Abstract
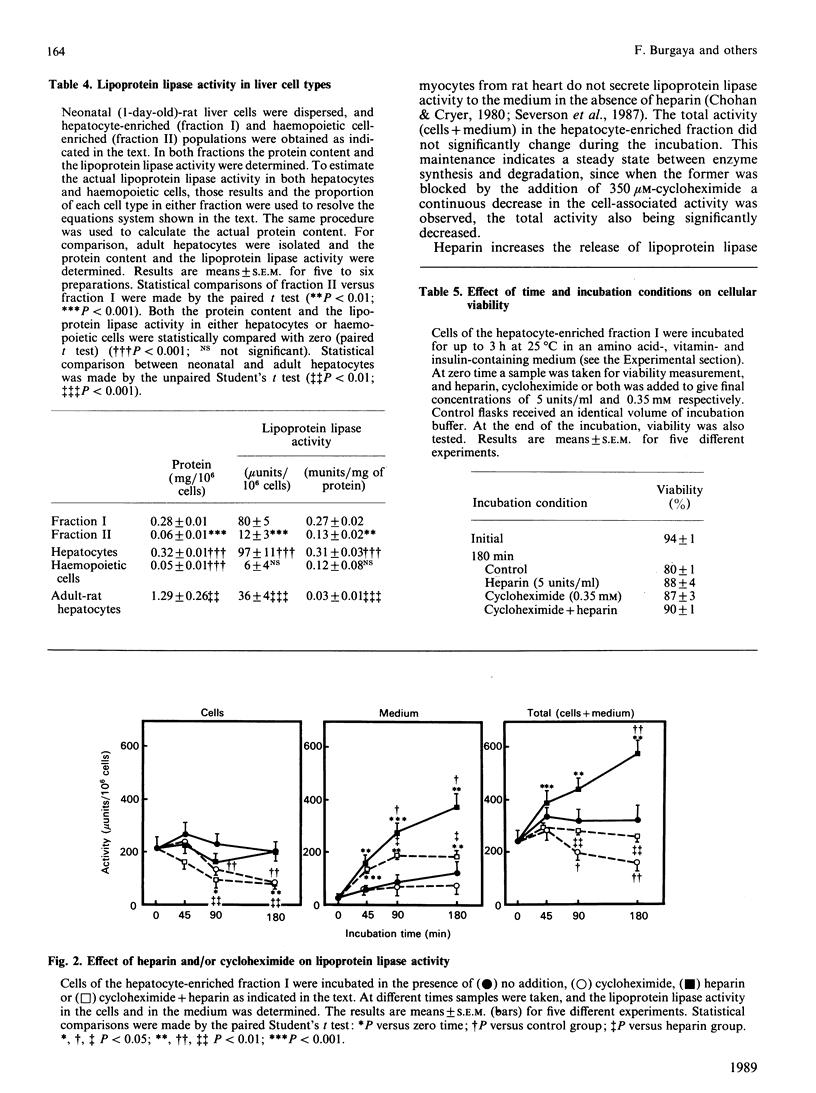
The lipoprotein lipase activity in the liver of neonatal (1 day old) rats was about 3 times that in the liver of adult rats. Perfusion of the neonatal liver with collagenase decreased the tissue-associated activity by 77%. When neonatal-rat liver cells were dispersed, hepatocyte-enriched (fraction I) and haemopoietic-cell-enriched (fraction II) populations were obtained. The lipoprotein lipase activity in fraction I was 7 times that in fraction II. On the basis of those activities and the proportion of both cell types in either fraction, it was estimated that hepatocytes contained most, if not all, the lipoprotein lipase activity detected in collagenase-perfused neonatal-rat livers. From those calculations it was also concluded that haemopoietic cells did not contain lipoprotein lipase activity. When the hepatocyte-enriched cell population was incubated at 25 degrees C for up to 3 h, a slow but progressive release of enzyme activity to the incubation medium was found. However, the total activity (cells + medium) did not significantly change through the incubation period. Cycloheximide produced a time-dependent decrease in the cell-associated activity. Heparin increased the amount of lipoprotein lipase activity released to the medium. Because the cell-associated activity was unchanged, heparin also produced a time-dependent increase in the total activity. In those cells incubated with heparin, cycloheximide did not affect the initial release of lipoprotein lipase activity to the medium, but blocked further release. The cell-associated activity was also decreased by the presence of cycloheximide in those cells. It is concluded that neonatal-rat hepatocytes synthesize active lipoprotein lipase.
Full text
PDF



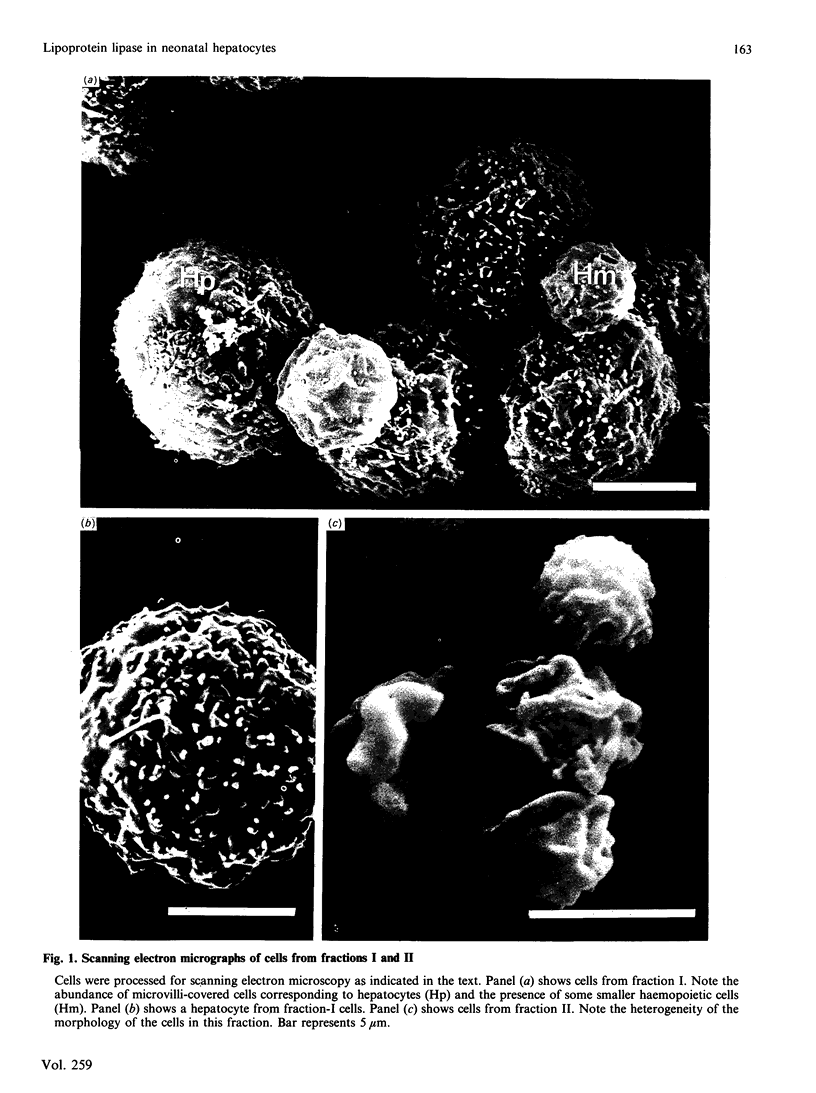


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behr S. R., Kraemer F. B. Regulation of the secretion of lipoprotein lipase by mouse macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 19;889(3):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Koh T. L. Identification of an adipose tissue-like lipoprotein lipase in perfusates of chicken liver. J Lipid Res. 1977 Nov;18(6):768–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Marita R. A. Dibutyryl cyclic AMP decreases the rate of lipoprotein lipase synthesis in cultured adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 5;879(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blázquez E., Perez Castillo A., de Diego J. G. Characterization of glucagon receptors in liver membranes and isolated hepatocytes during rat ontogenic development. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Feb;49(2-3):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek-Shaul T., Friedman G., Knobler H., Stein O., Etienne J., Stein Y. Importance of the different steps of glycosylation for the activity and secretion of lipoprotein lipase in rat preadipocytes studied with monensin and tunicamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 14;837(2):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Stein O., Stein Y. Lipoprotein lipase of cultured mesenchymal rat heart cells. I. Synthesis, secretion and releasability by heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 30;528(3):456–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Stein O., Stein Y. Pre- and post-natal development of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic triglyceride hydrolase activity in rat tissues. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Apr;26(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chohan P., Cryer A. Lipoprotein lipase activity of rat cardiac muscle. Changes in the enzyme activity during incubations of isolated cardiac-muscle cells in vitro. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):873–879. doi: 10.1042/bj1860873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A. Tissue lipoprotein lipase activity and its action in lipoprotein metabolism. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(5):525–541. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupp M., Bensadoun A., Melford K. Heparin decreases the degradation rate of lipoprotein lipase in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6383–6388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devirgiliis L. C., Dini L., Di Pierro A., Leoni S., Spagnuolo S., Stefanini S. An improved non-perfusion method for the isolation and purification of rat foetal and neonatal hepatocytes. Cell Mol Biol Incl Cyto Enzymol. 1981;27(6):687–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Shaw W., Greten H., Brown W. V. Purification from human plasma of a heparin-released lipase with activity against triglyceride and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6756–6761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emura I., Sekiya M., Ohnishi Y. Four types of presumptive hemopoietic stem cells in the human fetal liver. Arch Histol Jpn. 1983 Dec;46(5):645–662. doi: 10.1679/aohc.46.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck S., Semb H., Tavernier J., Bjursell G., Olivecrona T. Tissue-specific regulation of guinea pig lipoprotein lipase; effects of nutritional state and of tumor necrosis factor on mRNA levels in adipose tissue, heart and liver. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90484-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman G., Chajek-Shaul T., Stein O., Noe L., Etienne J., Stein Y. Beta-adrenergic stimulation enhances translocation, processing and synthesis of lipoprotein lipase in rat heart cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 11;877(1):112–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinberg D. R., Ramírez I., Vilaró S., Reina M., Llobera M., Herrera E. Starvation enhances lipoprotein lipase activity in the liver of the newborn rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 8;833(2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamdar S. C., Moon M., Bow S., Fallon H. J. Hepatic lipid metabolism. Age-related changes in triglyceride metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1978 Aug;19(6):763–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen G. L., Baly D. L., Brannon P. M., Bensadoun A. Synthesis and secretion of lipolytic enzymes by cultured chicken hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11141–11148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson L., Hansson G. K., Bondjers G., Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Immunohistochemical localization of lipoprotein lipase in human adipose tissue. Atherosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;51(2-3):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(84)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner T. G., Svenson K. L., Lusis A. J., Schotz M. C. The sequence of cDNA encoding lipoprotein lipase. A member of a lipase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8463–8466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler H., Chajek-Shaul T., Stein O., Etienne J., Stein Y. Modulation of lipoprotein lipase in the intact rat by cholera toxin--an irreversible agonist of cyclic AMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 12;795(2):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitersdorf E., Stein O., Stein Y. Synthesis and secretion of triacylglycerol lipase by cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 6;794(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llobera M., Montes A., Herrera E. Lipoprotein lipase activity in liver of the rat fetus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):272–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90613-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuno H., Tsujita T., Nakanishi H., Yoshida A., Fukunishi R., Okuda H. Lipoprotein lipase-like activity in the liver of mice with Sarcoma 180. J Lipid Res. 1984 May;25(5):419–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Lipolytic enzymes and plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:667–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Chernick S. S., Scow R. O. Effect of combined lipase deficiency (cld/cld) on hepatic and lipoprotein lipase activities in liver and plasma of newborn mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 15;876(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Chernick S. S., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Paterniti J. R., Jr, Brown W. V., Scow R. O. Combined lipase deficiency (cld/cld) in mice. Demonstration that an inactive form of lipoprotein lipase is synthesized. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2552–2557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterniti J. R., Jr, Brown W. V., Ginsberg H. N., Artzt K. Combined lipase deficiency (cld): a lethal mutation on chromosome 17 of the mouse. Science. 1983 Jul 8;221(4606):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.6857276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen M. E., Cohen M., Schotz M. C. Immunocytochemical localization of the functional fraction of lipoprotein lipase in the perfused heart. J Lipid Res. 1983 May;24(5):512–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Distribution of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase between plasma and tissues: effect of hypertriglyceridemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 4;837(3):262–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajaram O. V., Clark M. G., Barter P. J. Differences in the metabolism of very-low-density lipoproteins by isolated beating-heart cells and the isolated perfused rat heart. Evidence for collagenase-released extracellular lipoprotein lipase. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):431–438. doi: 10.1042/bj1860431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez I., Kryski A. J., Ben-Zeev O., Schotz M. C., Severson D. L. Characterization of triacylglycerol hydrolase activities in isolated myocardial cells from rat heart. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):229–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2320229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez I., Llobera M., Herrera E. Circulating triacylglycerols, lipoproteins, and tissue lipoprotein lipase activities in rat mothers and offspring during the perinatal period: effect of postmaturity. Metabolism. 1983 Apr;32(4):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez I., Severson D. L. Effect of diabetes on acid and neutral triacylglycerol lipase and on lipoprotein lipase activities in isolated myocardial cells from rat heart. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):233–238. doi: 10.1042/bj2380233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze H. P., Hühn W., Franke H., Dargel R. A simple method for the isolation of highly enriched hormone-sensitive parenchymal liver cells from fetal rats. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1984;43(11):1227–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb H., Olivecrona T. Mechanisms for turnover of lipoprotein lipase in guinea pig adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 4;921(1):104–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb H., Peterson J., Tavernier J., Olivecrona T. Multiple effects of tumor necrosis factor on lipoprotein lipase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8390–8394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Carroll R., Kryski A., Jr, Ramírez I. Short-term incubation of cardiac myocytes with isoprenaline has no effect on heparin-releasable or cellular lipoprotein lipase activity. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):289–292. doi: 10.1042/bj2480289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Lee M., Carroll R. Secretion of lipoprotein lipase from myocardial cells isolated from adult rat hearts. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Jan;79(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00229393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soley M., Hollenberg M. D. Epidermal growth factor (urogastrone)-stimulated gluconeogenesis in isolated mouse hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 May 15;255(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90303-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. E., Schotz M. C. Release of lipoprotein lipase activity from isolated fat cells. II. Effect of heparin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):904–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. E., Whelan C. F., Schotz M. C. Release of lipoprotein lipase from fat cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):376–381. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90391-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Ailhaud G. A continuous flow method for the study of lipoprotein lipase secretion in adipose cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 12;875(2):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Amri E. Z., Etienne J., Négrel R., Ailhaud G. Maturation and secretion of lipoprotein lipase in cultured adipose cells. I. Intracellular activation of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4424–4431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Llobera M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase uptake by the liver: localization, turnover, and metabolic role. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):G711–G722. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.5.G711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Llobera M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Synthesis of lipoprotein lipase in the liver of newborn rats and localization of the enzyme by immunofluorescence. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):549–556. doi: 10.1042/bj2490549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Ramírez I., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T., Llobera M. Lipoprotein lipase in liver. Release by heparin and immunocytochemical localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 25;959(2):106–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Reina M., Ramírez I., Llobera M. Intralipid administration induces a lipoprotein lipase-like activity in the livers of starved adult rats. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):273–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2360273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallinder L., Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Rapid removal to the liver of intravenously injected lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 26;575(1):166–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallinder L., Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Hepatic and extrahepatic uptake of intravenously injected lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 4;795(3):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K. Isolation of hepatocytes from newborn rats. Arch Toxicol. 1980 Mar;44(1-3):99–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00303186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]