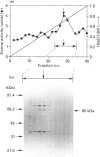
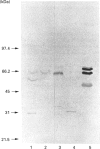
Abstract
A meiotic DNA polymerase [DNA nucleotidyltransferase (DNA-directed), EC 2.7.7.7], which likely has a role in meiotic DNA repair, was isolated from a mushroom, Agaricus bisporus. The purified fraction displays three bands in SDS/PAGE, at molecular masses of 72 kDa, 65 kDa and 36 kDa. Optimal activity is at pH 7.0-8.0 in the presence of 5 mM Mg2+ and 50 mM KCl and at 28-30 degrees C, which is the temperature for meiosis. This enzyme is resistant to N-ethylmaleimide and sensitive to 2',3'-dideoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate, suggesting that it is a beta-like DNA polymerase. These characteristics are similar to those of Coprinus DNA polymerase beta [Sakaguchi and Lu (1982) Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 752-757]. In Western-blot analysis, the antiserum against the Coprinus polymerase reacts only with the 65 kDa band, which coincides with the molecular mass of the Coprinus polymerase. Western-blot analysis also showed that the antiserum could react with crude extracts not only from the Agaricales family, to which Agaricus and Coprinus belong, but also from different mushroom families and Saccharomyces. The Agaricus polymerase activity can be found only in the meiotic-cell-rich fraction, but the enzyme is also present in the somatic cells in an inactive state.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Amodio F. J., Jenkins M., Gutmann E. D., Ferris F. L. Studies with DNA-cellulose chromatography. I. DNA-binding proteins from Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:289–305. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M., Bambara R. A., Campbell J. L., Chang L. M., Downey K. M., Hübscher U., Lee M. Y., Linn S. M., So A. G., Spadari S. Revised nomenclature for eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Aug 17;191(3):617–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa Y., Yamada R. H., Kohno M. Presence of two DNA polymerases in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C., Cooper P. K., Ganesan A. K., Smith C. A. DNA repair in bacteria and mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Barnes D. E. Mammalian DNA ligases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:251–281. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Takami K., Sono A., Sakaguchi K. A meiotic DNA polymerase from Coprinus cinereus: further purification and characterization. Chromosoma. 1993 Nov;102(9):631–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00352311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrino F. W., Loeb L. A. Animal cell DNA polymerases in DNA repair. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90012-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi K., Boyd J. B. Purification and characterization of a DNA polymerase beta from Drosophila*. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10406–10411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi K., Lu B. C. Meiosis in Coprinus: characterization and activities of two forms of DNA polymerase during meiotic stages. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):752–757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlabach A., Fridlender B., Bolden A., Weissbach A. DNA-dependent DNA polymerases from HeLa cell nuclei. II. Template and substrate utilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):879–885. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90793-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Santocanale C., Ropp P. A., Longhese M. P., Plevani P., Lucchini G., Sugino A. Purification and characterization of a new DNA polymerase from budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A probable homolog of mammalian DNA polymerase beta. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):27148–27153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern H., Hotta Y. Biochemical controls of meiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:37–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:513–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]