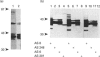Abstract
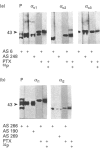
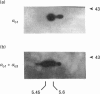
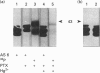
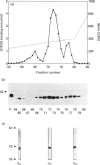
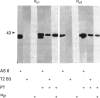
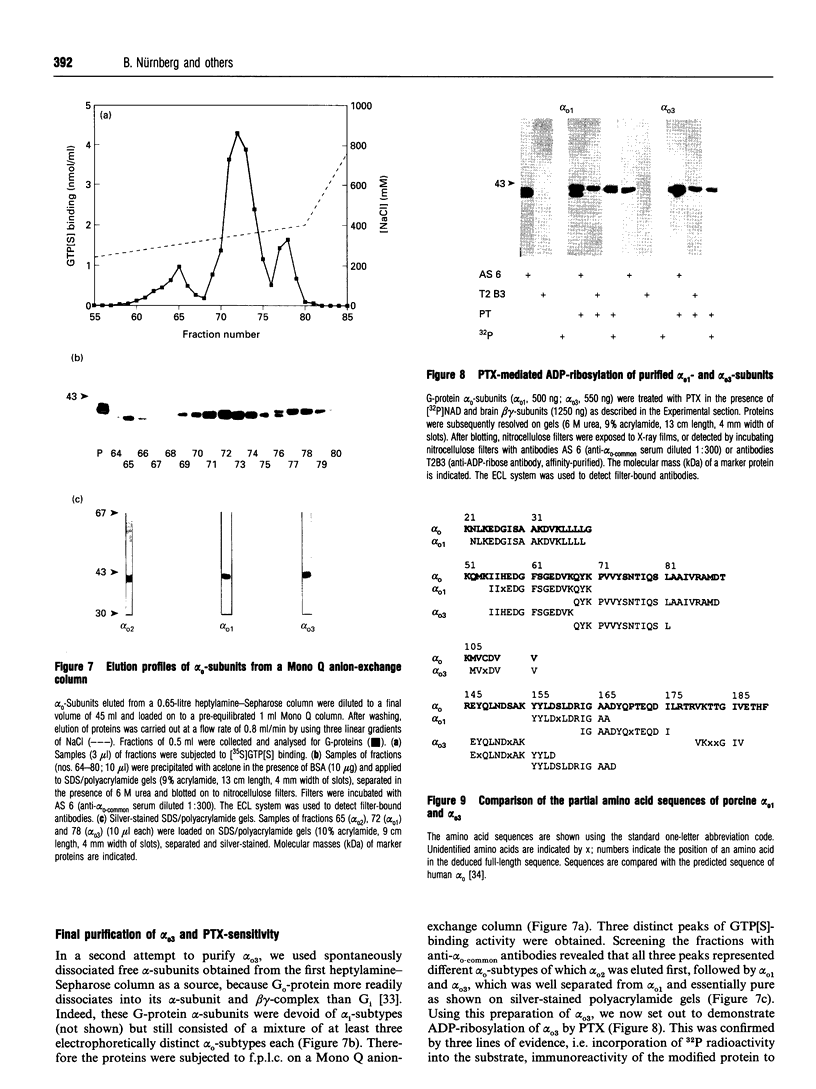
Three distinct G-protein alpha o-subtypes, i.e. alpha o1, alpha o2 and a newly observed 'alpha o3', are present in membranes of mammalian brain, each appearing as two isoforms on SDS/PAGE. Only alpha o1 and alpha o2 appear to be substrates for pertussis toxin (PTX) when membranes or partially purified proteins are examined. In order to elucidate the apparent PTX-resistance of the third alpha o-subtype, we purified alpha o3 from porcine and bovine brain membranes. During the purification procedures, alpha o3 occurred in its dissociated monomeric form and, together with beta gamma-complexes, as a heterotrimer. In a first attempt, we used purified G-protein alpha i/alpha o-mixtures to obtain a final separation of alpha o3. By using f.p.l.c. anion-exchange chromatography on a Mono Q column, complete separation of alpha i1 and alpha o2 was achieved. Partial resolution of alpha o1, alpha i2 and alpha o3 was observed; alpha o3 was eluted between alpha o1 and alpha i2. If alpha o-subunits free from alpha i contaminants were loaded on to the Mono Q column, all three alpha o-subtypes were resolved. The identity of the third subtype as an alpha o-subtype was confirmed by sequence analysis of tryptic fragments. All three alpha o-subtypes bound GTP[S]. Purified alpha o3 was ADP-ribosylated when subjected to PTX treatment in the presence of beta gamma-subunits, and on SDS/PAGE the mobility of alpha o3 was similar to that of ADP-ribosylated alpha o1. On the basis of results obtained with subtype-specific antibodies, the third alpha o-subtype is immunologically more related to alpha o1 than to alpha o2. Purified alpha o3 failed to reconstitute carbachol-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ current in PTX-pretreated SH-SY5Y-cells, whereas alpha o1 and alpha o2 did successfully restore this effect. We conclude that the novel alpha o3 forms differs from alpha o1 and alpha o2 in its primary structure and may be involved in signal-transduction pathways other than those described for alpha o1 and alpha o2.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertrand P., Sanford J., Rudolph U., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. At least three alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding two alpha subunits of the Go GTP-binding protein can be expressed in a single tissue. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18576–18580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Brown A. M. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):163–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosserhoff A., Wallach J., Frank R. W. Micropreparative separation of peptides derived from sodium dodecyl sulphate-solubilized proteins. J Chromatogr. 1989 Jun 28;473(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)91291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Carty D. J., Birnbaumer L., Iyengar R. Purification of G proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:177–188. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95164-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J. R., Snyderman R. Molecular cloning of a new human G protein. Evidence for two Gi alpha-like protein families. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 13;219(1):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Backlund P. S., Jr, Rossiter K., Carter A., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. Purification of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins from brain: identification of a novel form of Go. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7085–7090. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Kapatos G. Developmental expression of Go in neuronal cultures from rat mesencephalon and hypothalamus. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):1995–2001. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen T. B., Eskild W., Hansson V. Evidence for a novel splice variant of the alpha subunit of Go in rat male haploid germ cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91606-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. H., Rudolph U., Sanford J., Bertrand P., Olate J., Nelson C., Moss L. G., Boyd A. E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Molecular cloning of a novel splice variant of the alpha subunit of the mammalian Go protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11220–11226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Neer E. J. Subunit interactions of native and ADP-ribosylated alpha 39 and alpha 41, two guanine nucleotide-binding proteins from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1105–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inanobe A., Shibasaki H., Takahashi K., Kobayashi I., Tomita U., Ui M., Katada T. Characterization of four G0-type proteins purified from bovine brain membranes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 24;263(2):369–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81416-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Rich K. A., Herberg J. T., Grenet D., Mumby S., Codina J. Identification of a new GTP-binding protein. A Mr = 43,000 substrate for pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9239–9245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñiguez-Lluhi J., Kleuss C., Gilman A. G. The importance of G-protein beta lambda subunits. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;3(7):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90122-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. K., Loflin P. T., Aboul-Ela N., Mingmuang M., Moss J., Jobson E. L. Modification of plasma membrane protein cysteine residues by ADP-ribose in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10825–10828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Two guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in rat brain serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. Interaction of the alpha-subunits with beta gamma-subunits in development of their biological activities. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8182–8191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Ewel C., Rosenthal W., Schultz G., Wittig B. Assignment of G-protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):43–48. doi: 10.1038/353043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Shibasaki H., Takahashi K., Kikkawa S., Ui M., Katada T. Purification of GTP-binding proteins from bovine brain membranes. Identification of heterogeneity of the alpha-subunit of Go proteins. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81815-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Shibasaki H., Takahashi K., Tohyama K., Kurachi Y., Ito H., Ui M., Katada T. Purification and characterization of five different alpha subunits of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins in bovine brain membranes. Their physiological properties concerning the activities of adenylate cyclase and atrial muscarinic K+ channels. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 31;191(2):499–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz M. J., Lee Y. C. Quantitative hydrolysis of thioglycosides. Anal Biochem. 1976 Mar;71(1):318–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. Purification and characterization of subforms of the guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins G alpha i and G alpha o. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):687–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz K. L., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Schultz G. mu and delta opioid receptors differentially couple to G protein subtypes in membranes of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90314-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Hilz H. Production of anti-(ADP-ribose) antibodies with the aid of a dinucleotide-pyrophosphatase-resistant hapten and their application for the detection of mono(ADP-ribosyl)ated polypeptides. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):157–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Koch R., Fanick W., Hilz H. ADP-ribosyl proteins formed by pertussis toxin are specifically cleaved by mercury ions. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Jul;369(7):579–583. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.2.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney I., Milligan G. Identification of two distinct isoforms of the guanine nucleotide binding protein G0 in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells: independent regulation during cyclic AMP-induced differentiation. J Neurochem. 1990 Dec;55(6):1890–1898. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb05773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang I. H., Sternweis P. C. Isolation of the alpha subunits of GTP-binding regulatory proteins by affinity chromatography with immobilized beta gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7814–7818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Mattera R., Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Field J. B., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D. ADP-ribosylation of membrane components by pertussis and cholera toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:566–572. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Koesling D., Rudolph U., Kleuss C., Pallast M., Yajima M., Schultz G. Identification and characterization of the 35-kDa beta subunit of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins by an antiserum raised against transducin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Okajima F., Katada T., Kondo Y. Molecular heterogeneity of the subclasses of islet-activating protein (pertussis toxin)-sensitive GTP-binding proteins in porcine thyroid tissue. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Sep;281(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer N. M., Toro M. J., Entman M. L., Birnbaumer L. G-protein distribution in canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and sarcolemma: comparison to rabbit skeletal muscle membranes and to brain and erythrocyte G-proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Dec;259(2):431–440. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90509-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hescheler J., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Hinsch K. D., Klinz F. J., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Gausepohl H., Frank R. Involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins in the hormonal inhibition of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ currents in an insulin-secreting cell line (RINm5F). J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18025–18033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki H., Kozasa T., Takahashi K., Inanobe A., Kaziro Y., Ui M., Katada T. Amino acid sequence determination of the novel forms of Go alpha purified from bovine brain membranes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):268–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80814-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Codina J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Gi2 mediates alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G alpha C-terminal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicher K., Klinz F. J., Rudolph U., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Schultz G., Rosenthal W. Identification of the G-protein alpha-subunit encoded by alpha o2 cDNA as a 39 kDa pertussis toxin substrate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicher K., Nuernberg B., Jäger B., Rosenthal W., Schultz G. Heterogeneity of three electrophoretically distinct Go alpha-subunits in mammalian brain. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80770-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Wilkie T. M., Simon M. I. Alternative splicing produces transcripts encoding two forms of the alpha subunit of GTP-binding protein Go. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6477–6481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanuma S., Endo H. Mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation of Gi by eukaryotic cysteine-specific mono(ADP-ribosyl) transferase attenuates inhibition of adenylate cyclase by epinephrine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 9;1010(2):246–249. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanuma S., Kawashima K., Endo H. Eukaryotic mono(ADP-ribosyl)transferase that ADP-ribosylates GTP-binding regulatory Gi protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5485–5489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Toyama R., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Matsuoka M., Kaziro Y. Structure of the human gene and two rat cDNAs encoding the alpha chain of GTP-binding regulatory protein Go: two different mRNAs are generated by alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Nürnberg B., Ulibarri I., Kaldenberg-Stasch S., Schultz G., Jakobs K. H. Guanine nucleotide-specific phosphate transfer by guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein beta-subunits. Characterization of the phosphorylated amino acid. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18111–18118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]