Abstract
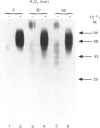
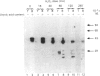
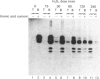
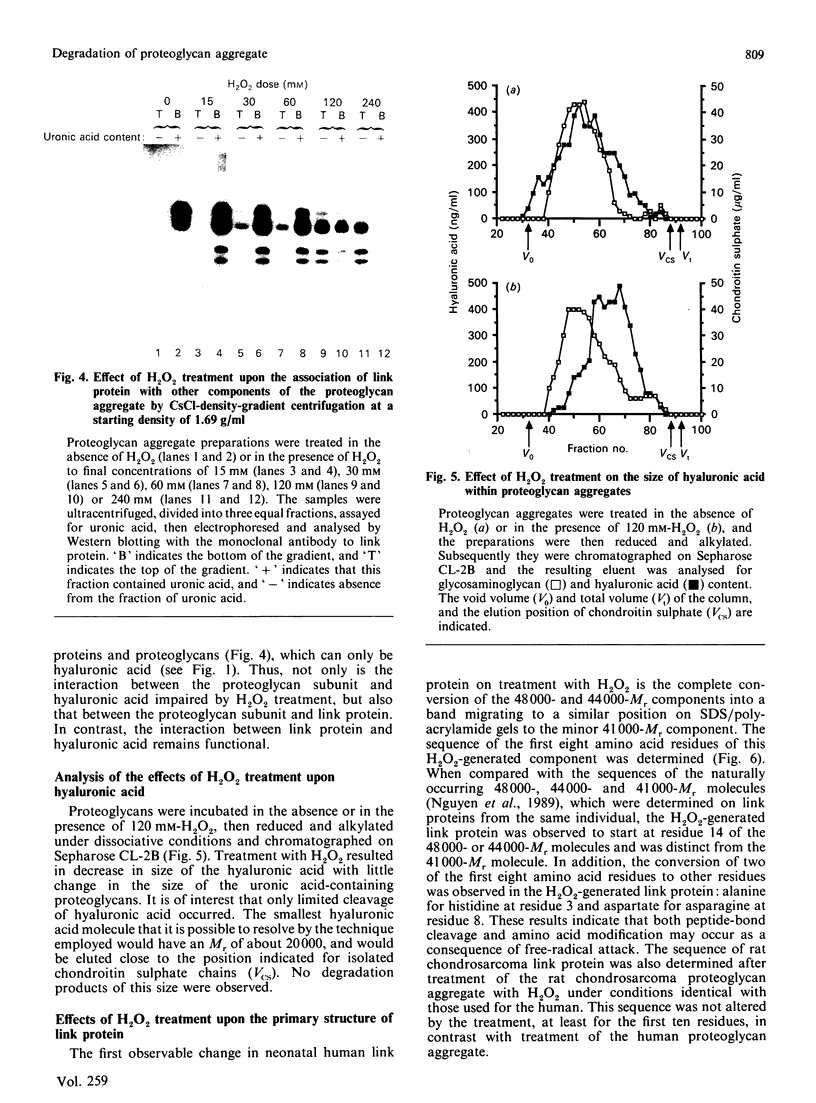
We have previously shown that treatment of neonatal human articular-cartilage proteoglycan aggregates with H2O2 results in loss of the ability of the proteoglycan subunits to interact with hyaluronic acid and in fragmentation of the link proteins [Roberts, Mort & Roughley (1987) Biochem. J. 247, 349-357]. We now show the following. (1) Hyaluronic acid in proteoglycan aggregates is also fragmented by treatment with H2O2. (2) Although H2O2 treatment results in loss of the ability of the proteoglycan subunits to interact with hyaluronic acid, the loss of this function is not attributable to substantial cleavage of the hyaluronic acid-binding region of the proteoglycan subunits. (3) In contrast, link proteins retain the ability to bind to hyaluronic acid following treatment with H2O2. (4) The interaction between the proteoglycan subunit and link protein is, however, abolished. (5) N-Terminal sequence analysis of the first eight residues of the major product of link protein resulting from H2O2 treatment revealed that cleavage occurred between residues 13 and 14, so that the new N-terminal amino acid is alanine. (6) In addition, a histidine (residue 16) is converted into alanine and an asparagine (residue 21) is converted into aspartate by the action of H2O2. (7) Rat link protein showed no cleavage or modifications in similar positions under identical conditions. (8) This species variation may be related to the different availability of histidine residues required for the co-ordination of the transition metal ion involved in hydroxyl-radical generation from H2O2. (9) Changes in function of these structural macromolecules as a result of the action of H2O2 may be consequences of both fragmentation and chemical modification.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartold P. M., Wiebkin O. W., Thonard J. C. The effect of oxygen-derived free radicals on gingival proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Jul;19(4):390–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb01012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates E. J., Harper G. S., Lowther D. A., Preston B. N. Effect of oxygen-derived reactive species on cartilage proteoglycan-hyaluronate aggregates. Biochem Int. 1984 May;8(5):629–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bors W., Michel C., Saran M. On the nature of biochemically generated hydroxyl radicals. Studies using the bleaching of p-nitrosodimethylaniline as a direct assay method. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):621–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. R., Christner J. E., Lee Y., Lentz M. Monoclonal antibodies as probes for determining the microheterogeneity of the link proteins of cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11348–11356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Christner J. E., Baker J. R., Couchman J. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against connective tissue proteoglycans. Fed Proc. 1985 Feb;44(2):386–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Sies H., Boveris A. Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):527–605. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung M. H., Kesner L., Chan P. C. Degradation of articular cartilage by copper and hydrogen peroxide. Agents Actions. 1984 Oct;15(3-4):328–335. doi: 10.1007/BF01972367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper B., Creeth J. M., Donald A. S. Studies of the limited degradation of mucus glycoproteins. The mechanism of the peroxide reaction. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):615–626. doi: 10.1042/bj2280615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Cooper B., Donald A. S., Clamp J. R. Studies of the limited degradation of mucus glycoproteins. The effect of dilute hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):323–332. doi: 10.1042/bj2110323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T., Roberts C. R., Forni L. G. Oxygen-centred free radicals can efficiently degrade the polypeptide of proteoglycans in whole cartilage. Biosci Rep. 1984 Dec;4(12):1017–1026. doi: 10.1007/BF01116694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farndale R. W., Buttle D. J., Barrett A. J. Improved quantitation and discrimination of sulphated glycosaminoglycans by use of dimethylmethylene blue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 4;883(2):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald R. A., Moak S. A. Degradation of hyaluronic acid by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Inflammation. 1986 Mar;10(1):15–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00916037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2190001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. The importance of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human diseases. Mol Aspects Med. 1985;8(2):89–193. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(85)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame P. J., Christner J. E., Baker J. R. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. The link protein and proteoglycan amino-terminal globular domains have similar structures. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17768–17778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame P. J., Christner J. E., Baker J. R. The primary structure of link protein from rat chondrosarcoma proteoglycan aggregate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3519–3535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen Q., Murphy G., Roughley P. J., Mort J. S. Degradation of proteoglycan aggregate by a cartilage metalloproteinase. Evidence for the involvement of stromelysin in the generation of link protein heterogeneity in situ. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):61–67. doi: 10.1042/bj2590061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Miller A., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Physical properties of the hyaluronate binding region of proteoglycan from pig laryngeal cartilage. Densitometric and small-angle neutron scattering studies of carbohydrates and carbohydrate-protein macromolecules. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):69–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Thurieau C., Jollès P. Link protein interactions with hyaluronate and proteoglycans. Characterization of two distinct domains in bovine cartilage link proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13269–13272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. R., Mort J. S., Roughley P. J. Treatment of cartilage proteoglycan aggregate with hydrogen peroxide. Relationship between observed degradation products and those that occur naturally during aging. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):349–357. doi: 10.1042/bj2470349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostand K. S., Baker J. R., Caterson B., Christner J. E. Isolation and characterization of mouse articular cartilage proteoglycans using preformed CsCl density gradients in the Beckman Airfuge. A rapid semi-micro procedure for proteoglycan isolation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):703–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Poole A. R., Mort J. S. The heterogeneity of link proteins isolated from human articular cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11908–11914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J. Age-related changes in the structure of the proteoglycan subunits from human articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuni A., Chevion M., Czapski G. Unusual copper-induced sensitization of the biological damage due to superoxide radicals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12632–12635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Tigwell M. J., Sajdera S. W. Loss of basophilic (sulphated) material from sections of cartilage treated with periodate solution. Histochem J. 1972 Mar;4(2):155–167. doi: 10.1007/BF01004974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton H. C., Vile G. F., Winterbourn C. C. Radical driven Fenton reactions--evidence from paraquat radical studies for production of tetravalent iron in the presence and absence of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Aug 1;256(2):462–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90603-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengblad A. Quantitative analysis of hyaluronate in nanogram amounts. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):101–105. doi: 10.1042/bj1850101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Winterbourn C. C. Myeloperoxidase-dependent oxidative inactivation of neutrophil neutral proteinases and microbicidal enzymes. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):277–280. doi: 10.1042/bj2450277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Peppin G., Ortiz X., Ragsdale C., Test S. T. Oxidative autoactivation of latent collagenase by human neutrophils. Science. 1985 Feb 15;227(4688):747–749. doi: 10.1126/science.2982211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. F., Halliwell B., Richmond R., Skowroneck W. R. The role of superoxide and hydroxyl radicals in the degradation of hyaluronic acid induced by metal ions and by ascorbic acid. J Inorg Biochem. 1981 Apr;14(2):127–134. doi: 10.1016/s0162-0134(00)80033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]