Abstract
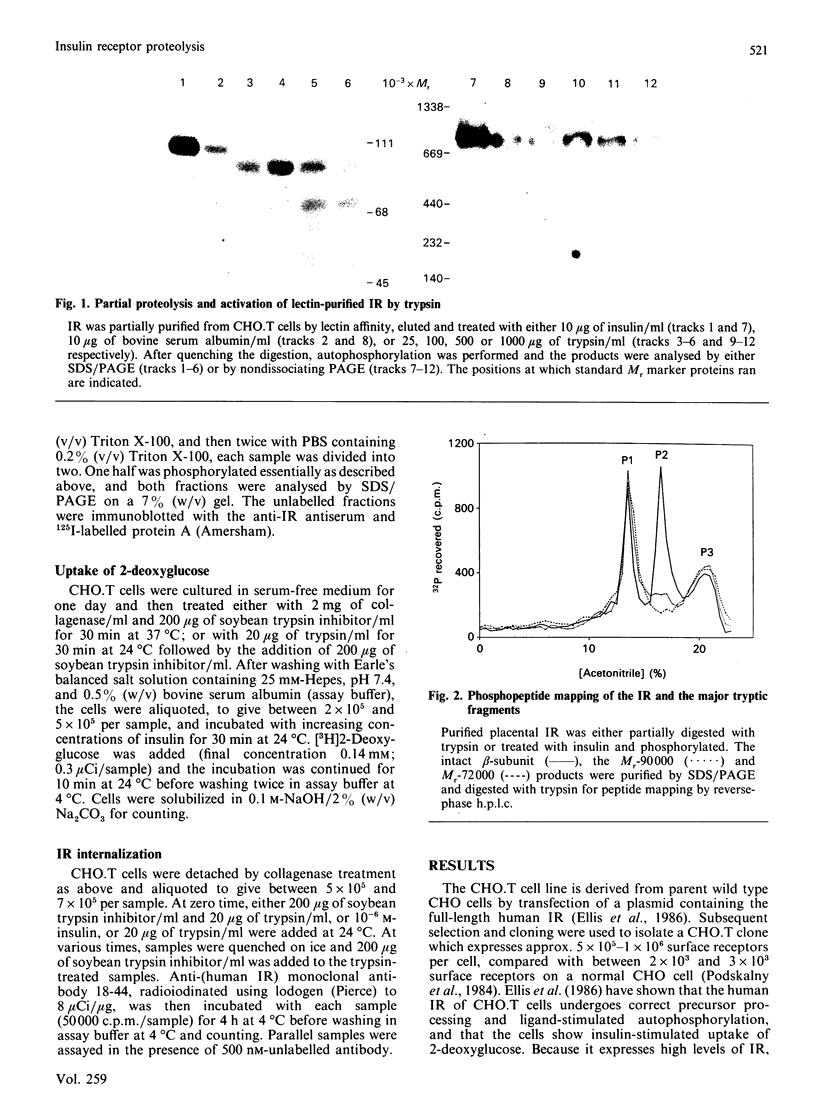
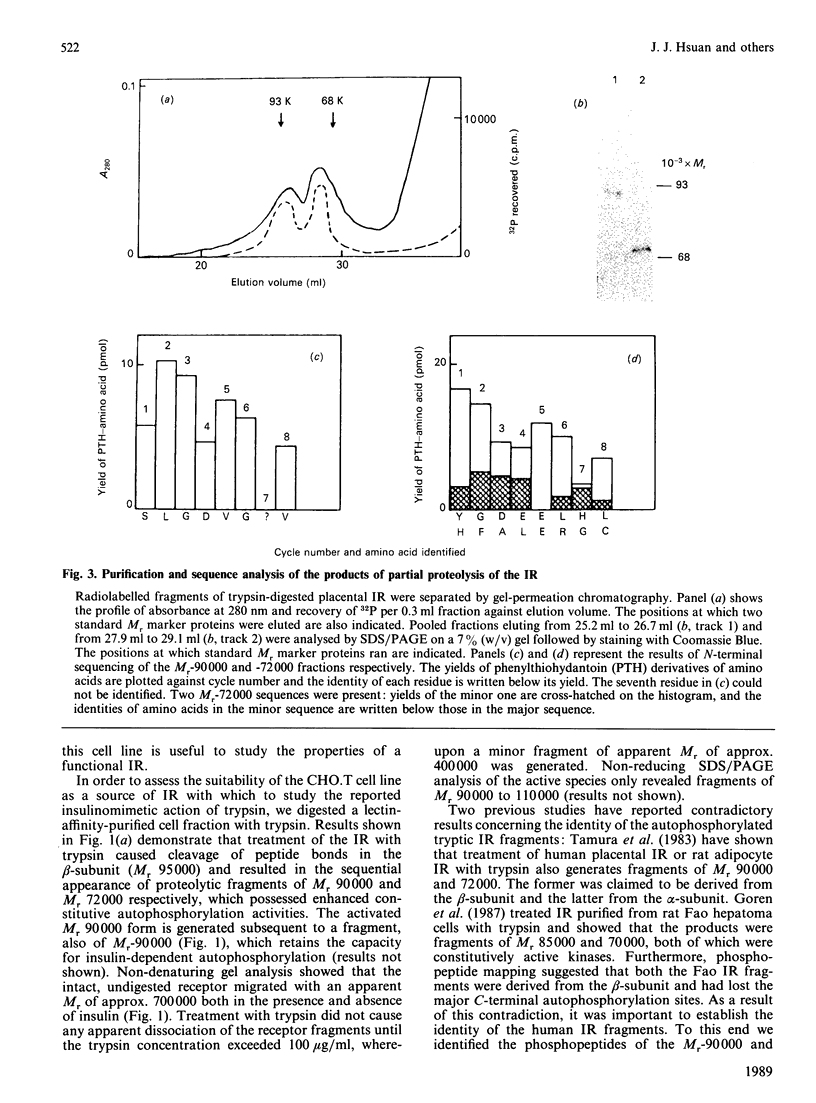
Structural modification induced by partial digestion with trypsin has been shown to stimulate the tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor both in solution and in intact cells [Tamura, Fujita-Yamaguchi & Larner (1983) J. Biol. Chem. 258, 14749-14752; Goren, White & Kahn (1987) Biochemistry 26, 2374-2382; Leef & Larner (1987) J. Biol. Chem. 262, 14837-14842]. Furthermore, experiments involving deletion of sequences encoding the extracellular domain of the insulin receptor suggest that it may function as a protooncogene in fibroblasts [Wang et al., (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 5725-5729]. To further understand the structural requirements that generate this activity, the major activated fragments generated in solution following trypsin digestion have been characterized here, one of which is shown to have a similar amino acid sequence to a transforming protein. Furthermore, treatment with trypsin of intact Chinese hamster ovary cells that overexpress the human insulin receptor stimulates both autophosphorylation of the receptor and 2-deoxyglucose uptake into the cells, but does not enhance receptor internalization. Unlike digestion in solution, no proteolysis or loss of activity of the activated insulin receptor beta-subunit could be detected using intact cells, even at high trypsin concentrations, despite the existence of extracellular sites that are readily cleaved by trypsin in the solubilized receptor. These studies provide further detail of a mechanism used during trypsinization of cells in culture which mimics activation of the insulin receptor and contributes to stimulation of growth.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berhanu P., Olefsky J. M., Tsai P., Thamm P., Saunders D., Brandenburg D. Internalization and molecular processing of insulin receptors in isolated rat adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4069–4073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Scott W., Waugh S. M., DiBella E., Pilch P. F. The insulin receptor. Structural basis for high affinity ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8395–8401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Cunningham D. D. Initiation of check cell division by trypsin action at the cell surface. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):602–606. doi: 10.1038/268602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chvatchko Y., Van Obberghen E., Fehlmann M. Internalization and recycling of insulin receptors in hepatoma cells. Absence of regulation by receptor occupancy. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):111–117. doi: 10.1042/bj2220111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Fava R. A. Internalization of functional epidermal growth factor:receptor/kinase complexes in A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12351–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousin J. L., Samson M., Pilch P. F., Fehlmann M. Internalization of insulin receptors and HLA antigens in human hepatoma cells. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):403–410. doi: 10.1042/bj2420403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Yang-Feng T. L., Liao Y. C., Chen E., Gray A., McGrath J., Seeburg P. H., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J., Francke U. Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1132–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2999974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens P. M., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Shalloway D. Restriction of the in vitro and in vivo tyrosine protein kinase activities of pp60c-src relative to pp60v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2753–2763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Lopez S., Burlet H. Ligand-induced translocation of insulin receptors in intact rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10852–10860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Morgan D. O., Clauser E., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. A membrane-anchored cytoplasmic domain of the human insulin receptor mediates a constitutively elevated insulin-independent uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;1(1):15–24. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Carpentier J. L., Le Cam A., Thamm P., Saunders D., Brandenburg D., Orci L., Freychet P. Biochemical and morphological evidence that the insulin receptor is internalized with insulin in hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):82–87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Protein phosphorylation at tyrosine is induced by the v-erbB gene product in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren H. J., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Separate domains of the insulin receptor contain sites of autophosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2374–2382. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Downward D. J., Marsden J. J., Waterfield M. D. A radioimmunoassay for human epidermal growth factor receptor. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;141(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90454-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari J., Roth R. A. Defective internalization of insulin and its receptor in cells expressing mutated insulin receptors lacking kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15341–15344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Itin A. Purification of the insulin receptor from human placenta by chromatography on immobilized wheat germ lectin and receptor antibody. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12066–12072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Low level of cellular protein phosphorylation by nontransforming overproduced p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1058–1066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Koyasu S., Nishida E., Tobe K., Izumi T., Takaku F., Sakai H., Yahara I., Kasuga M. Tyrosine phosphorylation of common and specific sets of cellular proteins rapidly induced by insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and epidermal growth factor in an intact cell. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7342–7350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Neither arginine nor histidine can carry out the function of lysine-295 in the ATP-binding site of p60src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):751–757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. N., Savoie S., Bergeron J. J., Posner B. I. Characterization of rat liver endosomal fractions. In vivo activation of insulin-stimulable receptor kinase in these structures. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8462–8472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi K., Schwartz C., Creacy S., Larner J. Independent control of selected insulin-sensitive cell membrane and intracellular functions-the linkage of cell membrane and intracellular events controlled by insulin. III. The influence of trypsin on cell membrane hexose transport and on glycogen synthase and mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase activation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Jul 7;37(2):125–130. doi: 10.1007/BF02354936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson V. P., Ronnett G. V., Lane M. D. Rapid, reversible internalization of cell surface insulin receptors. Correlation with insulin-induced down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12139–12142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leef J. W., Larner J. Insulin-mimetic effect of trypsin on the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in intact adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14837–14842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Tryggvason K., Garbisa S., Hart I., Foltz C. M., Shafie S. Metastatic potential correlates with enzymatic degradation of basement membrane collagen. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):67–68. doi: 10.1038/284067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Ellis L., Rutter W. J., Roth R. A. Antibody-induced down-regulation of a mutated insulin receptor lacking an intact cytoplasmic domain. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 2;26(11):2959–2963. doi: 10.1021/bi00385a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Axelrod J. D., Colello J., Czech M. P. Unimpaired signal transduction by the adipocyte insulin receptor following its partial proteolytic fragmentation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1570–1575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podskalny J., McElduff A., Gorden P. Insulin receptors on Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells: altered insulin binding to glycosylation mutants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):70–75. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80335-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Rubin H. Release from density dependent growth inhibition by proteolytic enzymes. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):843–845. doi: 10.1038/227843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shia M. A., Rubin J. B., Pilch P. F. The insulin receptor protein kinase. Physicochemical requirements for activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14450–14455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shii K., Roth R. A. Inhibition of insulin degradation by hepatoma cells after microinjection of monoclonal antibodies to a specific cytosolic protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4147–4151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Tryptic activation of the insulin receptor. Proteolytic truncation of the alpha-subunit releases the beta-subunit from inhibitory control. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4852–4860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. A mutation at the ATP-binding site of pp60v-src abolishes kinase activity, transformation, and tumorigenicity. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1772–1779. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K., Baron M. D., Heward J. M., Luzio J. P., Bellatin J., Lennox E. S. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with multiple epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):199–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2350199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Morrison B. D., Wilden P. A., Pessin J. E. Insulin-dependent intermolecular subunit communication between isolated alpha beta heterodimeric insulin receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16730–16738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Wilden P. A., Pessin J. E. Dithiothreitol activation of the insulin receptor/kinase does not involve subunit dissociation of the native alpha 2 beta 2 insulin receptor subunit complex. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7068–7074. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Larner J. Insulin-like effect of trypsin on the phosphorylation of rat adipocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14749–14752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Pierce M. W., Frackelton A. R., Nemenoff R. A., Avruch J. Identification of insulin receptor tyrosine residues autophosphorylated in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10212–10219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Lin B., Jong S. M., Dixon D., Ellis L., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Activation of transforming potential of the human insulin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5725–5729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nishida T., Miyajima N., Kawai S., Ooi T., Toyoshima K. The erbB gene of avian erythroblastosis virus is a member of the src gene family. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]