Abstract
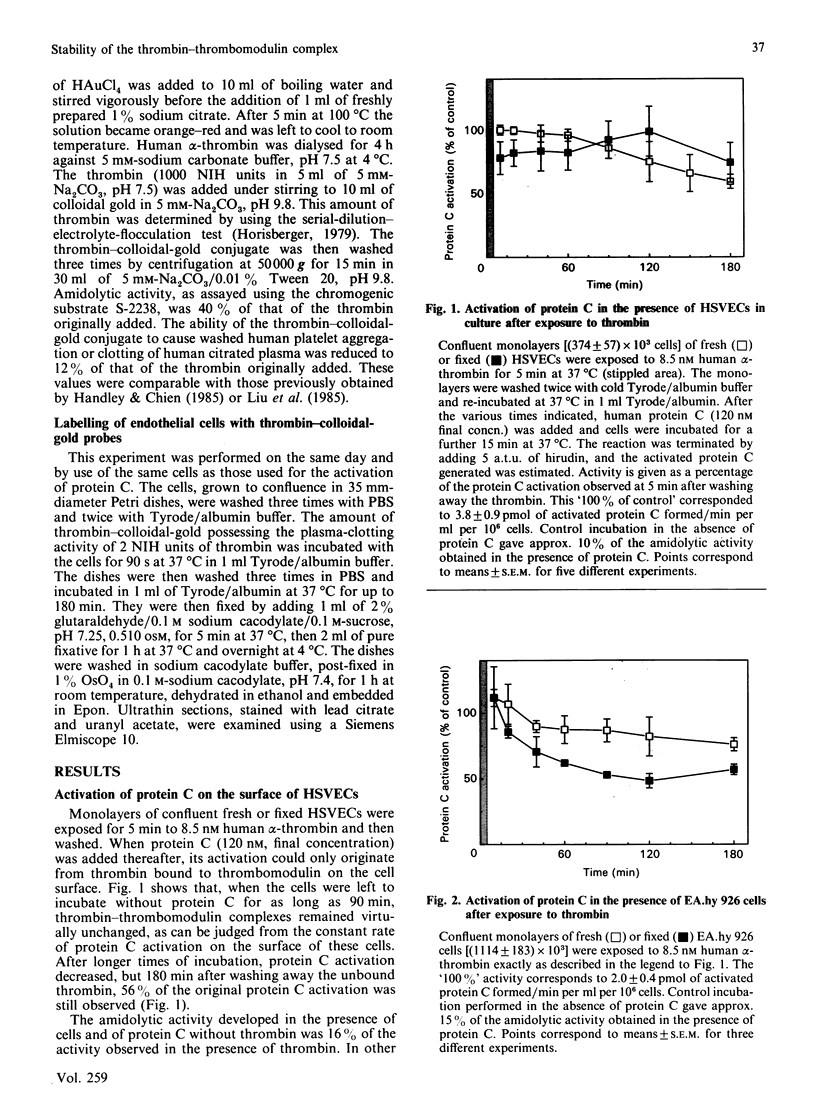
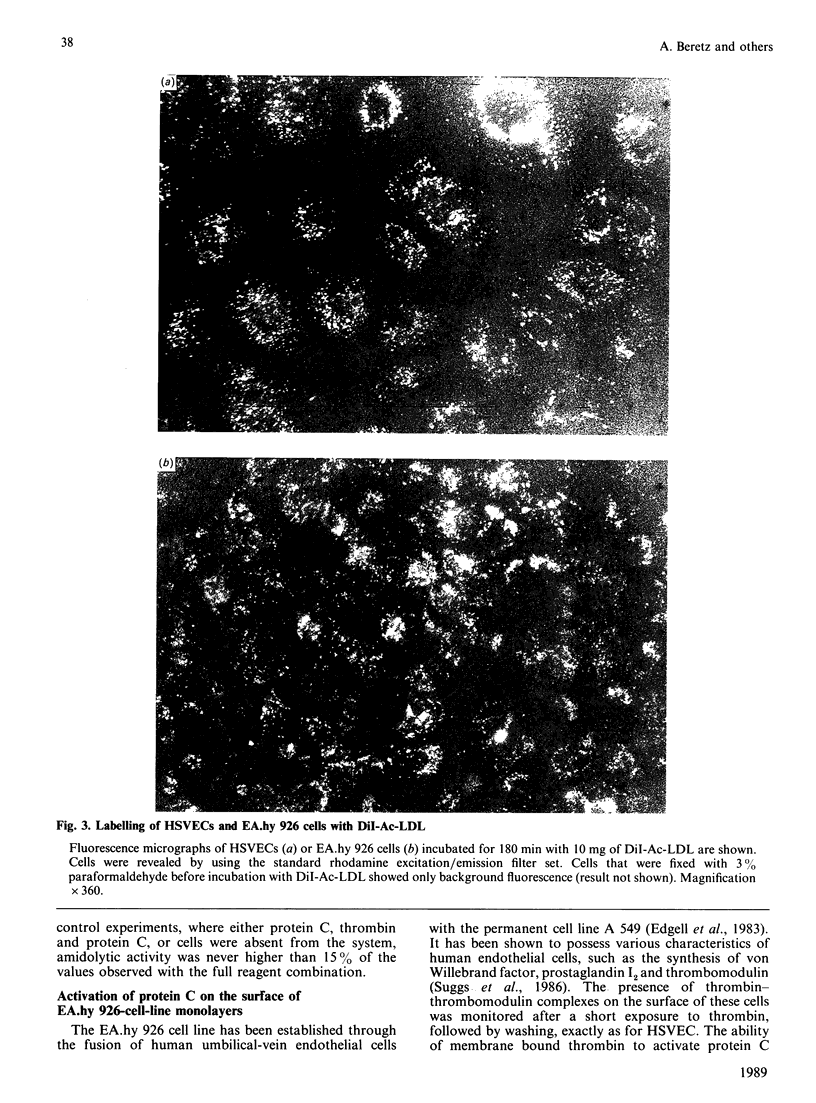
Protein C activation by alpha-thrombin on the surface of endothelial cells depends on an essential membrane-glycoprotein cofactor, thrombomodulin. In the present study we have monitored the activity of thrombin-thrombomodulin complexes on human saphenous-vein endothelial cells (HSVEC) or on the endothelial cell line EA.hy 926. Cell monolayers were exposed for 5 min to 8.5 nM human alpha-thrombin and then washed to remove unbound thrombin. The cells were then incubated at 37 degrees C for 5-180 min. At the end of the respective incubation periods, purified human protein C (120 nM) was added in order to assay the activity of the thrombin-thrombomodulin complexes present on the cell surface. HSVEC pre-exposed to thrombin retained their full capacity to promote protein C activation up to 90 min after free thrombin was removed. This capacity then decreased slowly to reach 56% of control value after 180 min of incubation. Original activity was 3.8 +/- 0.9 pmol of activated protein C formed/min per ml per 10(6) cells (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 5). The capacity of protein C activation of EA.hy 926 cells remained constant for 120 min after free thrombin was removed, then decreased to 76% of control after 180 min. Original activity was 2.0 +/- 0.4 pmol of activated protein C formed/min per ml per 10(6) cells (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 3). Similar results were obtained with cells fixed with 3% paraformaldehyde. However, during the 5-180 min incubation period, non-fixed cells of both types were capable of significantly internalizing fluorescent acetylated low-density lipoprotein. In the experimental protocol used here, an eventual inhibition of thrombin internalization by protein C can be excluded, as protein C is only added at the end of the incubation period. We conclude that there is no evidence of rapid internalization of thrombin-thrombomodulin complexes on HSVEC or the EA.hy 926 cell line, as assessed by the ability of membrane-bound thrombin to activate protein C.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Goldstein J. L., Südhof T. C., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. Acid-dependent ligand dissociation and recycling of LDL receptor mediated by growth factor homology region. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):760–765. doi: 10.1038/326760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., van Driel I. R., Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. The low density lipoprotein receptor. Identification of amino acids in cytoplasmic domain required for rapid endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4075–4082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgell C. J., McDonald C. C., Graham J. B. Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.3029867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet J. M., Gauchy J., Cazenave J. P. The effect of phospholipids on the activation of protein C by the human thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):151–157. doi: 10.1042/bj2380151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley D. A., Chien S. Ultrastructural studies of endothelial and platelet receptor binding of thrombin-colloidal gold probes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;39(2):391–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackman R. W., Beeler D. L., Fritze L., Soff G., Rosenberg R. D. Human thrombomodulin gene is intron depleted: nucleic acid sequences of the cDNA and gene predict protein structure and suggest sites of regulatory control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6425–6429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackman R. W., Beeler D. L., VanDeWater L., Rosenberg R. D. Characterization of a thrombomodulin cDNA reveals structural similarity to the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8834–8838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A. Culture of human endothelial cells. Transplant Proc. 1980 Sep;12(3 Suppl 1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Soyer C., Beretz A., Millon-Collard R., Abecassis J., Cazenave J. P. A simple in vitro model of mechanical injury of confluent cultured endothelial cells to study quantitatively the repair process. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Oct 21;56(2):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa S., Stearns D. J., Jackson K. W., Esmon C. T. A 10-kDa cyanogen bromide fragment from the epidermal growth factor homology domain of rabbit thrombomodulin contains the primary thrombin binding site. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):5993–5996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. Y., Handley D. A., Chien S. Gold labeling of thrombin and ultrastructural studies of thrombin-gold conjugate binding by fibrin. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 15;147(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I., Majerus P. W. Protein C inhibits endocytosis of thrombin-thrombomodulin complexes in A549 lung cancer cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1481–1484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I., Majerus P. W. The turnover of thrombin-thrombomodulin complex in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and A549 lung cancer cells. Endocytosis and degradation of thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15432–15438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H. H., Maruyama I., Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Isolation and characterization of thrombomodulin from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12246–12251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savion N., Isaacs J. D., Gospodarowicz D., Shuman M. A. Internalization and degradation of thrombin and up regulation of thrombin-binding sites in corneal endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4514–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs J. E., Madden M. C., Friedman M., Edgell C. J. Prostacyclin expression by a continuous human cell line derived from vascular endothelium. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):825–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kusumoto H., Deyashiki Y., Nishioka J., Maruyama I., Zushi M., Kawahara S., Honda G., Yamamoto S., Horiguchi S. Structure and expression of human thrombomodulin, a thrombin receptor on endothelium acting as a cofactor for protein C activation. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1891–1897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02448.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyta J. C., Via D. P., Butterfield C. E., Zetter B. R. Identification and isolation of endothelial cells based on their increased uptake of acetylated-low density lipoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2034–2040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D. Z., Dittman W. A., Ye R. D., Deaven L. L., Majerus P. W., Sadler J. E. Human thrombomodulin: complete cDNA sequence and chromosome localization of the gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4350–4357. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems C., Astaldi G. C., De Groot P. G., Janssen M. C., Gonsalvez M. D., Zeijlemaker W. P., Van Mourik J. A., Van Aken W. G. Media conditioned by cultured human vascular endothelial cells inhibit the growth of vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 May;139(1):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90332-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]