Abstract
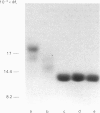
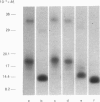
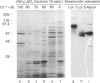
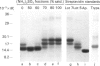
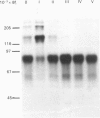
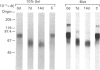
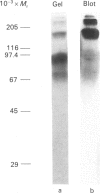
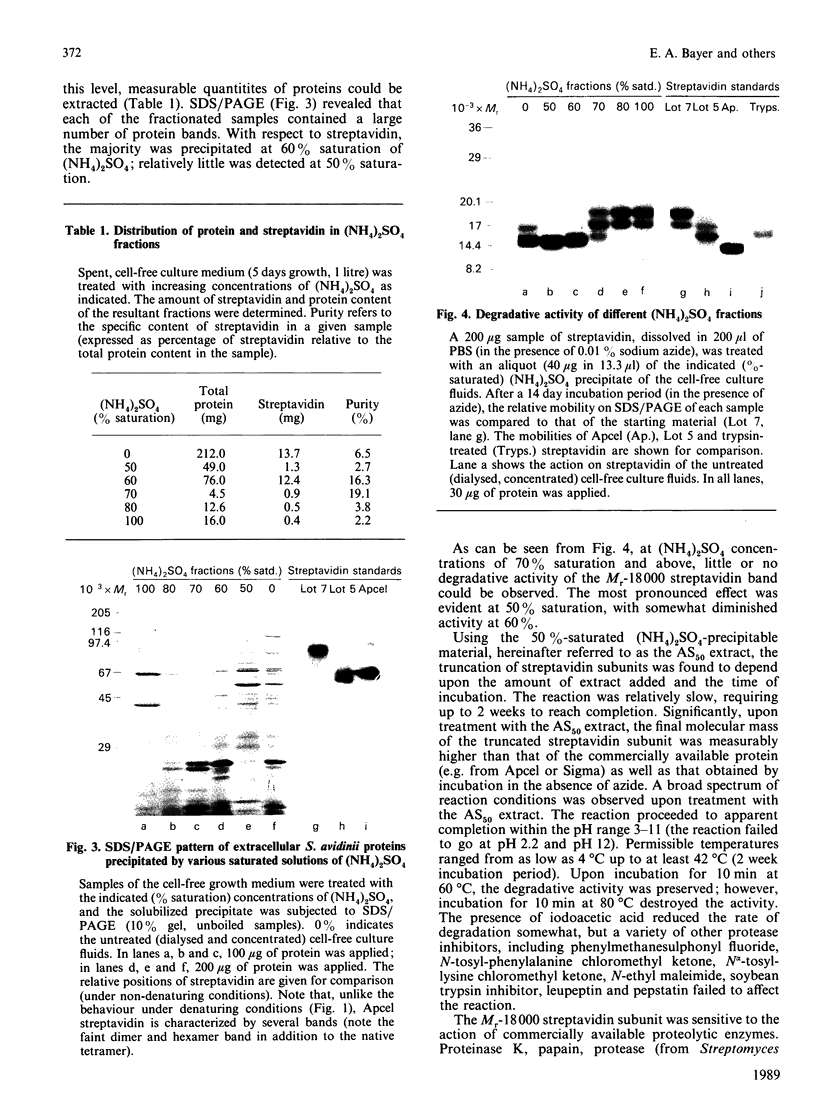
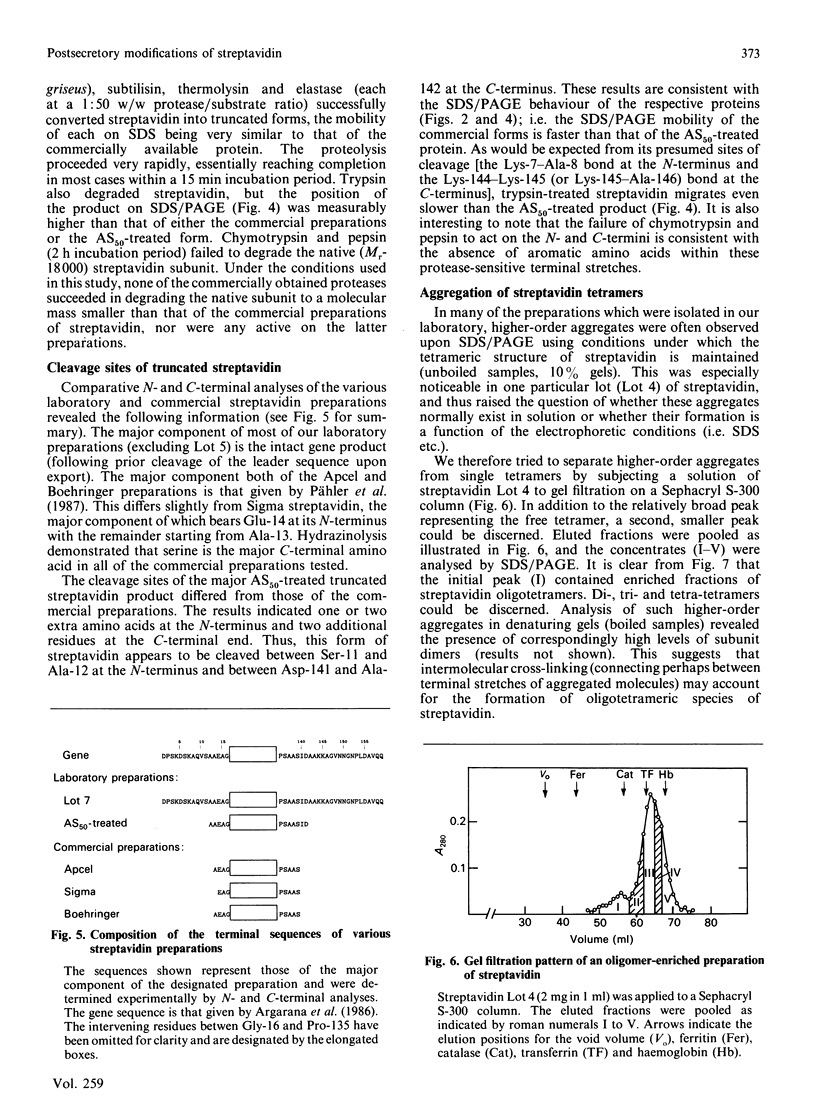
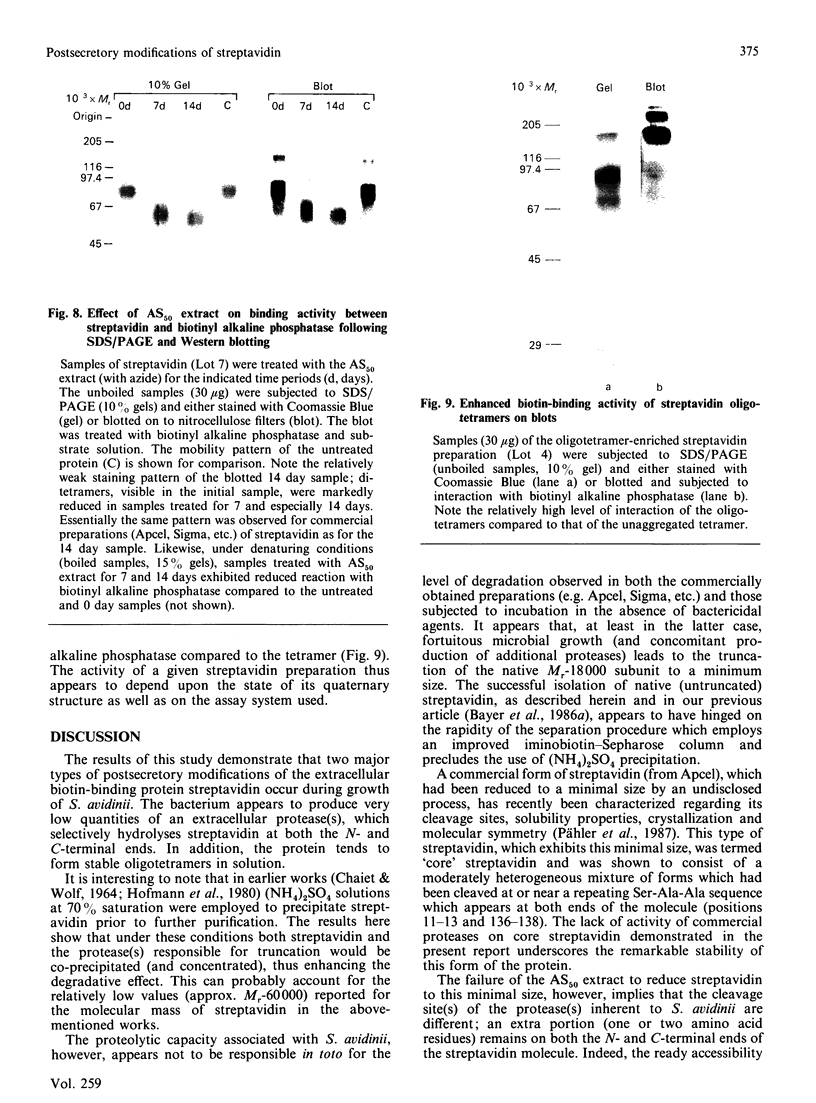
Streptavidin, an extracellular biotin-binding protein from Streptomyces avidinii, exhibits a multiplicity in its electrophoretic mobility pattern which depends both upon the conditions for growth of the bacterium and upon the protocol used in the purification of the protein. The observed structural heterogeneity appears to reflect the action of two types of postsecretory molecular events: proteolytic digestion of the intact Mr-18,000 subunit to a minimal molecular size (approx. Mr 14,000), and aggregation of the native tetramer into higher-order oligomeric forms. The extent of subunit degradation and/or tetrameric aggregation affects the capacity of a given streptavidin preparation to interact with biotin-conjugated proteins in different assay systems.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argaraña C. E., Kuntz I. D., Birken S., Axel R., Cantor C. R. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the streptavidin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1871–1882. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold E., Luo M., Vriend G., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C., Parks G. D., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Implications of the picornavirus capsid structure for polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Ben-Hur H., Gitlin G., Wilchek M. An improved method for the single-step purification of streptavidin. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1986 Sep;13(2):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(86)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Ben-Hur H., Wilchek M. A sensitive enzyme assay for biotin, avidin, and streptavidin. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The use of the avidin-biotin complex as a tool in molecular biology. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:1–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAIET L., WOLF F. J. THE PROPERTIES OF STREPTAVIDIN, A BIOTIN-BINDING PROTEIN PRODUCED BY STREPTOMYCETES. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:1–5. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Studies on the biotin-binding site of avidin. Lysine residues involved in the active site. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):923–926. doi: 10.1042/bj2420923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Studies on the biotin-binding site of avidin. Tryptophan residues involved in the active site. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):291–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2500291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Studies on the biotin-binding site of streptavidin. Tryptophan residues involved in the active site. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):279–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2560279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R. Carboxypeptidase Y in sequence determination of peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:84–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller Y., Gershoni J. M., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Biotin binding to avidin. Oligosaccharide side chain not required for ligand association. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):167–171. doi: 10.1042/bj2480167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K., Wood S. W., Brinton C. C., Montibeller J. A., Finn F. M. Iminobiotin affinity columns and their application to retrieval of streptavidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4666–4668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pähler A., Hendrickson W. A., Kolks M. A., Argaraña C. E., Cantor C. R. Characterization and crystallization of core streptavidin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13933–13937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAPLEY E. O., MATA J. M., MILLER I. M., DEMNY T. C., WOODRUFF H. B. ANTIBIOTIC MSD-235. I. PRODUCTION BY STREPTOMYCES AVIDINII AND STREPTOMYCES LAVENDULAE. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1963;161:20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Bayer E. A. The avidin-biotin complex in bioanalytical applications. Anal Biochem. 1988 May 15;171(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]