Abstract
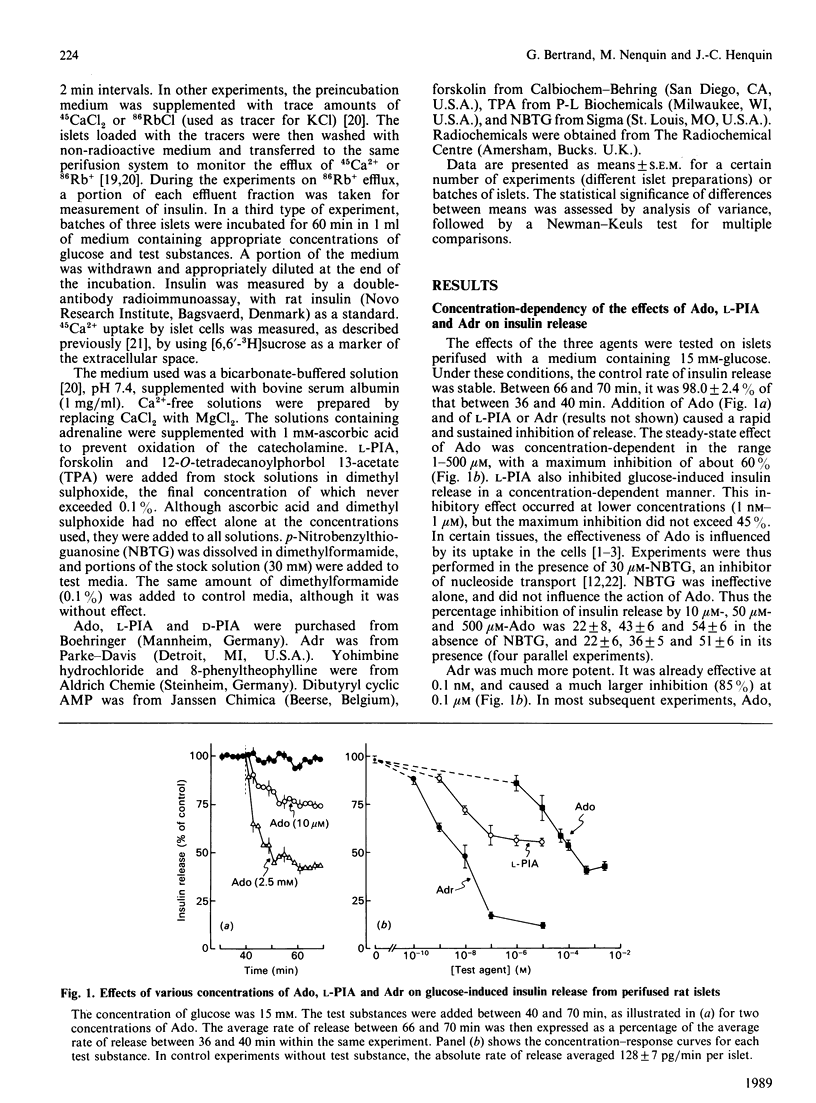
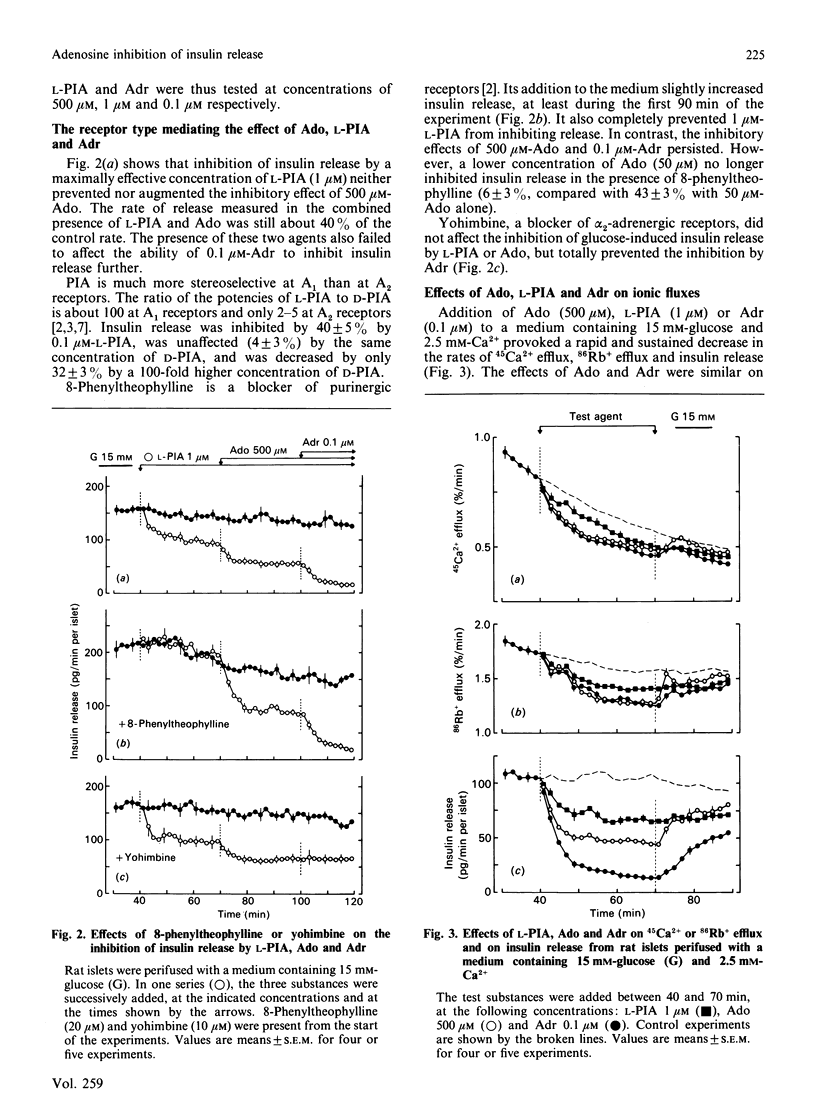
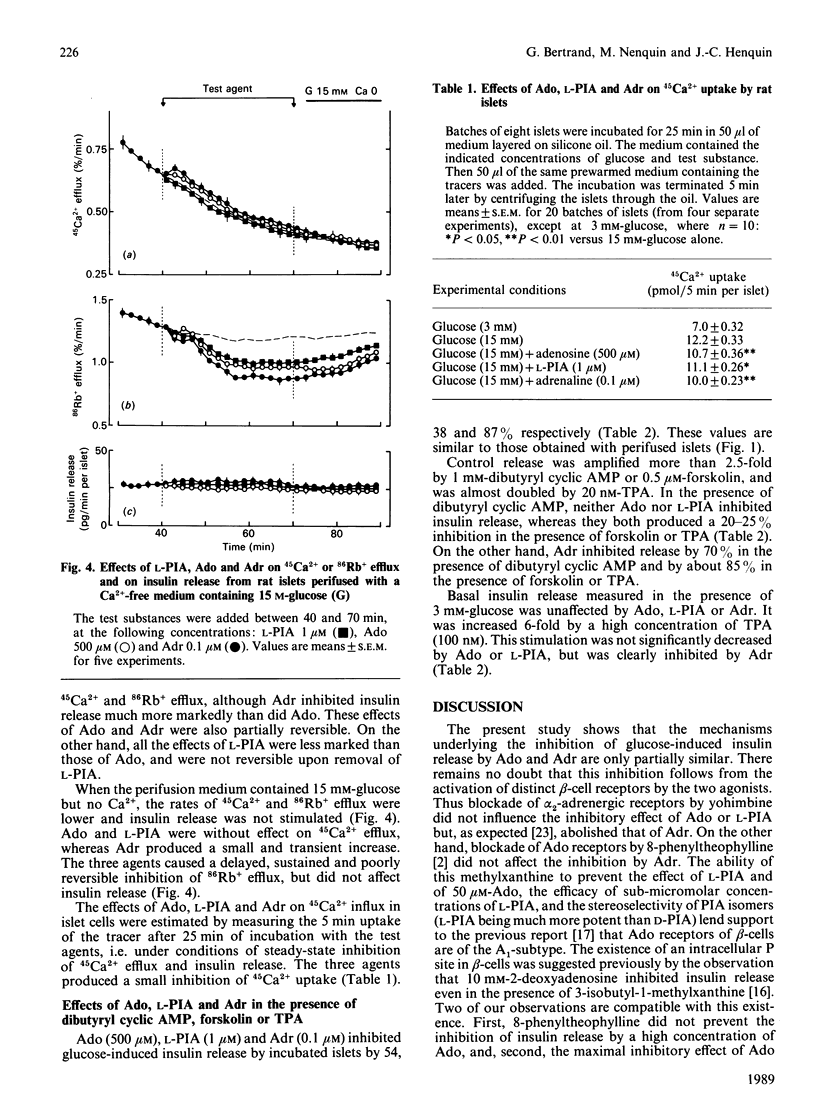
Rat islets were used to compare the mechanisms whereby adenosine and adrenaline inhibit insulin release. Adenosine (1 microM-2.5 mM) and its analogue N6(-)-phenylisopropyladenosine (L-PIA) (1 nM-10 microM) caused a concentration-dependent but incomplete (45-60%) inhibition of glucose-stimulated release. L-PIA was more potent than D-PIA [the N6(+) analogue], but much less than adrenaline, which caused nearly complete inhibition (85% at 0.1 microM). 8-Phenyltheophylline prevented the inhibitory effect of L-PIA and 50 microM-adenosine, but not that of 500 microM-adenosine or of adrenaline. In contrast, yohimbine selectively prevented the inhibition by adrenaline. Adenosine and L-PIA thus appear to exert their effects by activating membrane A1 receptors, whereas adrenaline acts on alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Adenosine, L-PIA and adrenaline slightly inhibited 45Ca2+ efflux, 86Rb+ efflux and 45Ca2+ influx in glucose-stimulated islets. The inhibition of insulin release by adenosine or L-PIA was totally prevented by dibutyryl cyclic AMP, but was only attenuated when adenylate cyclase was activated by forskolin or when protein kinase C was stimulated by a phorbol ester. Adrenaline, on the other hand, inhibited release under these conditions. It is concluded that inhibition of adenylate cyclase, rather than direct changes in membrane K+ and Ca2+ permeabilities, underlies the inhibition of insulin release induced by activation of A1-receptors. The more complete inhibition mediated by alpha 2-adrenergic receptors appears to result from a second mechanism not triggered by adenosine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson A. Nucleoside-stimulated insulin production by isolated mouse pancreatic islets. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:14–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belardinelli L., Isenberg G. Isolated atrial myocytes: adenosine and acetylcholine increase potassium conductance. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):H734–H737. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.244.5.H734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozem M., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. The ionic, electrical, and secretory effects of protein kinase C activation in mouse pancreatic B-cells: studies with a phorbol ester. Endocrinology. 1987 Sep;121(3):1025–1033. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-3-1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Taylor K. W. Effects of adenosine, 2-deoxyadenosine and N6-phenylisopropyladenosine on rat islet function and metabolism. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 15;204(3):689–696. doi: 10.1042/bj2040689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapal J., Loubatières-Mariani M. M., Petit P., Roye M. Evidence for an A2-subtype adenosine receptor on pancreatic glucagon secreting cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):565–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Rizza R. A., Gerich J. E., Cryer P. E. Regulation of glucose metabolism by sympathochromaffin catecholamines. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1988 Feb;4(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Forda S. R., Scott R. H. Calcium-dependent currents in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurones are inhibited by an adenosine analogue. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:47–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. M., Jackson T. B. Specificity of nucleotide-induced insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1974 Feb;94(2):388–394. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-2-388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Dunwiddie T. V. How does adenosine inhibit transmitter release? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Apr;9(4):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Garcia M. C., Bozem M., Hermans M. P., Nenquin M. Muscarinic control of pancreatic B cell function involves sodium-dependent depolarization and calcium influx. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2134–2142. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Lambert A. E. Cobalt inhibition of insulin secretion and calcium uptake by isolated rat islets. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1669–1677. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. The ionic, electrical, and secretory effects of endogenous cyclic adenosine monophosphate in mouse pancreatic B cells: studies with forskolin. Endocrinology. 1984 Sep;115(3):1125–1134. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-3-1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Opposite effects of intracellular Ca2+ and glucose on K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):66–68. doi: 10.1038/280066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillaire-Buys D., Bertrand G., Gross R., Loubatières-Mariani M. M. Evidence for an inhibitory A1 subtype adenosine receptor on pancreatic insulin-secreting cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 7;136(1):109–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90786-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Dall'Aglio E., Hollenbeck C., Chang H., Reaven G. M. Suppression of free fatty acids and triglycerides in normal and hypertriglyceridemic rats by the adenosine receptor agonist phenylisopropyladenosine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):715–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Rankin A. C. Ionic basis of the hyperpolarizing action of adenyl compounds on sinus venosus of the tortoise heart. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:111–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail N. A., El Denshary E. E., Montague W. Adenosine and the regulation of insulin secretion by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1977 May 15;164(2):409–413. doi: 10.1042/bj1640409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail N. A., El-Denshary E. S., Idahl L. A., Lindström P., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on insulin secretion, calcium uptake, and rubidium efflux in mouse pancreatic islets. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jun;118(2):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain K., Logothetopoulos J. Metabolic signals produced by purine ribonucleosides stimulate proinsulin biosynthesis and insulin secretion. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):461–467. doi: 10.1042/bj1700461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochem G., Nawrath H. Adenosine activates a potassium conductance in guinea-pig atrial heart muscle. Experientia. 1983 Dec 15;39(12):1347–1349. doi: 10.1007/BF01990096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Cooper D. M., Wolff J. Subclasses of external adenosine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2551–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Wolff J. Two distinct adenosine-sensitive sites on adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5482–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. J., Stone T. W. Adenosine reduces agonist-induced production of inositol phosphates in rat aorta. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;39(12):1010–1014. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1987.tb03149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatieres-Mariani M. M., Chapal J., Lignon F., Valette G. Structural specificity of nucleotides for insulin secretory action from the isolated perfused rat pancreas. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov 16;59(3-4):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. L., Skerritt J. H., Werz M. A. Adenosine agonists reduce voltage-dependent calcium conductance of mouse sensory neurones in cell culture. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:75–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G., Malaisse-Lagae F. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. I. Interaction of epinephrine and alkaline earth cations. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Dec;76(6):895–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Carpinelli A. R., Poloczek P., Winand J., Castagna M. Insulinotropic effect of the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in rat pancreatic islets. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3827–3831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Montague W. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by noradrenaline in rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):571–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2260571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Inhibition of dibutyryl cyclic AMP-induced insulin release by alpha-2 adrenergic stimulation. Life Sci. 1983 Jan 17;32(3):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. R., Oliver J. M. Nucleoside transport. II. Inhibition by p-nitrobenzylthioguanosine and related compounds. Can J Biochem. 1971 Feb;49(2):271–274. doi: 10.1139/o71-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Sebastião A. M. Adenosine receptors and calcium: basis for proposing a third (A3) adenosine receptor. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;26(3):179–209. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz W., Raberger G., Kraupp O. Evidence for glucagon-releasing activity of vasoactive adenosine analogues in the conscious dog. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;304(3):249–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00507965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suárez J., Valles V. E., Chagoya de Sánchez V. Effect of adenosine on the serum levels of glucose, insulin and glucagon in vivo. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(87)90127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamagawa T., Henquin J. C. Epinephrine modifications of insulin release and of 86Rb+ or 45Ca2+ fluxes in rat islets. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):E245–E252. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.3.E245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thams P., Capito K., Hedeskov C. J. Endogenous substrate proteins for Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent, Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):247–253. doi: 10.1042/bj2210247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Jackson M. B. Adenosine-activated potassium conductance in cultured striatal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4857–4861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M. A., Steffes M. W., Estensen R. D. Phorbol myristate acetate: effect of a tumor promoter on insulin release from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1978 Mar;102(3):706–711. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-3-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Knowlton S. D., Martin D. B. Nucleotide and nucleoside stimulation of glucagon secretion. Endocrinology. 1975 Oct;97(4):932–936. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-4-932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Andersson A., Brolin S., Hellerström C. Effects of glucose, leucine and adenosine on insulin release, 45Ca2+ net uptake, NADH/NAD ratios and oxygen consumption of islets isolated from fed and starved mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983 Apr;30(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenkeller D. E., Sharp G. W. Effects of forskolin on insulin release and cyclic AMP content in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):2311–2313. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-2311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. Purine receptors in mammalian tissues: pharmacology and functional significance. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:315–345. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Somatostatin- and epinephrine-induced modifications of 45Ca++ fluxes and insulin release in rat pancreatic islets maintained in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1165–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


