Abstract
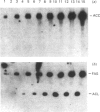
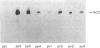
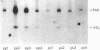
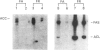
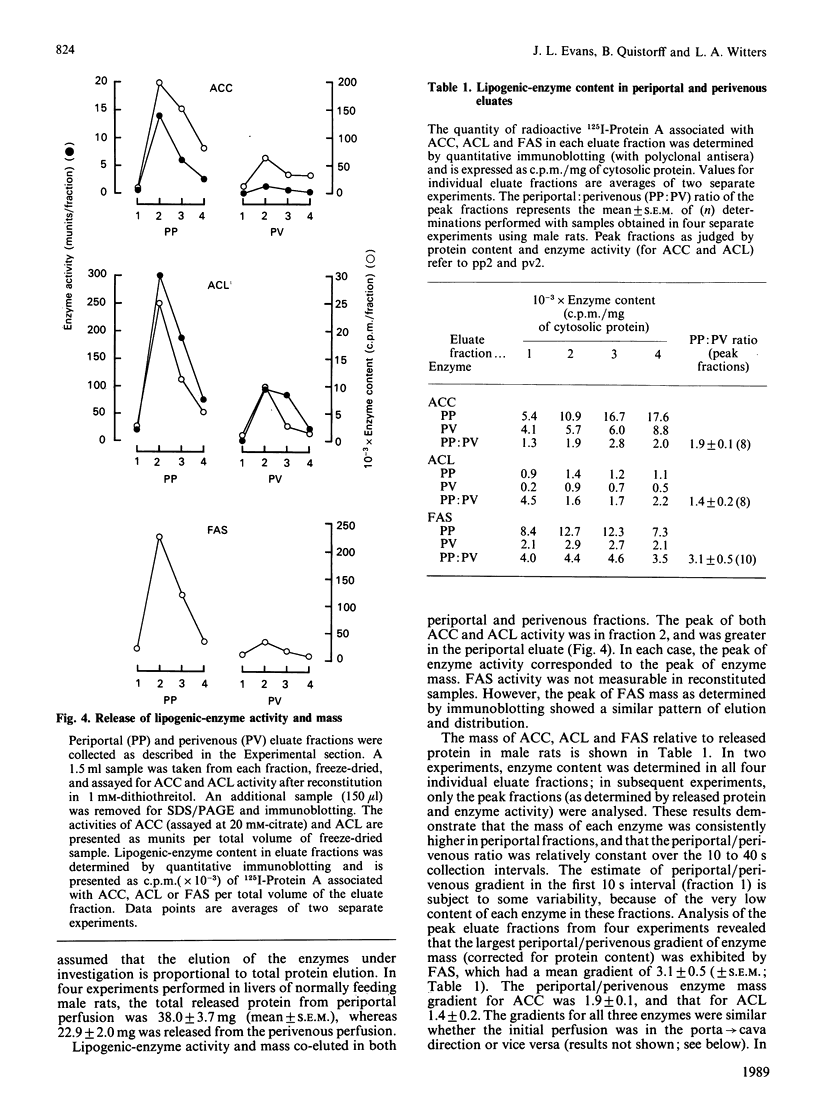
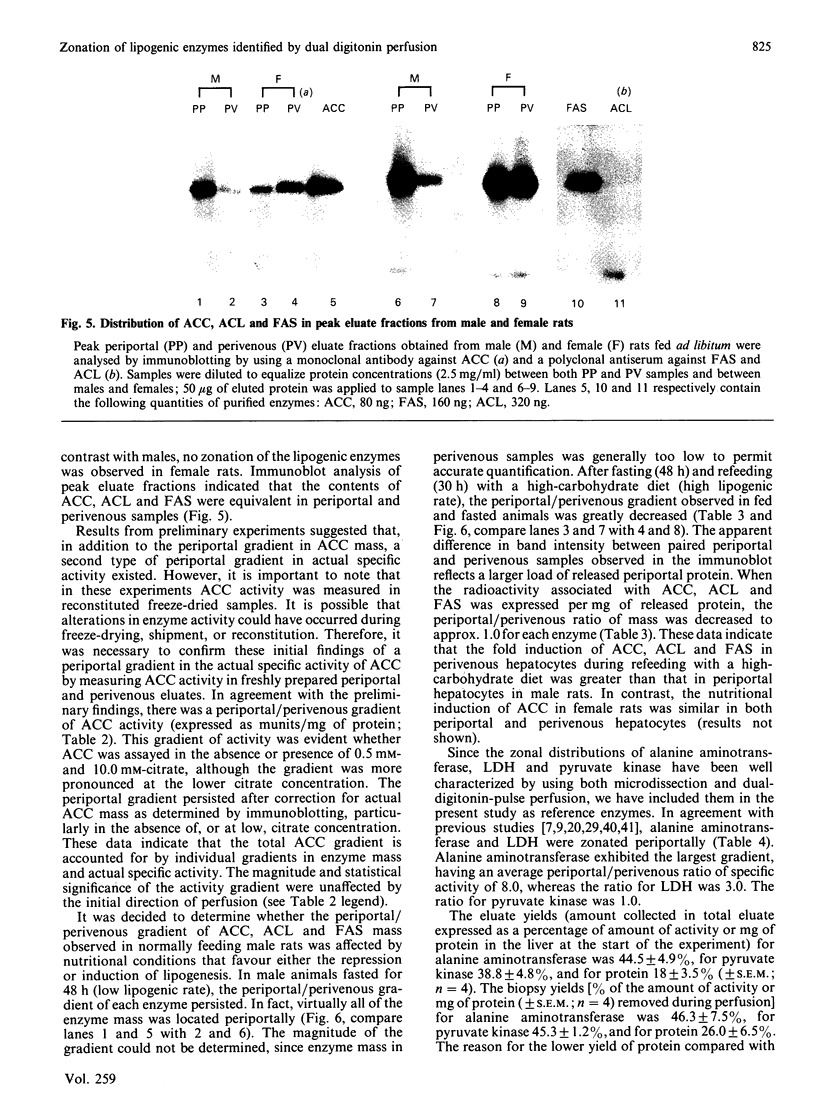
The zonal distribution within rat liver of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ATP citrate-lyase and fatty acid synthase, the principal enzymes of fatty acid synthesis, was investigated by using dual-digitonin-pulse perfusion. Analysis of enzyme mass by immunoblotting revealed that, in normally feeding male rats, the periportal/perivenous ratio of acetyl-CoA carboxylase mass was 1.9. The periportal/perivenous ratio of ATP citrate-lyase mass was 1.4, and fatty acid synthase exhibited the largest periportal/perivenous mass gradient, having a ratio of 3.1. This pattern of enzyme distribution was observed in male rats only; in females, the periportal/perivenous ratio of enzyme mass was nearly equal. The periportal/perivenous gradients for acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ATP citrate-lyase and fatty acid synthase observed in fed (and fasted) males were abolished when animals were fasted (48 h) and refed (30 h) with a high-carbohydrate/low-fat diet. As determined by enzyme assay of eluates obtained from the livers of normally feeding male rats, there is also periportal zonation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity, expressed either as units per mg of eluted protein or units per mg of acetyl-CoA carboxylase protein, suggesting the existence of gradients in both enzyme mass and specific activity. From these results, we conclude that the enzymes of fatty acid synthesis are zonated periportally in the liver of the normally feeding male rat.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. C., Kowaloff E. M., Witters L. A., Dennihy D. T., Avruch J. Purification of a hepatic 123,000-dalton hormone-stimulated 32P-peptide and its identification as ATP-citrate lyase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8052–8056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels H., Vogt B., Jungermann K. Glycogen synthesis via the indirect gluconeogenic pathway in the periportal and via the direct glucose utilizing pathway in the perivenous zone of perfused rat liver. Histochemistry. 1988;89(3):253–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00493149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass N. M., Barker M. E., Manning J. A., Jones A. L., Ockner R. K. Acinar heterogeneity of fatty acid binding protein expression in the livers of male, female and clofibrate-treated rats. Hepatology. 1989 Jan;9(1):12–21. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Julkunen A., Penttilä K. E., Lindros K. O. Effect of phenobarbital on the distribution of drug metabolizing enzymes between periportal and perivenous rat hepatocytes prepared by digitonin-collagenase liver perfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Feb;240(2):663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick A. C., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Use of rapid gel-permeation chromatography to explore the inter-relationships between polymerization, phosphorylation and activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Effects of insulin and phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):773–782. doi: 10.1042/bj2410773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Katz J. Zonation of glycogen and glucose syntheses, but not glycolysis, in rat liver. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):99–104. doi: 10.1042/bj2550099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. L., Witters L. A. Quantitation by immunoblotting of the in vivo induction and subcellular distribution of hepatic acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jul;264(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90575-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R., Mecke D. Heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthetase among rat liver parenchymal cells in situ and in primary culture. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):567–570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giffhorn S., Katz N. R. Glucose-dependent induction of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in rat hepatocyte cultures. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):343–350. doi: 10.1042/bj2210343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D. Hepatocyte heterogeneity in glutamine and ammonia metabolism and the role of an intercellular glutamine cycle during ureogenesis in perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):269–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamil H., Madsen N. B. Phosphorylation state of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. I. Linear inverse relationship to activity ratios at different citrate concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):630–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K. Functional heterogeneity of periportal and perivenous hepatocytes. Enzyme. 1986;35(3):161–180. doi: 10.1159/000469338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K. Metabolic zonation of liver parenchyma: significance for the regulation of glycogen metabolism, gluconeogenesis, and glycolysis. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Jan;3(1):269–293. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kari F. W., Yoshihara H., Thurman R. G. Urea synthesis from ammonia in periportal and pericentral regions of the liver lobule. Effect of oxygen. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., McGarry J. D. The glucose paradox. Is glucose a substrate for liver metabolism? J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):1901–1909. doi: 10.1172/JCI111610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N. R., Fischer W., Giffhorn S. Distribution of enzymes of fatty acid and ketone body metabolism in periportal and perivenous rat-liver tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):103–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N. R., Fischer W., Ick M. Heterogeneous distribution of ATP citrate lyase in rat-liver parenchyma. Microradiochemical determination in microdissected periportal and perivenous liver tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):297–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N. R., Giffhorn S. Glucose- and insulin-independent induction of ATP citrate lyase in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 15;212(1):65–71. doi: 10.1042/bj2120065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N., Teutsch H. F., Jungermann K., Sasse D. Heterogeneous reciprocal localization of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and of glucokinase in microdissected periportal and perivenous rat liver tissue. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 15;83(2):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)81021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li A. C., Tanaka R. D., Callaway K., Fogelman A. M., Edwards P. A. Localization of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthase in the rat liver and intestine is affected by cholestyramine and mevinolin. J Lipid Res. 1988 Jun;29(6):781–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindros K. O., Penttilä K. E. Digitonin-collagenase perfusion for efficient separation of periportal or perivenous hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):757–760. doi: 10.1042/bj2280757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loud A. V. A quantitative stereological description of the ultrastructure of normal rat liver parenchymal cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):27–46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunzer M. A., Manning J. A., Ockner R. K. Inhibition of rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by long chain acyl coenzyme A and fatty acid. Modulation by fatty acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5483–5487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura T., Kashiwagi T., Meren H., Thurman R. G. Gluconeogenesis predominates in periportal regions of the liver lobule. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):409–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst I., Schwartz P., Jungermann K. Induction in primary culture of 'gluconeogenic' and 'glycolytic' hepatocytes resembling periportal and perivenous cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(2):271–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06775.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pösö A. R., Penttilä K. E., Suolinna E. M., Lindros K. O. Urea synthesis in freshly isolated and in cultured periportal and perivenous hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):263–267. doi: 10.1042/bj2390263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quistorff B., Dich J., Grunnet N. Periportal and perivenous hepatocytes retain their zonal characteristics in primary culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1055–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quistorff B. Gluconeogenesis in periportal and perivenous hepatocytes of rat liver, isolated by a new high-yield digitonin/collagenase perfusion technique. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):221–226. doi: 10.1042/bj2290221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quistorff B., Grunnet N., Cornell N. W. Digitonin perfusion of rat liver. A new approach in the study of intra-acinar and intracellular compartmentation in the liver. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 15;226(1):289–297. doi: 10.1042/bj2260289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quistorff B., Grunnet N. Dual-digitonin-pulse perfusion. Concurrent sampling of periportal and perivenous cytosol of rat liver for determination of metabolites and enzyme activities. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):87–95. doi: 10.1042/bj2430087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder H. NADP-dependent dehydrogenases in rat liver parenchyma. III. The description of a liponeogenic area on the basis of histochemically demonstrated enzyme activities and the neutral fat content during fasting and refeeding. Histochemistry. 1981;72(4):579–615. doi: 10.1007/BF00493277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse D., Katz N., Jungermann K. Functional heterogeneity of rat liver parenchyma and of isolated hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I., Kawka D. W., Kazazis D. M., Alberts A. W., Chen J. S., Huff J. W., Ness G. C. Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase-containing hepatocytes are distributed periportally in normal and mevinolin-treated rat livers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5556–5560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoops J. K., Ross P., Arslanian M. J., Aune K. C., Wakil S. J., Oliver R. M. Physicochemical studies of the rat liver and adipose fatty acid synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7418–7426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teutsch H. F., Rieder H. NADP-dependent dehydrogenases in rat liver parenchyma. II. Comparison of qualitative and quantitative G6PDH distribution patterns with particular reference to sex differences. Histochemistry. 1979 Feb 26;60(1):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00495727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thampy K. G., Wakil S. J. Activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Purification and properties of a Mn2+-dependent phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6318–6323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurman R. G., Kauffman F. C. Sublobular compartmentation of pharmacologic events (SCOPE): metabolic fluxes in periportal and pericentral regions of the liver lobule. Hepatology. 1985 Jan-Feb;5(1):144–151. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper J. P., Witters L. A. In vitro phosphorylation and inactivation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase purified by avidin affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 13;715(2):162–169. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAGELOS P. R., ALBERTS A. W., MARTIN D. B. Studies on the mechnism of activation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by citrate. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas J. L., O'Connor E., Roche E., Knecht E., Grisolia S. Analysis by flow cytometry of rat hepatocytes from different acinar zones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):535–541. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90964-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wals P. A., Palacin M., Katz J. The zonation of liver and the distribution of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4876–4881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh F. A. Changes in distribution of enzymes within the liver lobule during adaptive increases. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Feb;20(2):107–111. doi: 10.1177/20.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Friedman S. A., Bacon G. W. Microsomal acetyl-CoA carboxylase: evidence for association of enzyme polymer with liver microsomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3639–3643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Moriarity D., Martin D. B. Regulation of hepatic acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by insulin and glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6644–6649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Vogt B. A new method for the isolation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Lipid Res. 1981 Feb;22(2):364–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Watts T. D., Daniels D. L., Evans J. L. Insulin stimulates the dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5473–5477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]