Abstract
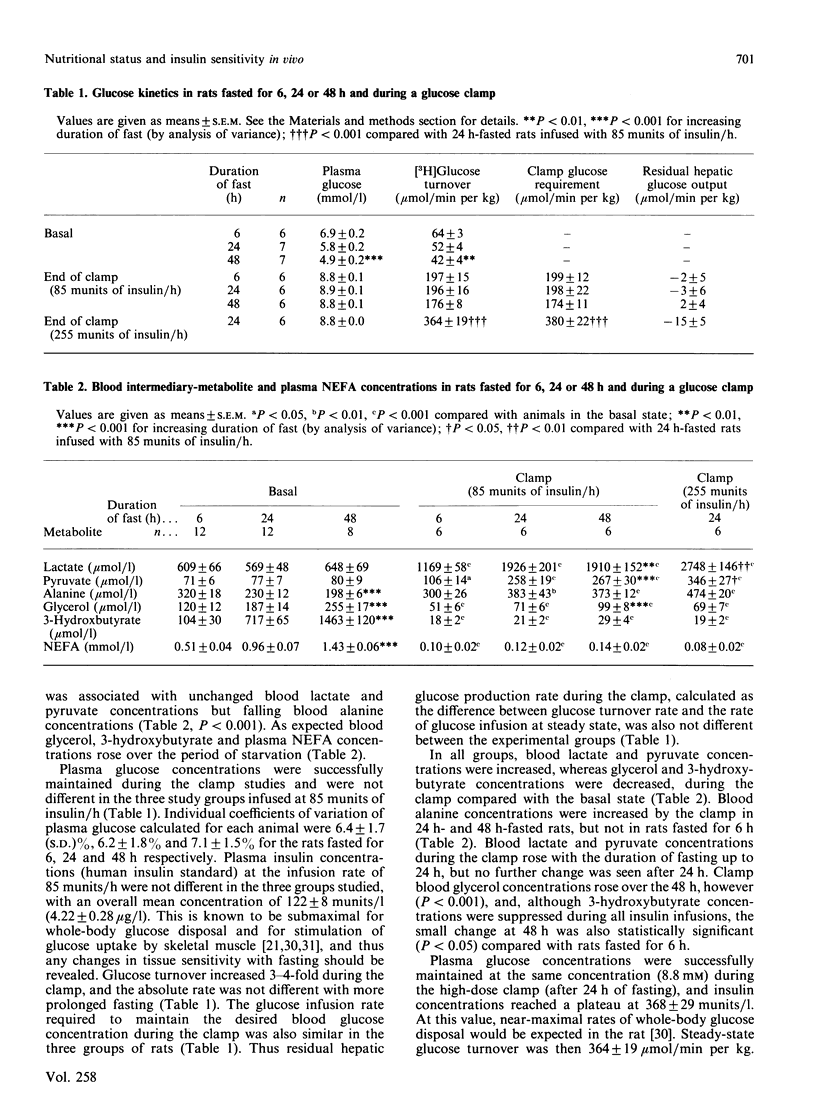
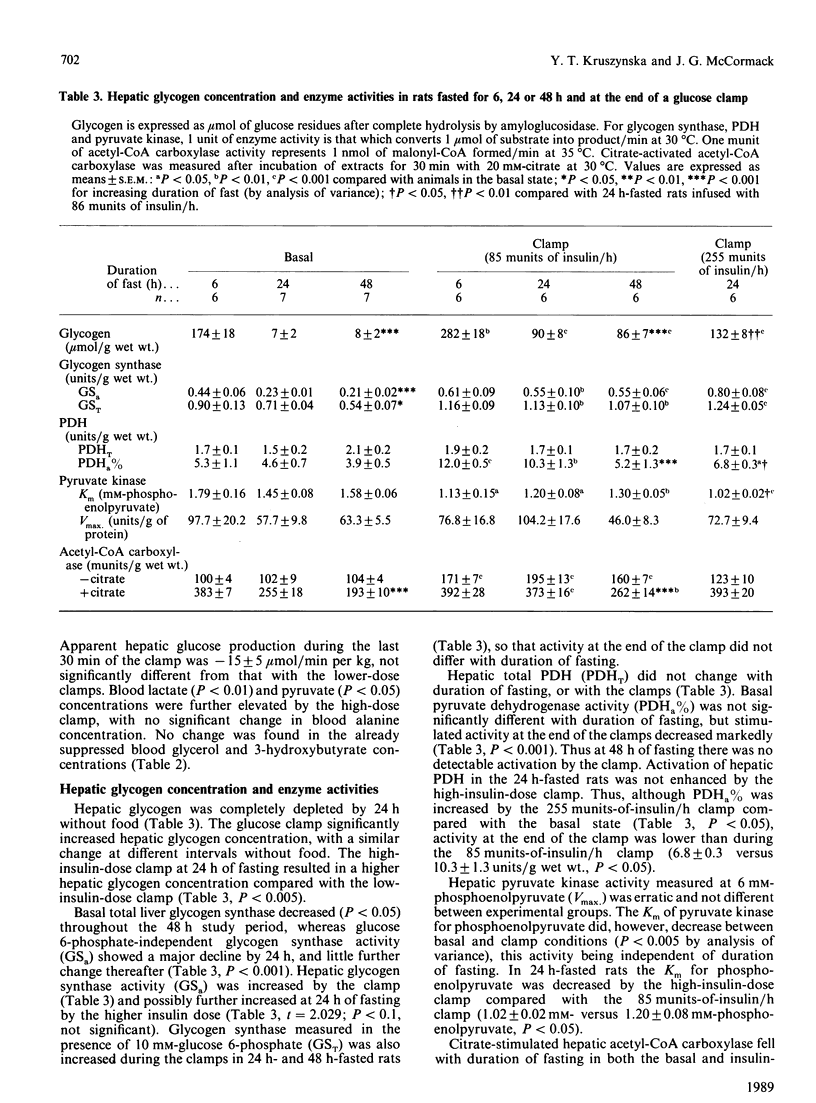
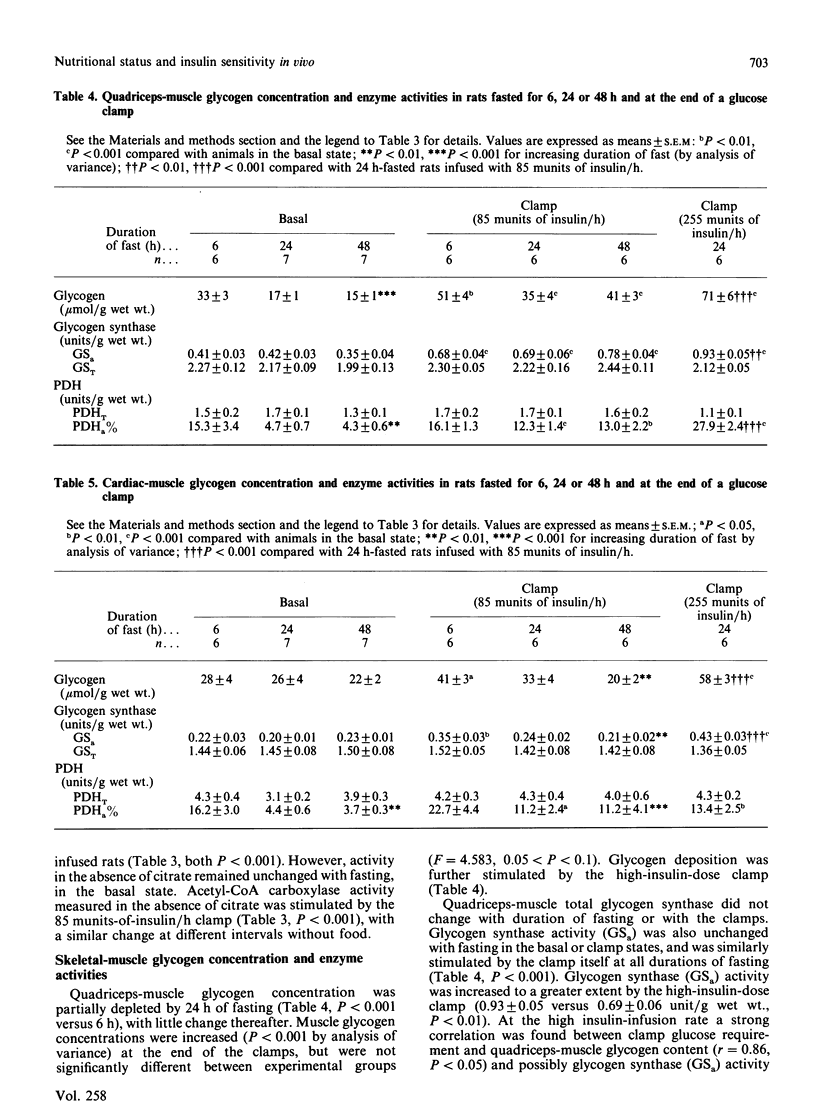
The hyperinsulinaemic-glucose-clamp technique, in combination with measurement of glucose turnover in conscious unrestrained rats, was used to assess the effects of nutritional status on insulin sensitivity in vivo and glucose metabolism. Liver, heart and quadriceps skeletal-muscle glycogen content and activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) and glycogen synthase were measured both basally and at the end of a 2.5 h glucose clamp (insulin 85 munits/h) in rats 6, 24 and 48 h after food withdrawal. Clamp glucose requirement and glucose turnover were unchanged by fasting. Activation of glycogen synthase and glycogen deposition in liver and skeletal muscle during the clamps were also not impaired in rats after a prolonged fast. By contrast with skeletal muscle, activation of cardiac-muscle glycogen synthase and glycogen deposition during the clamps were markedly impaired by 24 h of fasting and were undetectable at 48 h. Skeletal-muscle PDH activity fell with more prolonged fasting (6 h, 15.3 +/- 3.4%; 24 h, 4.7 +/- 0.7%; 48 h, 4.3 +/- 0.6% active; P less than 0.005), but at 24 and 48 h was stimulated by the clamp to values unchanged by the duration of fasting. Stimulation of cardiac PDH activity by the clamp was, however, impaired in rats fasted for 24 or 48 h. Basal hepatic PDH did not change significantly with fasting (6 h, 5.3 +/- 1.1%; 24 h, 4.6 +/- 0.7%; 48 h, 3.9 +/- 0.5%), and, although it could be partly restored at 24 h, very little stimulation occurred at 48 h. Hepatic pyruvate kinase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity were both stimulated by the clamps, and this was not impaired with more prolonged fasting. During the glucose clamps, blood concentrations of lactate, pyruvate and alanine were increased to a greater extent in rats fasted for 24 and 48 h than in rats studied 6 h after food withdrawal. The findings suggest that, although sensitivity to insulin of whole-body glucose disposal is unchanged with fasting, there may be qualitative differences in the metabolism of glucose.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alleyne G. A., Trust P. M., Flores H., Robinson H. Glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in malnourished children. Br J Nutr. 1972 May;27(3):585–592. doi: 10.1079/bjn19720128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Hagg S. A., Goodman M. N., Ruderman N. B. Glucose metabolism in perfused skeletal muscle. Effects of starvation, diabetes, fatty acids, acetoacetate, insulin and exercise on glucose uptake and disposition. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):191–202. doi: 10.1042/bj1580191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beylot M., Khalfallah Y., Riou J. P., Cohen R., Normand S., Mornex R. Effects of ketone bodies on basal and insulin-stimulated glucose utilization in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jul;63(1):9–15. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church J. M., Hill G. L. Impaired glucose metabolism in surgical patients improved by intravenous nutrition: assessment by the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp. Metabolism. 1988 Jun;37(6):505–509. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis-Prior P. B., Trethewey J., Stewart G. A., Hanley T. The contribution of different organs and tissues of the rat to assimilation of glucose. Diabetologia. 1969 Dec;5(6):384–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00427976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Soman V., Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., Felig P. Insulin binding to monocytes and insulin action in human obesity, starvation, and refeeding. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):204–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI109108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Denton R. M., Edgell N. J., Bridges B. J., Poole G. P. Acute regulation of pyruvate kinase activity in rat epididymal adipose tissue by insulin. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):523–531. doi: 10.1042/bj1800523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G., Marshall S. E. Persistence of the effect of insulin on pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in rat white and brown adipose tissue during the preparation and subsequent incubation of mitochondria. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):441–452. doi: 10.1042/bj2170441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denyer G. S., Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Kinase activator protein mediates longer-term effects of starvation on activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):347–354. doi: 10.1042/bj2390347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. M., Lebovitz H. E. Effect of fasting on insulin secretion and action in mice. Endocrinology. 1970 Feb;86(2):313–321. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré P., Leturque A., Burnol A. F., Penicaud L., Girard J. A method to quantify glucose utilization in vivo in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue of the anaesthetized rat. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):103–110. doi: 10.1042/bj2280103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French T. J., Holness M. J., MacLennan P. A., Sugden M. C. Effects of nutritional status and acute variation in substrate supply on cardiac and skeletal-muscle fructose 2,6-bisphosphate concentrations. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):773–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2500773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. J., Randle P. J. Reversible phosphorylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat skeletal-muscle mitochondria. Effects of starvation and diabetes. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):635–646. doi: 10.1042/bj2190635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. N., Ruderman N. B. Insulin sensitivity of rat skeletal muscle: effects of starvation and aging. Am J Physiol. 1979 May;236(5):E519–E523. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.5.E519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. F., Frayn K. N., Rose J. G. Rates of glucose utilization and glucogenesis in rats in the basal state induced by halothane anaesthesia. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 15;162(3):643–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1620643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holness M. J., French T. J., Sugden M. C. Hepatic glycogen synthesis on carbohydrate re-feeding after starvation. A regulatory role for pyruvate dehydrogenase in liver and extrahepatic tissues. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj2350441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holness M. J., MacLennan P. A., Palmer T. N., Sugden M. C. The disposition of carbohydrate between glycogenesis, lipogenesis and oxidation in liver during the starved-to-fed transition. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):325–330. doi: 10.1042/bj2520325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issad T., Pénicaud L., Ferré P., Kandé J., Baudon M. A., Girard J. Effects of fasting on tissue glucose utilization in conscious resting rats. Major glucose-sparing effect in working muscles. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):241–244. doi: 10.1042/bj2460241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Roshania R. D., Hawa M. I., Sim B. M., DiSilvio L. Impact of glucose ingestion on hepatic and peripheral glucose metabolism in man: an analysis based on simultaneous use of the forearm and double isotope techniques. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Sep;63(3):541–549. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-3-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Kraegen E. W. Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E567–E574. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Kraegen E. W., Chisholm D. J. Effects of exercise training on in vivo insulin action in individual tissues of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):657–666. doi: 10.1172/JCI112019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James W. P., Coore H. G. Persistent impairment of insulin secretion and glucose tolerance after malnutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Apr;23(4):386–389. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.4.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Akanuma Y., Iwamoto Y., Kosaka K. Effects of fasting and refeeding of insulin receptors and glucose metabolism in rat adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1977 May;100(5):1384–1390. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-5-1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L. D., Glickman M. G., Rapoport S., Ferrannini E., DeFronzo R. A. Splanchnic and peripheral disposal of oral glucose in man. Diabetes. 1983 Jul;32(7):675–679. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.7.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J., Cooper R. H., Whitehouse S., Pask H. T., Denton R. M. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat heart. Mechanism of regulation of proportions of dephosphorylated and phosphorylated enzyme by oxidation of fatty acids and ketone bodies and of effects of diabetes: role of coenzyme A, acetyl-coenzyme A and reduced and oxidized nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):327–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1540327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase/activator in rat heart mitochondria, Assay, effect of starvation, and effect of protein-synthesis inhibitors of starvation. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):103–111. doi: 10.1042/bj2060103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., James D. E., Bennett S. P., Chisholm D. J. In vivo insulin sensitivity in the rat determined by euglycemic clamp. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):E1–E7. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.1.E1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Chisholm D. J. Dose-response curves for in vivo insulin sensitivity in individual tissues in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):E353–E362. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.3.E353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruszynska Y. T., Home P. D., Alberti K. G. Comparison of portal and peripheral insulin delivery on carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1985 Mar;28(3):167–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00273866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruszynska Y. T., Home P. D., Alberti K. G. In vivo regulation of liver and skeletal muscle glycogen synthase activity by glucose and insulin. Diabetes. 1986 Jun;35(6):662–667. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.6.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Freychet P. Effect of fasting and streptozotocin diabetes on insulin binding and action in the isolated mouse soleus muscle. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1505–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI109609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. U., Lee H. K., Koh C. S., Min H. K. Artificial induction of intravascular lipolysis by lipid-heparin infusion leads to insulin resistance in man. Diabetologia. 1988 May;31(5):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00277409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd B., Burrin J., Smythe P., Alberti K. G. Enzymic fluorometric continuous-flow assays for blood glucose, lactate, pyruvate, alanine, glycerol, and 3-hydroxybutyrate. Clin Chem. 1978 Oct;24(10):1724–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Studies on the interactions of Ca2+ and pyruvate in the regulation of rat heart pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. Effects of starvation and diabetes. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 15;202(2):419–427. doi: 10.1042/bj2020419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Moore S. V., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Efficient hepatic glycogen synthesis in refeeding rats requires continued carbon flow through the gluconeogenic pathway. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6958–6963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Effects of fasting on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation in isolated rat adipocytes: relationships between insulin receptors and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1450–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI108601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pénicaud L., Kandé J., Le Magnen J., Girard J. R. Insulin action during fasting and refeeding in rat determined by euglycemic clamp. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 1):E514–E518. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.5.E514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J. Fuel selection in animals. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Oct;14(5):799–806. doi: 10.1042/bst0140799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J., Newsholme E. A., Garland P. B. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. 8. Effects of fatty acids, ketone bodies and pyruvate, and of alloxan-diabetes and starvation, on the uptake and metabolic fate of glucose in rat heart and diaphragm muscles. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):652–665. doi: 10.1042/bj0930652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. R., Edgar P. J., Pozefsky T., Chhetri M. K., Prout T. E. Insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in adults with protein-calorie malnutrition. Metabolism. 1975 Sep;24(9):1073–1084. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansbie D., Brownsey R. W., Crettaz M., Denton R. M. Acute effects in vivo of anti-insulin serum on rates of fatty acid synthesis and activities of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in liver and epididymal adipose tissue of fed rats. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):413–416. doi: 10.1042/bj1600413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiebaud D., Jacot E., DeFronzo R. A., Maeder E., Jequier E., Felber J. P. The effect of graded doses of insulin on total glucose uptake, glucose oxidation, and glucose storage in man. Diabetes. 1982 Nov;31(11):957–963. doi: 10.2337/diacare.31.11.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Diggle T. A., Denton R. M. Sensitivity of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase to magnesium ions. Similar effects of spermine and insulin. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):83–91. doi: 10.1042/bj2380083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagournis M., Skillman R. G. Glucose intolerance mechanism after starvation. Metabolism. 1970 Feb;19(2):170–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa T., Krans H. M. Reduced glucose transport and increased binding of insulin in adipocytes from diabetic and fasted rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 1;538(3):563–570. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Ilic V., Jones R. G. Evidence that the stimulation of lipogenesis in the mammary glands of starved lactating rats re-fed with a chow diet is dependent on continued hepatic gluconeogenesis during the absorptive period. Effects of a gluconeogenic inhibitory, mercaptopicolinic acid, in vivo. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):727–733. doi: 10.1042/bj2280727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L., RABINOWITZ D. ROLES OF INSULIN AND GROWTH HORMONE, BASED ON STUDIES OF FOREARM METABOLISM IN MAN. Medicine (Baltimore) 1963 Nov;42:385–402. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196311000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


