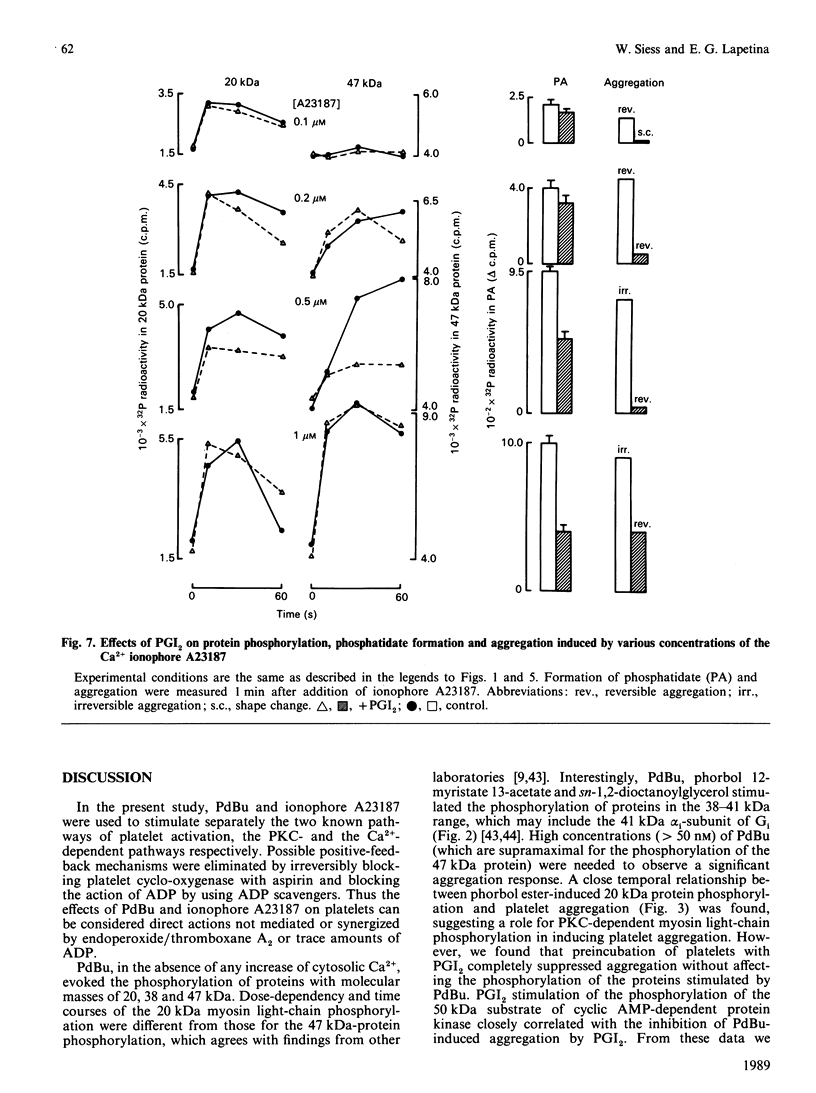
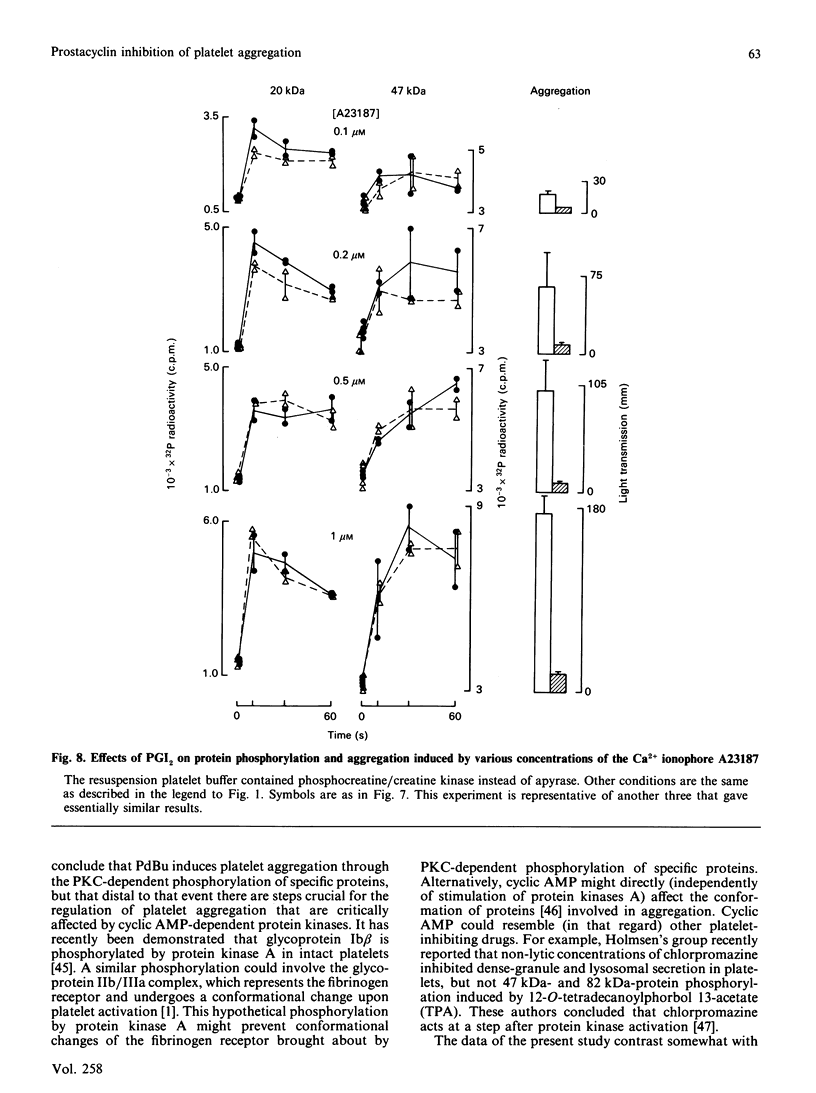
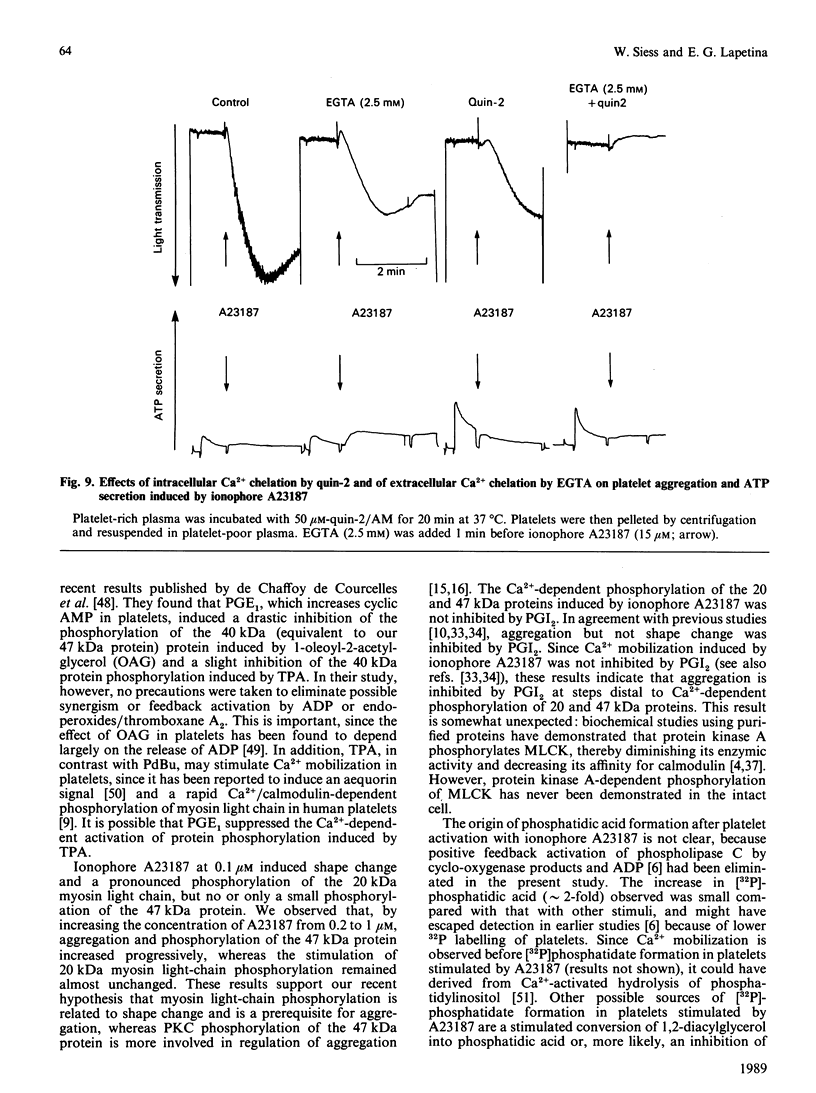
Abstract
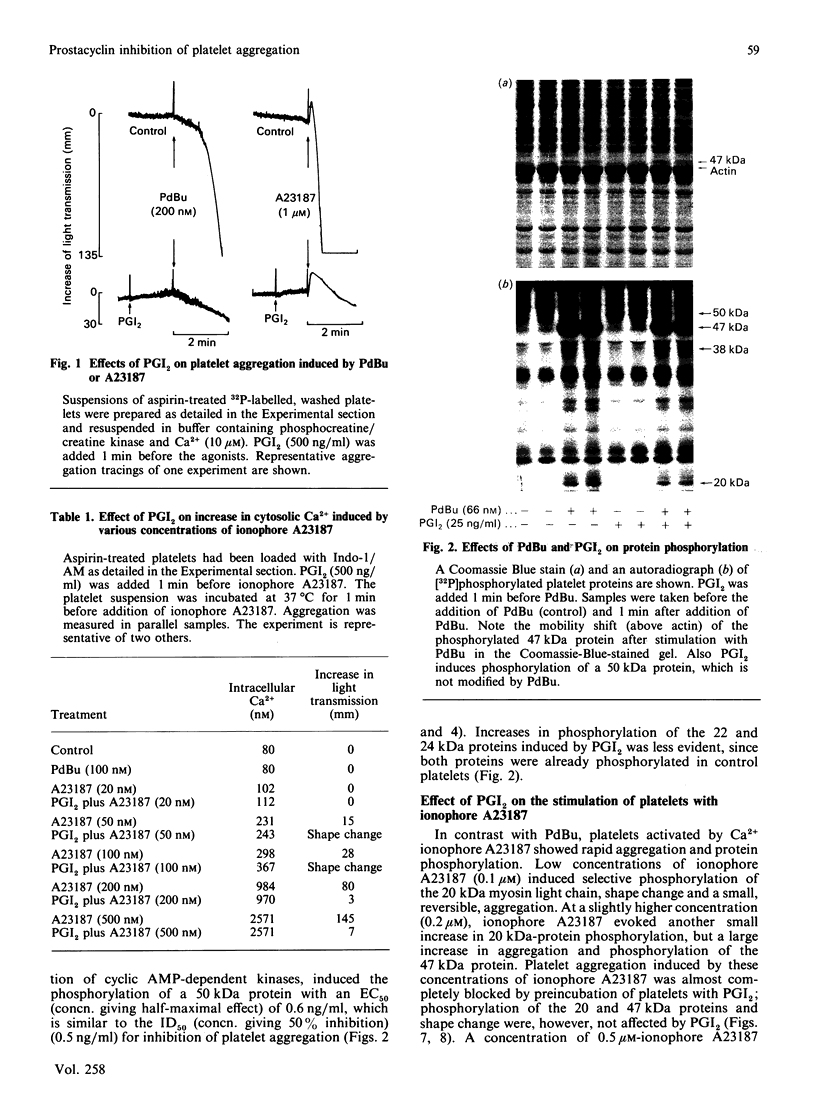
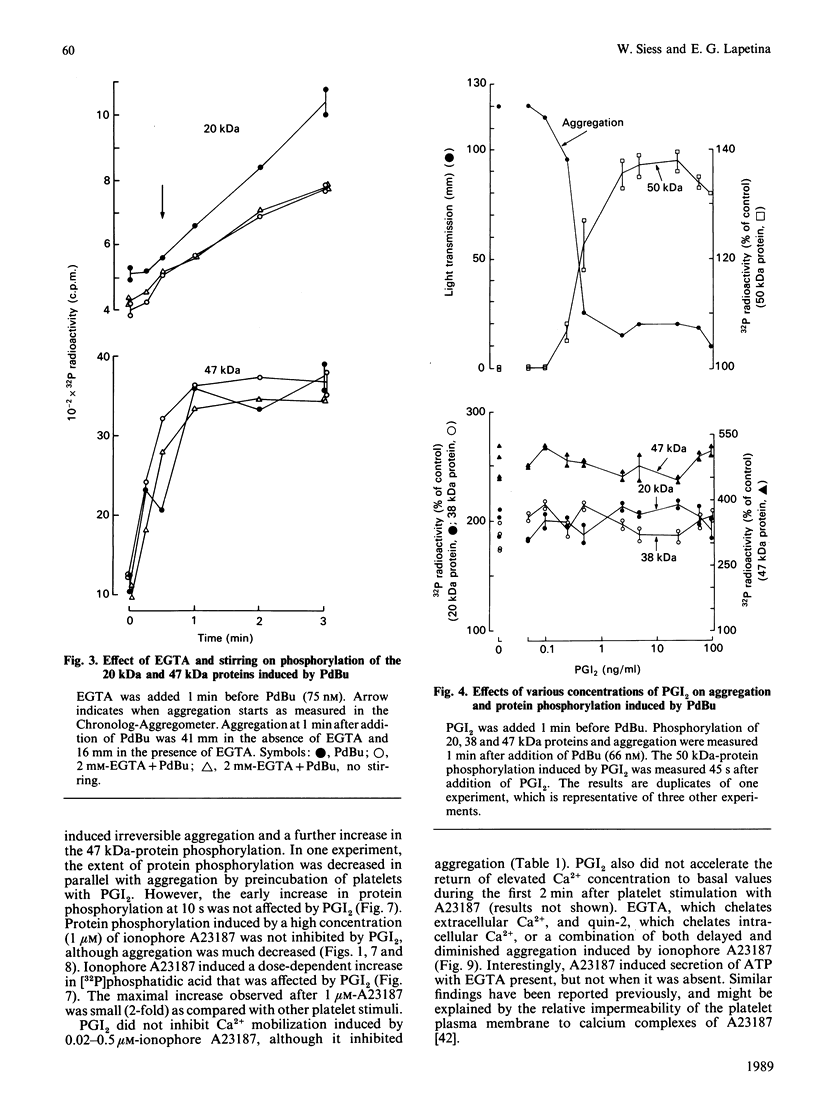
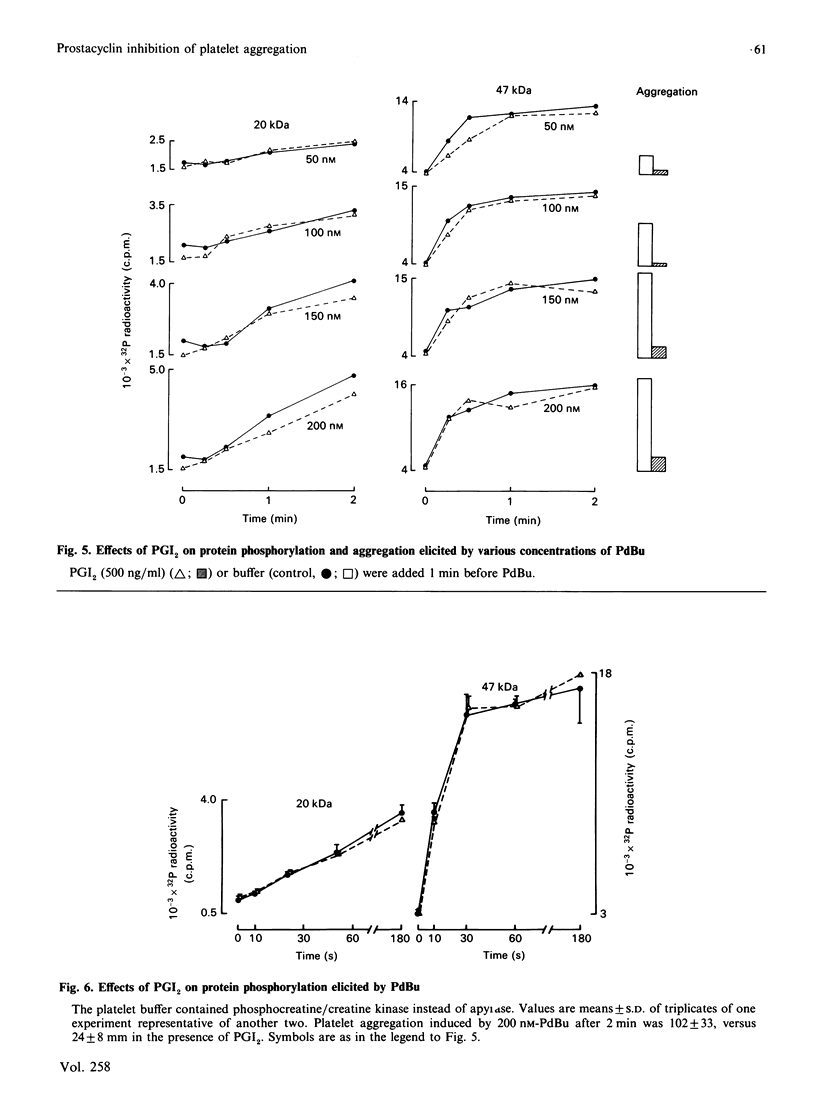
Suspensions of aspirin-treated, 32P-prelabelled, washed platelets containing ADP scavengers in the buffer were activated with either phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PdBu) or the Ca2+ ionophore A23187. High concentrations of PdBu (greater than or equal to 50 nM) induced platelet aggregation and the protein kinase C (PKC)-dependent phosphorylation of proteins with molecular masses of 20 (myosin light chain), 38 and 47 kDa. No increase in cytosolic Ca2+ was observed. Preincubation of platelets with prostacyclin (PGI2) stimulated the phosphorylation of a 50 kDa protein [EC50 (concn. giving half-maximal effect) 0.6 ng of PGI2/ml] and completely abolished platelet aggregation [ID50 (concn. giving 50% inhibition) 0.5 ng of PGI2/ml] induced by PdBu, but had no effect on phosphorylation of the 20, 38 and 47 kDa proteins elicited by PdBu. The Ca2+ ionophore A23187 induced shape change, aggregation, mobilization of Ca2+, rapid phosphorylation of the 20 and 47 kDa proteins and the formation of phosphatidic acid. Preincubation of platelets with PGI2 (500 ng/ml) inhibited platelet aggregation, but not shape change, Ca2+ mobilization or the phosphorylation of the 20 and 47 kDa proteins induced by Ca2+ ionophore A23187. The results indicate that PGI2, through activation of cyclic AMP-dependent kinases, inhibits platelet aggregation at steps distal to protein phosphorylation evoked by protein kinase C and Ca2+-dependent protein kinases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S. Regulation of contractile proteins by phosphorylation. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):1863–1866. doi: 10.1172/JCI111148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby B., Kowalska M. A., Wernick E., Rigmaiden M., Daniel J. L., Smith J. B. Differences in the mode of action of 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-glycerol and phorbol ester in platelet activation. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(5):473–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsinde J., Diez E., Mollinedo F. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):502–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Marr J., Yang D. C., Guiliani D., Rafelson M. E., Jr Adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 23;422(1):60–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushfield M., McNicol A., MacIntyre D. E. Inhibition of platelet-activating-factor-induced human platelet activation by prostaglandin D2. Differential sensitivity of platelet transduction processes and functional responses to inhibition by cyclic AMP. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):267–271. doi: 10.1042/bj2320267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collazos J. M., Sanchez A. cAMP reduces the affinity of Ca2+-triggered secretion in platelets. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 4;215(1):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad G. W., Rink T. J. Platelet activating factor raises intracellular calcium ion concentration in macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):439–450. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch M. F., Lapetina E. G. A role for Gi in control of thrombin receptor-phospholipase C coupling in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3363–3371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J. A Ca2+-and modulator-dependent myosin light chain kinase from non-muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1352–1359. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Molish I. R., Rigmaiden M., Stewart G. Evidence for a role of myosin phosphorylation in the initiation of the platelet shape change response. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9826–9831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein M. B., Egan J. J., Opas E. E. Reversal of thrombin-induced myosin phosphorylation and the assembly of cytoskeletal structures in platelets by the adenylate cyclase stimulants prostaglandin D2 and forskolin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1260–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein M. B., Egan J. J., Sha'afi R. I., White J. The cytoplasmic concentration of free calcium in platelets is controlled by stimulators of cyclic AMP production (PGD2, PGE1, forskolin). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 15;113(2):598–604. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91768-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer T. H., White G. C., 2nd Partial purification and characterization of thrombolamban, a 22,000 dalton cAMP-dependent protein kinase substrate in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):700–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90424-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Reynolds C. C., Johnson M. M. Identification of glycoprotein Ib beta as one of the major proteins phosphorylated during exposure of intact platelets to agents that activate cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12627–12631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Sanchez A., Rink T. J. Stimulus-response coupling in human platelets. Changes evoked by platelet-activating factor in cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with the fluorescent calcium indicator quin2. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):819–827. doi: 10.1042/bj2180819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Lynham J. A., Fox J. E. Effects of collagen, ionophore A23187 and prostaglandin E1 on the phosphorylation of specific proteins in blood platelets. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):397–406. doi: 10.1042/bj1780397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. R., Eaton C. R., Adelstein R. S. Regulation of human platelet myosin light chain kinase by the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):252–256. doi: 10.1038/291252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hettasch J. M., Le Breton G. C. Modulation of Ca2+ fluxes in isolated platelet vesicles: effects of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase inhibitor on Ca2+ sequestration and release. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 22;931(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A. Evidence that the platelet plasma membrane is impermeable to calcium and magnesium complexes of A23187. A23187-induced secretion is inhibited by MG2+ and Ca2+, and requires aggregation and active cyclooxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10449–10452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Scrutton M. C. Cyclic nucleotides control a system which regulates Ca2+ sensitivity of platelet secretion. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):66–68. doi: 10.1038/309066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käser-Glanzmann R., Gerber E., Lüscher E. F. Regulation of the intracellular calcium level in human blood platelets: cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent phosphorylation of a 22,000 dalton component in isolated Ca2+-accumulating vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 12;558(3):344–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käser-Glanzmann R., Jakäbovä M., George J. N., Lüscher E. F. Stimulation of calcium uptake in platelet membrane vesicles by adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 2;466(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Billah M. M., Cuatrecasas P. The phosphatidylinositol cycle and the regulation of arachidonic acid production. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):367–369. doi: 10.1038/292367a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. Prostacyclin inhibition of phosphatidic acid synthesis in human platelets is not mediated by protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91410-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Watson S. P. Ionophore A23187 stimulates phosphorylation of the 40,000 dalton protein in human platelets without phospholipase C activation. Life Sci. 1986 Aug 25;39(8):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Gryglewski R., Bunting S., Vane J. R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):663–665. doi: 10.1038/263663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka M., Nishikawa M., Adelstein R. S., Hidaka H. Phorbol ester-induced activation of human platelets is associated with protein kinase C phosphorylation of myosin light chains. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):490–492. doi: 10.1038/306490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. J., Suárez-Quian C. A., Swank R. A., Klausner R. D. The inhibitory effect of cyclic AMP on phosphatidylinositol kinase is not mediated by the cAMP dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):561–567. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90565-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opstvedt A., Rongved S., Aarsaether N., Lillehaug J. R., Holmsen H. Differential effects of chlorpromazine on secretion, protein phosphorylation and phosphoinositide metabolism in stimulated platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):159–166. doi: 10.1042/bj2380159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Activation of phospholipase D by chemotactic peptide in HL-60 granulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannocchia A., Hardisty R. M. Cyclic AMP inhibits platelet activation independently of its effect on cytosolic free calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):339–345. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Smith S. W., Tsien R. Y. Cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in human platelets: Ca2+ thresholds and Ca-independent activation for shape-change and secretion. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 1;148(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Rink T. J. Inhibition by forskolin of cytosolic calcium rise, shape change and aggregation in quin2-loaded human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 19;188(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80890-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salama S. E., Haslam R. J. Characterization of the protein kinase activities of human platelet supernatant and particulate fractions. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):285–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2180285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Boehlig B., Weber P. C., Lapetina E. G. Prostaglandin endoperoxide analogues stimulate phospholipase C and protein phosphorylation during platelet shape change. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1141–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Ca2+ mobilization primes protein kinase C in human platelets. Ca2+ and phorbol esters stimulate platelet aggregation and secretion synergistically through protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Phorbol esters sensitize platelets to activation by physiological agonists. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1373–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Siegel F. L., Lapetina E. G. Arachidonic acid stimulates the formation of 1,2-diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid in human platelets. Degree of phospholipase C activation correlates with protein phosphorylation, platelet shape change, serotonin release, and aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11236–11242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Nishizuka Y. Counteraction of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activation by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in platelets. J Biochem. 1982 Jan;91(1):403–406. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. T., Scrutton M. C. Intracellular calcium fluxes in human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):421–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann R., Bauer S., Göbel C., Hofmann F., Jakobs K. H., Walter U. Demonstration of cGMP-dependent protein kinase and cGMP-dependent phosphorylation in cell-free extracts of platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 1;158(1):203–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. A., Johnson P. C., Smith M., Salzman E. W. Aequorin detects increased cytoplasmic calcium in platelets stimulated with phorbol ester or diacylglycerol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 27;133(1):98–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91846-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. The rapid formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets by thrombin is inhibited by prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13199–13203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H., Gerrard J. M. Effects of the lonophore A23187 on blood platelets I. Influence on aggregation and secretion. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):135–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. A., Murphy W., Haslam R. J. Effects of activation of protein kinase C on the agonist-induced stimulation and inhibition of cyclic AMP formation in intact human platelets. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):667–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2430667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chaffoy de Courcelles D., Roevens P., Van Belle H. Prostaglandin E1 and forskolin antagonize C-kinase activation in the human platelet. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):93–99. doi: 10.1042/bj2440093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]