchers K., Scheirle G., Schäfer K. P. Structural comparison of recombinant pulmonary surfactant protein SP-A derived from two human coding sequences: implications for the chain composition of natural human SP-A. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jan;4(1):88–94. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iwaarden F., Welmers B., Verhoef J., Haagsman H. P., van Golde L. M. Pulmonary surfactant protein A enhances the host-defense mechanism of rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):91–98. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iwaarden J. F., van Strijp J. A., Visser H., Haagsman H. P., Verhoef J., van Golde L. M. Binding of surfactant protein A (SP-A) to herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells is mediated by the carbohydrate moiety of SP-A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25039–25043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]