Abstract
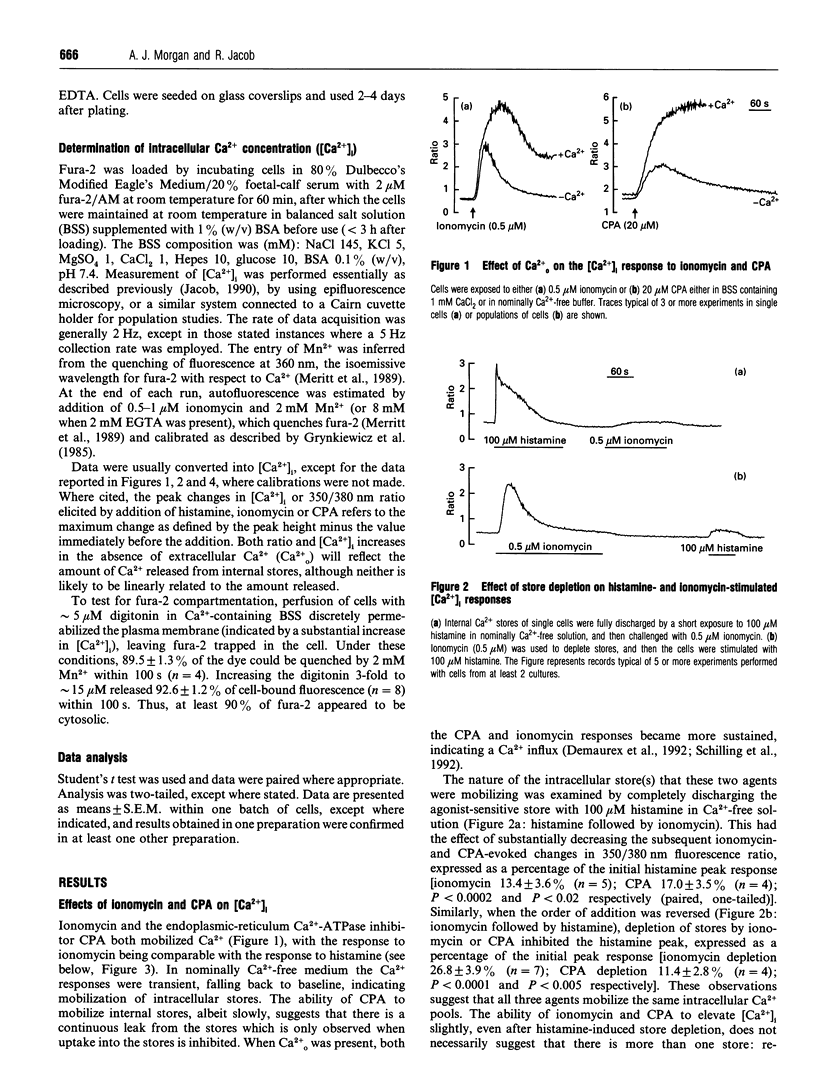
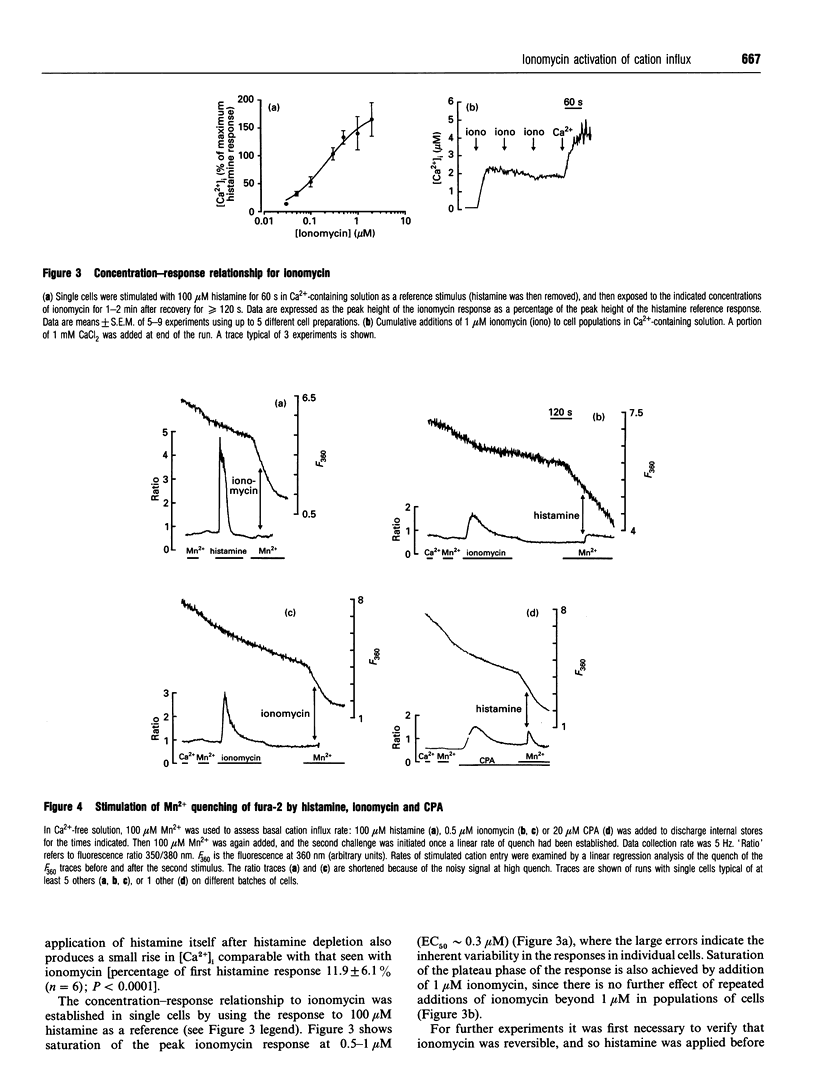
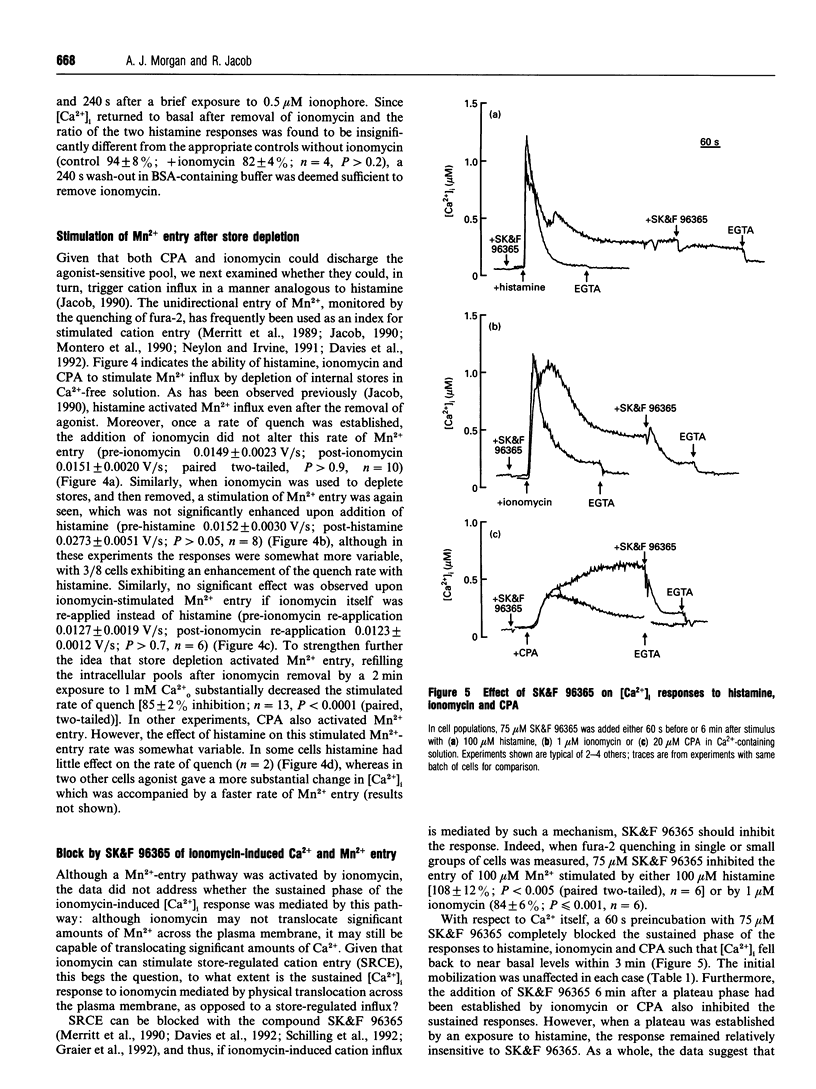
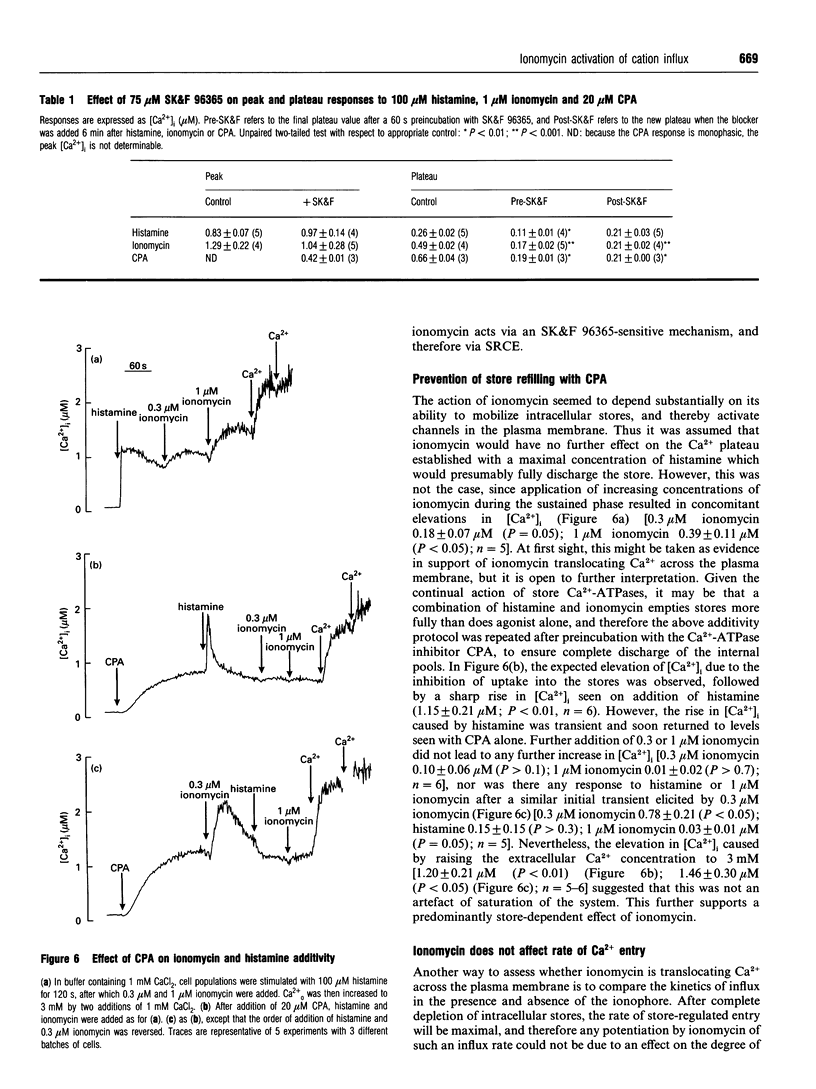
In fura-2-loaded ECV304 cells ionomycin elicited a saturable biphasic change in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), where the initial phase represented mobilization of intracellular stores and the sustained component represented Ca2+ influx. To examine whether ionomycin could stimulate influx via a store-dependent mechanism. Mn2+ entry was monitored by the quenching of fura-2 fluorescence: influx was enhanced even after ionomycin wash-out, provided that internal stores were not refilled with Ca2+. Moreover, the maximal rate of histamine-stimulated Mn2+ entry was unaffected by ionomycin, suggesting a common route of entry. The Ca(2+)-entry blocker SK&F 96365 inhibited both the ionomycin-induced Mn2+ entry and the sustained [Ca2+]i response to the ionophore (leaving the initial peak [Ca2+]i response unaffected). In other experiments, although addition of ionomycin further increased the plateau phase induced by 100 microM histamine, the increase was completely abolished by pretreatment with the store Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitor cyclopiazonic acid (CPA). Furthermore, in store-depleted cells, re-addition of 1 mM extracellular Ca2+ (in the presence of CPA plus histamine) led to a rapid rise in [Ca2+]i, dependent on Ca2+ influx, with kinetics that were not enhanced by ionomycin. These data suggest that ionomycin acts primarily at the level of the internal Ca2+ stores, so that, at the concentrations used here (< or = 1 microM), it increases Ca2+ (and Mn2+) influx via activation of endogenous entry pathways and not by plasmalemmal translocation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Ionomycin acts as an ionophore to release TRH-regulated Ca2+ stores from GH4C1 cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):C887–C891. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.6.C887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert P. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Relationship of thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced spike and plateau phases in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentrations to hormone secretion. Selective blockade using ionomycin and nifedipine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15350–15363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso M. T., Alvarez J., Montero M., Sanchez A., García-Sancho J. Agonist-induced Ca2+ influx into human platelets is secondary to the emptying of intracellular Ca2+ stores. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):783–789. doi: 10.1042/bj2800783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo A. R., García-Sancho J. Mobilization of intracellular calcium by extracellular ATP and by calcium ionophores in the Ehrlich ascites-tumour cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 7;941(1):48–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregestovski P., Bakhramov A., Danilov S., Moldobaeva A., Takeda K. Histamine-induced inward currents in cultured endothelial cells from human umbilical vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):429–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byron K. L., Babnigg G., Villereal M. L. Bradykinin-induced Ca2+ entry, release, and refilling of intracellular Ca2+ stores. Relationships revealed by image analysis of individual human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):108–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabello O. A., Schilling W. P. Vectorial Ca2+ flux from the extracellular space to the endoplasmic reticulum via a restricted cytoplasmic compartment regulates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-stimulated Ca2+ release from internal stores in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 15;295(Pt 2):357–366. doi: 10.1042/bj2950357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies E. V., Campbell A. K., Hallett M. B. Dissociation of store release from transmembrane influx of calcium in human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 23;313(2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81426-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaurex N., Schlegel W., Varnai P., Mayr G., Lew D. P., Krause K. H. Regulation of Ca2+ influx in myeloid cells. Role of plasma membrane potential, inositol phosphates, cytosolic free [Ca2+], and filling state of intracellular Ca2+ stores. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):830–839. doi: 10.1172/JCI115958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Pozzan T. Effect of membrane potential on divalent cation transport catalyzed by the "electroneutral" ionophores A23187 and ionomycin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19630–19636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Zottini M., Clementi E., Zacchetti D., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Intracellular Ca2+ pools in PC12 cells. Three intracellular pools are distinguished by their turnover and mechanisms of Ca2+ accumulation, storage, and release. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20159–20167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonteriz R. I., Garcia-Sancho J., Gandia L., Lopez M. G., Garcia A. G. Permeation and inactivation by calcium and manganese of bovine adrenal chromaffin cell calcium channels. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):C818–C824. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.4.C818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennon M. C., Bird G. S., Kwan C. Y., Putney J. W., Jr Actions of vasopressin and the Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitor, thapsigargin, on Ca2+ signaling in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8230–8233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graier W. F., Groschner K., Schmidt K., Kukovetz W. R. SK&F 96365 inhibits histamine-induced formation of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 14;186(3):1539–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81582-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):353–356. doi: 10.1038/355353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and Ca2+ entry: toward a proliferation or a simplification? FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3085–3091. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.12.1325932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. S., Berggren P. O. Mobilization of Ca2+ by thapsigargin and 2,5-di-(t-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone in permeabilized insulin-secreting RINm5F cells: evidence for separate uptake and release compartments in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ pool. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):423–429. doi: 10.1042/bj2930423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. Agonist-stimulated divalent cation entry into single cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:55–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Williamson J. R. Characteristics of inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ release from permeabilized hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14658–14664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. Y., Takemura H., Obie J. F., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Effects of MeCh, thapsigargin, and La3+ on plasmalemmal and intracellular Ca2+ transport in lacrimal acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1006–C1015. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Busse R. Refilling of endothelial calcium stores without bypassing the cytosol. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):108–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80519-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. J., Grinstein S. Ionomycin activates electrogenic Ca2+ influx in rat thymic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 15;296(Pt 1):33–39. doi: 10.1042/bj2960033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy S. A., Hallam T. J., Merritt J. E. Activation of protein kinase C in human neutrophils attenuates agonist-stimulated rises in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration by inhibiting bivalent-cation influx and intracellular Ca2+ release in addition to stimulating Ca2+ efflux. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):357–364. doi: 10.1042/bj2640357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Jacob R., Hallam T. J. Use of manganese to discriminate between calcium influx and mobilization from internal stores in stimulated human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1522–1527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. Regulation of cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded rat parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17362–17369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montero M., Alvarez J., Garcia-Sancho J. Uptake of Ca2+ and refilling of intracellular Ca2+ stores in Ehrlich-ascites-tumour cells and in rat thymocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj2710535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Schoeffield M. S., Fimmel C. J., Pandol S. J. Agonist-sensitive calcium pool in the pancreatic acinar cell. II. Characterization of reloading. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 1):G229–G235. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.2.G229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Irvine R. F. Thrombin attenuates the stimulatory effect of histamine on Ca2+ entry in confluent human umbilical vein endothelial cell cultures. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4251–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papp B., Enyedi A., Pászty K., Kovács T., Sarkadi B., Gárdos G., Magnier C., Wuytack F., Enouf J. Simultaneous presence of two distinct endoplasmic-reticulum-type calcium-pump isoforms in human cells. Characterization by radio-immunoblotting and inhibition by 2,5-di-(t-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):297–302. doi: 10.1042/bj2880297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C., Fahim M. Pharmacology and toxicology of the monovalent carboxylic ionophores. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:465–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1986 Feb;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Capacitative calcium entry revisited. Cell Calcium. 1990 Nov-Dec;11(10):611–624. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90016-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Inositol phosphates and calcium entry. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;26:143–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J. Receptor-mediated calcium entry. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson I. M., Cheek T. R., Burgoyne R. D. Ca2+ influx induced by the Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitors 2,5-di-(t-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone and thapsigargin in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):457–463. doi: 10.1042/bj2880457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouy D., Anglés-Cano E. The mechanism of activation of plasminogen at the fibrin surface by tissue-type plasminogen activator in a plasma milieu in vitro. Role of alpha 2-antiplasmin. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 1;271(1):51–57. doi: 10.1042/bj2710051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Røtnes J. S., Iversen J. G. Thapsigargin reveals evidence for fMLP-insensitive calcium pools in human leukocytes. Cell Calcium. 1992 Aug;13(8):487–500. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90017-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeant P., Clarkson W. D., Sage S. O., Heemskerk J. W. Calcium influx evoked by Ca2+ store depletion in human platelets is more susceptible to cytochrome P-450 inhibitors than receptor-mediated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1992 Oct;13(9):553–564. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90035-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling W. P., Cabello O. A., Rajan L. Depletion of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive intracellular Ca2+ store in vascular endothelial cells activates the agonist-sensitive Ca(2+)-influx pathway. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):521–530. doi: 10.1042/bj2840521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling W. P., Rajan L., Strobl-Jager E. Characterization of the bradykinin-stimulated calcium influx pathway of cultured vascular endothelial cells. Saturability, selectivity, and kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12838–12848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauderman K. A., Pruss R. M. Dissociation of Ca2+ entry and Ca2+ mobilization responses to angiotensin II in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18349–18355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles M. K., Craig M. E., Gunnell S. L., Pfeiffer D. R., Taylor R. W. The formation constants of ionomycin with divalent cations in 80% methanol/water. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8336–8342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Sawasaki Y., Hata J., Mukai K., Goto T. Spontaneous transformation and immortalization of human endothelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;26(3 Pt 1):265–274. doi: 10.1007/BF02624456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of calcium entry by the tumor promoter thapsigargin in parotid acinar cells. Evidence that an intracellular calcium pool and not an inositol phosphate regulates calcium fluxes at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12266–12271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törnquist K. Activation of calcium entry by cyclopiazonic acid in thyroid FRTL-5 cells. Cell Calcium. 1993 May;14(5):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(93)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vostal J. G., Fratantoni J. C. Econazole inhibits thapsigargin-induced platelet calcium influx by mechanisms other than cytochrome P-450 inhibition. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 15;295(Pt 2):525–529. doi: 10.1042/bj2950525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


