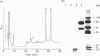Abstract
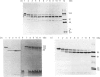
Limited proteolysis of C1 inhibitor (C1-INH) by neutrophil elastase, Pseudomonas elastase and snake venoms resulted in initial cleavage within the molecule's N-terminus followed by further cleavage within the molecule's C-terminally placed reactive centre. N-Terminal proteolysis occurred at peptide bonds 14-15, 36-37 and 40-41. This had no effect on either the inhibitory activity or the heat-stability of C1-INH. Proteolysis within the reactive centre occurred at peptide bonds 439-440, 440-441, 441-442 and 442-443. Cleavage at any one of these sites inactivated C1-INH and conferred enhanced heat-stability upon a previously heat-labile molecule. Released neutrophil proteinases also cleaved and inactivated C1-INH, suggesting that they may physiologically regulate C1-INH during inflammatory episodes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badwey J. A., Karnovsky M. L. Active oxygen species and the functions of phagocytic leukocytes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banda M. J., Clark E. J., Sinha S., Travis J. Interaction of mouse macrophage elastase with native and oxidized human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1314–1317. doi: 10.1172/JCI112955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty K., Bieth J., Travis J. Kinetics of association of serine proteinases with native and oxidized alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor and alpha-1-antichymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3931–3934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. C., Skriver K., Nielsen E., Thøgersen H. C., Wiman B., Donaldson V. H., Eddy R. L., Marrinan J., Radziejewska E., Huber R. Human C1 inhibitor: primary structure, cDNA cloning, and chromosomal localization. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4292–4301. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower M. S., Harpel P. C. Proteolytic cleavage and inactivation of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor and C1 inactivator by human polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9849–9854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Owen M. C. Plakalbumin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, antithrombin and the mechanism of inflammatory thrombosis. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):730–732. doi: 10.1038/317730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R., Owen M., Brennan S., Vaughan L. Carboxy terminal fragment of human alpha-1-antitrypsin from hydroxylamine cleavage: homology with antithrombin III. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):1032–1037. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91983-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. A. Human C1 inhibitor: improved isolation and preliminary structural characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):5001–5007. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson K. W., Esmon N., Tang J. Streptokinase and staphylokinase. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):387–394. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Travis J. Inactivation of human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor by thiol proteinases. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 1;163(3):639–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1630639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Fish W. W., Björk I. The thrombin cleavage site in bovine antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80532-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress L. F., Catanese J. J. Identification of the cleavage sites resulting from enzymatic inactivation of human antithrombin III by Crotalus adamanteus proteinase II in the the presence and absence of heparin. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7432–7438. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress L. F., Catanese J., Hirayama T. Analysis of the effects of snake venom proteinases on the activity of human plasma C1 esterase inhibitor, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and alpha 2-antiplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 15;745(2):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress L. F., Kurecki T., Chan S. K., Laskowski M., Sr Characterization of the inactive fragment resulting from limited proteolysis of human alpha1-proteinase inhibitor by Crotalus adamanteus proteinase II. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5317–5320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennick M., Brew S. A., Ingham K. C. Changes in protein conformation and stability accompany complex formation between human C1 inhibitor and C1-s. Biochemistry. 1985 May 7;24(10):2561–2568. doi: 10.1021/bi00331a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman J. Heat lability of alpha1-antitrypsin variants. Chest. 1973 Nov;64(5):579–584. doi: 10.1378/chest.64.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebermann H., Tokuoka R., Deisenhofer J., Huber R. Human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Crystal structure analysis of two crystal modifications, molecular model and preliminary analysis of the implications for function. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):531–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Harada M., Iwata T. Purification of human plasma alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor and its inactivation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. J Biochem. 1984 Mar;95(3):795–804. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Watorek W., Travis J. The inactivation of human plasma alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor by proteinases from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14330–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Catanese J. J., Kress L. F., Travis J. Primary structure of the reactive site of human C1-inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2432–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., de Agostini A., Schifferli J. A., Colman R. W. Biochemistry and pathophysiology of human C1 inhibitor: current issues. Complement. 1985;2(2-3):111–126. doi: 10.1159/000467851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Lyerly D., Kreger A., Travis J. Inactivation of human plasma alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor by a metalloproteinase from Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 4;704(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. P., Dean R. T. Fragmentation of proteins by free radicals and its effect on their susceptibility to enzymic hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):399–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2340399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]