Abstract
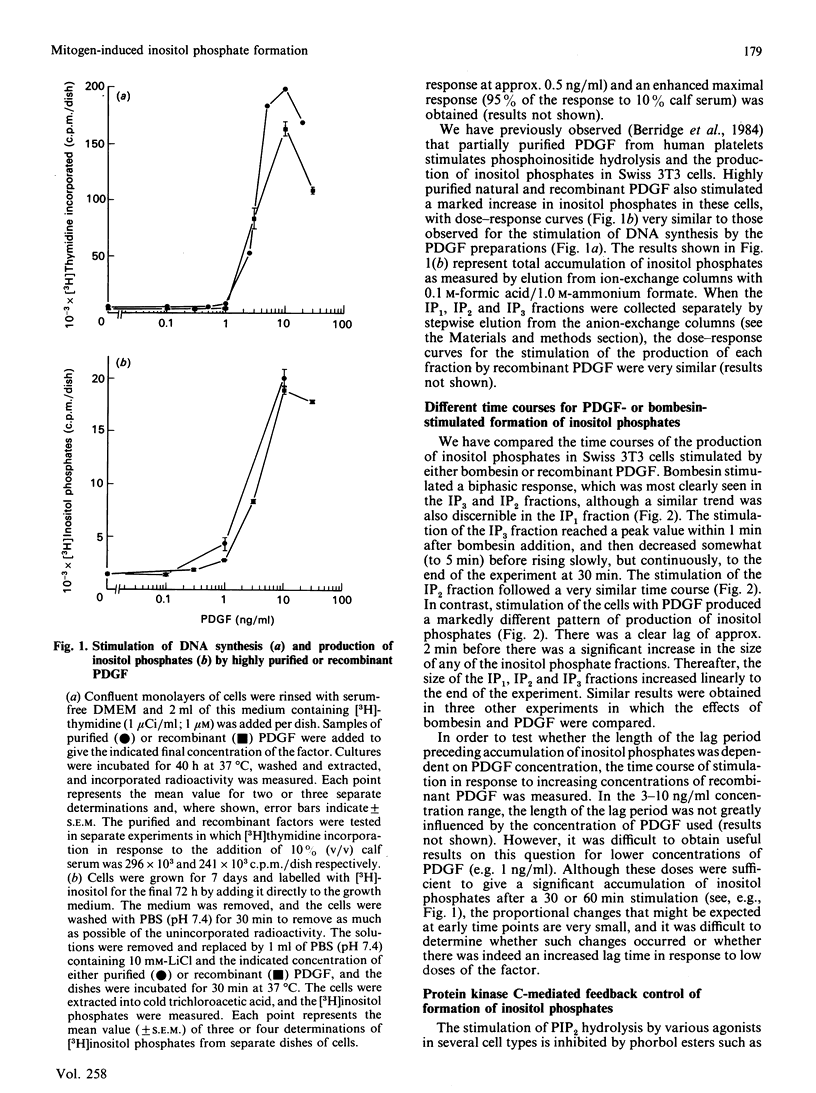
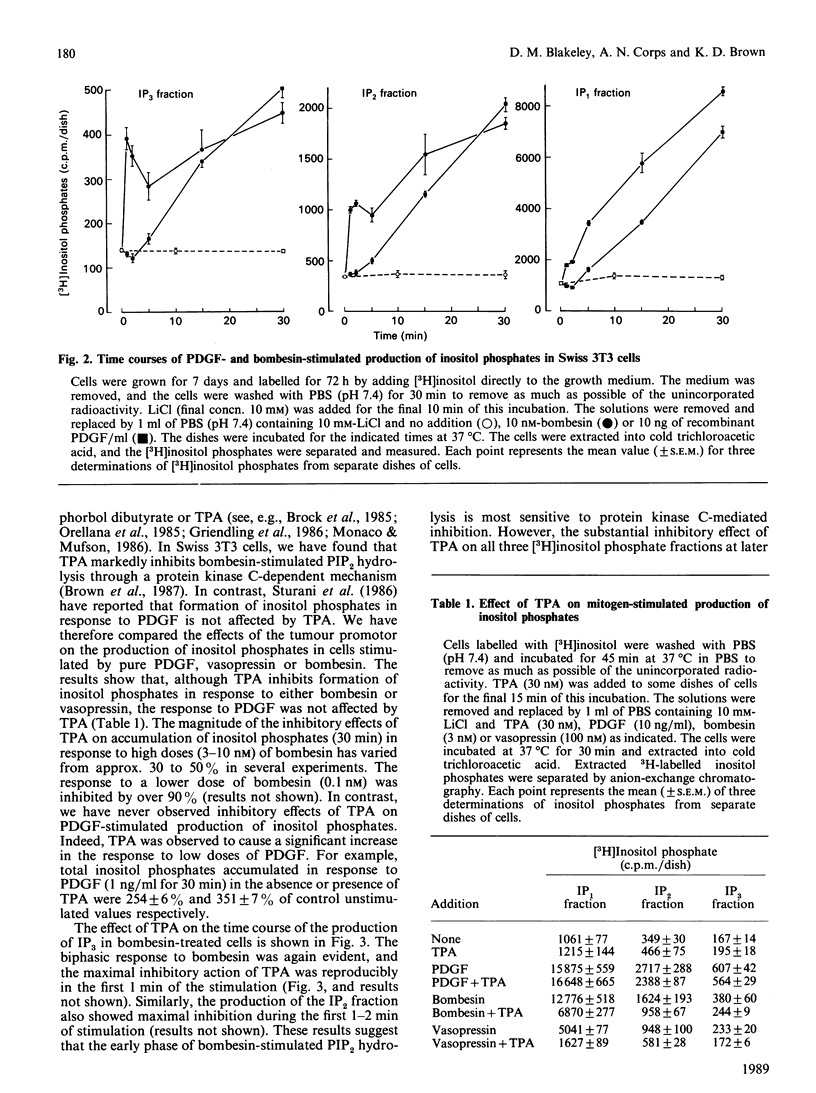
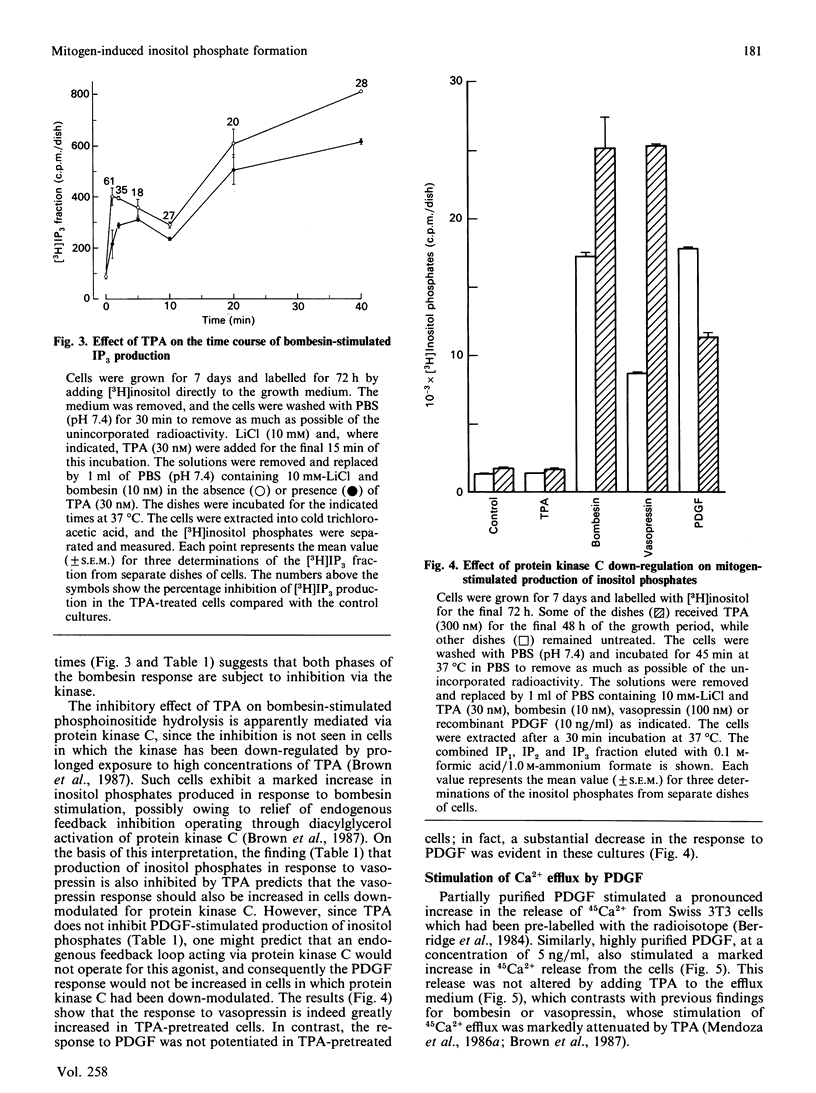
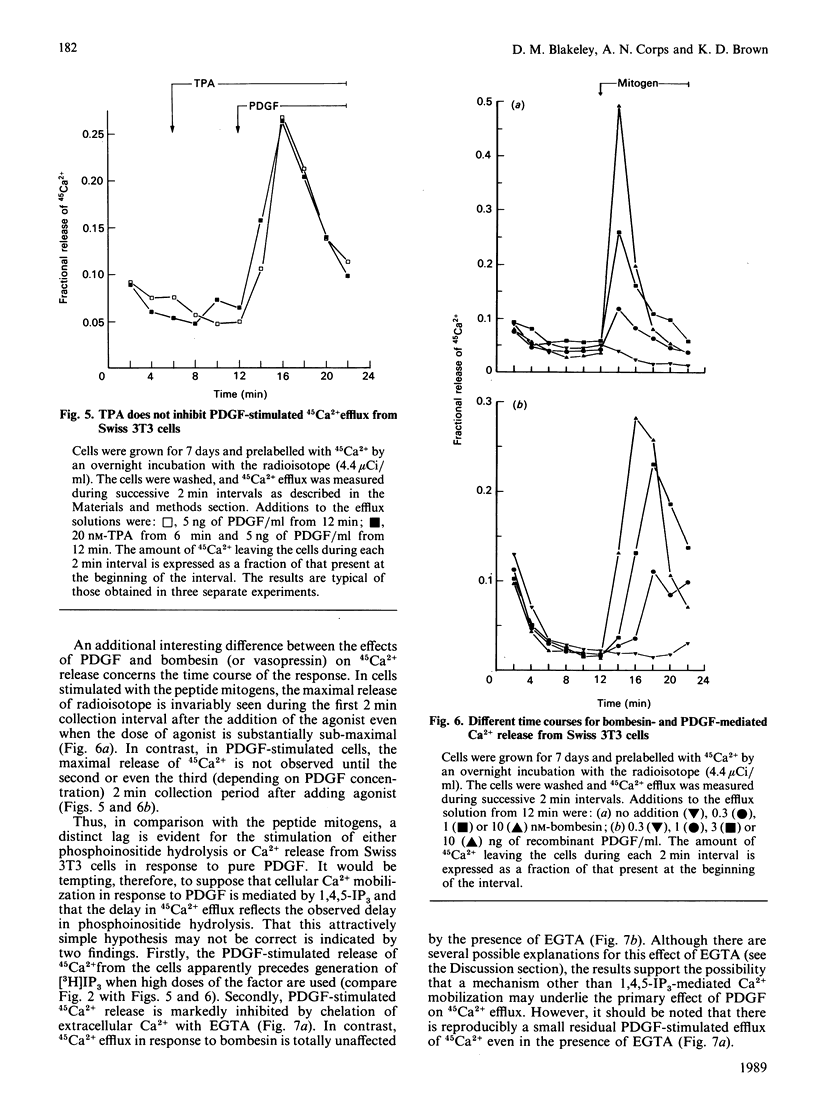
Highly purified platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) or recombinant PDGF stimulate DNA synthesis in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. The dose-response curves for the natural and recombinant factors were similar, with half-maximal responses at 2-3 ng/ml and maximal responses at approx. 10 ng/ml. Over this dose range, both natural and recombinant PDGF stimulated a pronounced accumulation of [3H]inositol phosphates in cells labelled for 72 h with [3H]inositol. In addition, mitogenic concentrations of PDGF stimulated the release of 45Ca2+ from cells prelabelled with the radioisotope. However, in comparison with the response to the peptide mitogens bombesin and vasopressin, a pronounced lag was evident in both the generation of inositol phosphates and the stimulation of 45Ca2+ efflux in response to PDGF. Furthermore, although the bombesin-stimulated efflux of 45Ca2+ was independent of extracellular Ca2+, the PDGF-stimulated efflux was markedly inhibited by chelation of external Ca2+ by using EGTA. Neither the stimulation of formation of inositol phosphates nor the stimulation of 45Ca2+ efflux in response to PDGF were affected by tumour-promoting phorbol esters such as 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA). In contrast, TPA inhibited phosphoinositide hydrolysis and 45Ca2+ efflux stimulated by either bombesin or vasopressin. Furthermore, whereas formation of inositol phosphates in response to both vasopressin and bombesin was increased in cells in which protein kinase C had been down-modulated by prolonged exposure to phorbol esters, the response to PDGF was decreased in these cells. These results suggest that, in Swiss 3T3 cells, PDGF receptors are coupled to phosphoinositidase activation by a mechanism that does not exhibit protein kinase C-mediated negative-feedback control and which appears to be fundamentally different from the coupling mechanism utilized by the receptors for bombesin and vasopressin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Fate of immunoprecipitable protein kinase C in GH3 cells treated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15194–15199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Brock T. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Early agonist-mediated ionic events in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Calcium mobilization is associated with intracellular acidification. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5065–5072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Cobbold P. H., Cuthbertson K. S. Spatial and temporal aspects of cell signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):325–343. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Brown K. D. Inositol trisphosphate formation and calcium mobilization in Swiss 3T3 cells in response to platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):195–201. doi: 10.1042/bj2220195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Duronio V., Cuatrecasas P. Rapid formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylcholine: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Watson S. P., Cuatrecasas P. Lack of association of epidermal growth factor-, insulin-, and serum-induced mitogenesis with stimulation of phosphoinositide degradation in BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):723–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Witters L. A., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Quamo S. N. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13304–13315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. II. Specific binding to cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5161–5171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Rittenhouse S. E., Powers C. W., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Phorbol ester and 1-oleoyl-2-acetylglycerol inhibit angiotensin activation of phospholipase C in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14158–14162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blakeley D. M., Hamon M. H., Laurie M. S., Corps A. N. Protein kinase C-mediated negative-feedback inhibition of unstimulated and bombesin-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):631–639. doi: 10.1042/bj2450631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blakeley D. M. Inhibition of the binding of 125I-labelled epidermal growth factor to mouse cells by a mitogen in goat mammary secretions. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):465–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2120465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blay J., Irvine R. F., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. Reduction of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity by heterologous ligands: evidence for a mechanism involving the breakdown of phosphoinositides and the activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S. H., Hoban C. J., Owen A. J., Geyer R. P. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates rapid polyphosphoinositide breakdown in fetal human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Sep;124(3):391–396. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo D. M., Gaudino G., Naldini L., Comoglio P. M. Receptor for bombesin with associated tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4641–4649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Rozengurt E. Vasopressin induces selective desensitization of its mitogenic response in Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1924–1928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Regulation of cell growth and transformation by tyrosine-specific protein kinases: the search for important cellular substrate proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:125–161. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69075-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corps A. N., Rees L. H., Brown K. D. A peptide that inhibits the mitogenic stimulation of Swiss 3T3 cells by bombesin or vasopressin. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):781–784. doi: 10.1042/bj2310781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide B. L., Krebs E. G., Ross R., Pike L. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Tumor promoter enhances mitogenesis by PDGF with little effect on PDGF binding. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Feb;126(2):254–258. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Keating M. T., Ives H. E., Williams L. T. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors expressed by cDNA transfection couple to a diverse group of cellular responses associated with cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1482–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Contractions induced by a calcium-triggered release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of single skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):469–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frackelton A. R., Jr, Tremble P. M., Williams L. T. Evidence for the platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor in vivo. Immunopurification using a monoclonal antibody to phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7909–7915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Rittenhouse S. E., Brock T. A., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Sustained diacylglycerol formation from inositol phospholipids in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5901–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa-Sasaki H. Early changes in inositol lipids and their metabolites induced by platelet-derived growth factor in quiescent Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):99–109. doi: 10.1042/bj2320099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Nakahata N., Lovenberg T. W., DiGuiseppi J., Herman B., Earp H. S., Harden T. K. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the rapid accumulation of inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate and a rise in cytosolic calcium mobilized from intracellular stores in A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):2951–2956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Blakeley D. M., Brown K. D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J. Effects of bombesin and insulin on inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate and inositol (1,3,4)trisphosphate formation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Berridge M. J. Inositol tetrakis- and pentakisphosphates in GH4 cells. J Exp Biol. 1985 Nov;119:395–401. doi: 10.1242/jeb.119.1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M., Meisenhelder J., Brown K. D., Gould K. L., Gould S. J., Hunter T. Early phosphorylation events following the treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells with bombesin and the mammalian bombesin-related peptide, gastrin-releasing peptide. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2889–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ives H. E., Daniel T. O. Interrelationship between growth factor-induced pH changes and intracellular Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Seeburg P. H., Gray A., Ullrich A., Scrace G. The c-sis gene encodes a precursor of the B chain of platelet-derived growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):921–928. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Pouysségur EGF and insulin action in fibroblasts. Evidence that phosphoinositide hydrolysis is not an essential mitogenic signalling pathway. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):344–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leal F., Williams L. T., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Evidence that the v-sis gene product transforms by interaction with the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.2996133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Rivas A., Mendoza S. A., Nånberg E., Sinnett-Smith J., Rozengurt E. Ca2+-mobilizing actions of platelet-derived growth factor differ from those of bombesin and vasopressin in Swiss 3T3 mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5768–5772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphee C. H., Drummond A. H., Otto A. M., Jimenez de Asua L. Prostaglandin F2 alpha stimulates phosphatidylinositol turnover and increases the cellular content of 1,2-diacylglycerol in confluent resting Swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Apr;119(1):35–40. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041190107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuoka K., Fukami K., Nakanishi O., Kawai S., Takenawa T. Mitogenesis in response to PDGF and bombesin abolished by microinjection of antibody to PIP2. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):640–643. doi: 10.1126/science.2829356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., McKenna M. P., Taylor D. L. A transient rise in cytosolic calcium follows stimulation of quiescent cells with growth factors and is inhibitable with phorbol myristate acetate. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):372–379. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza S. A., Lopez-Rivas A., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Phorbol esters and diacylglycerol inhibit vasopressin-induced increases in cytoplasmic-free Ca2+ and 45Ca2+ efflux in Swiss 3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jun;164(2):536–545. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza S. A., Schneider J. A., Lopez-Rivas A., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Early events elicited by bombesin and structurally related peptides in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. II. Changes in Na+ and Ca2+ fluxes, Na+/K+ pump activity, and intracellular pH. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2223–2233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco M. E., Mufson R. A. Phorbol ester inhibition of the hormone-stimulated phosphoinositide cycle in WRK-1 cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):171–175. doi: 10.1042/bj2360171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Tertoolen L. G., de Laat S. W. Growth factors immediately raise cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8066–8069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistér M., Hammacher A., Mellström K., Siegbahn A., Rönnstrand L., Westermark B., Heldin C. H. A glioma-derived PDGF A chain homodimer has different functional activities from a PDGF AB heterodimer purified from human platelets. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):791–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90421-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., Solski P. A., Brown J. H. Phorbol ester inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis and calcium mobilization in cultured astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5236–5239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Eakes A. T. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the production of phosphatidylinositol monophosphate and the breakdown of polyphosphoinositides in A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1644–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Rosen O. M. Stimulation of polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis by thrombin in membranes from human fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):49–57. doi: 10.1042/bj2450049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Vogel A. The platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Pettican P. Vasopressin stimulation of mouse 3T3 cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Sinnett-Smith J. Bombesin stimulation of DNA synthesis and cell division in cultures of Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Rodriguez-Pena A., Young S., Rozengurt E., Parker P. J. Quantitation of protein kinase C by immunoblot--expression in different cell lines and response to phorbol esters. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jan;130(1):111–117. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroobant P., Waterfield M. D. Purification and properties of porcine platelet-derived growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2963–2967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturani E., Vicentini L. M., Zippel R., Toschi L., Pandiella-Alonso A., Comoglio P. M., Meldolesi J. PDGF-induced receptor phosphorylation and phosphoinositide hydrolysis are unaffected by protein kinase C activation in mouse Swiss 3T3 and human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa N., Takuwa Y., Bollag W. E., Rasmussen H. The effects of bombesin on polyphosphoinositide and calcium metabolism in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Merritt J. E., Putney J. W., Jr, Rubin R. P. Effects of Ca2+ on phosphoinositide breakdown in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):765–772. doi: 10.1042/bj2380765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., van Paridon P. A., Verlaan I., de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Epidermal-growth-factor-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human A431 cells. Differences from the effect of bradykinin. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):857–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2520857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Hamamori Y., Fukumoto Y., Kaibuchi K., Takai Y. Epidermal growth factor increases c-myc mRNA without eliciting phosphoinositide turnover, protein kinase C activation, or calcium ion mobilization in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biochem. 1986 Dec;100(6):1631–1635. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Kaibuchi K., West B., Takai Y. Involvement of Ca2+ in platelet-derived growth factor-induced expression of c-myc oncogene in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 22;187(1):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81210-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Sweatt J. D., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulates inositol trisphosphate formation in cells which overexpress the EGF receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):688–695. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Rozengurt E. High-affinity receptors for peptides of the bombesin family in Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7616–7620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Early events elicited by bombesin and structurally related peptides in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. I. Activation of protein kinase C and inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2211–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


