Abstract
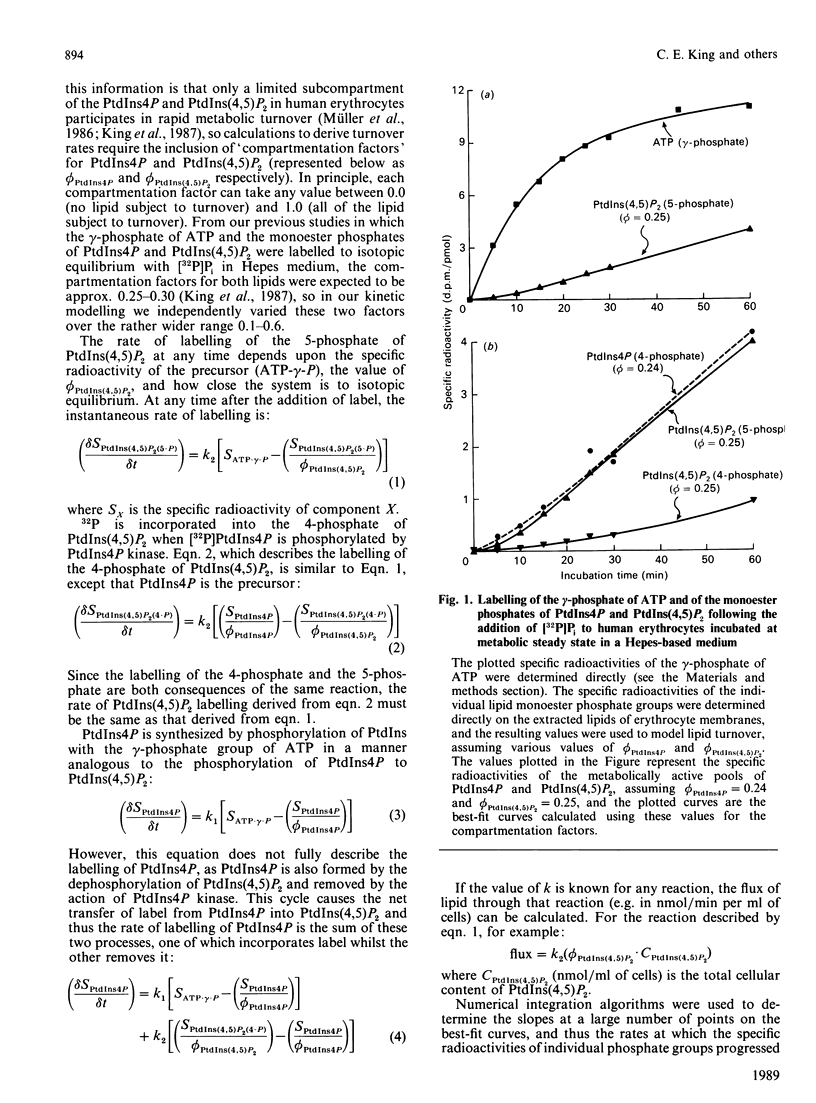
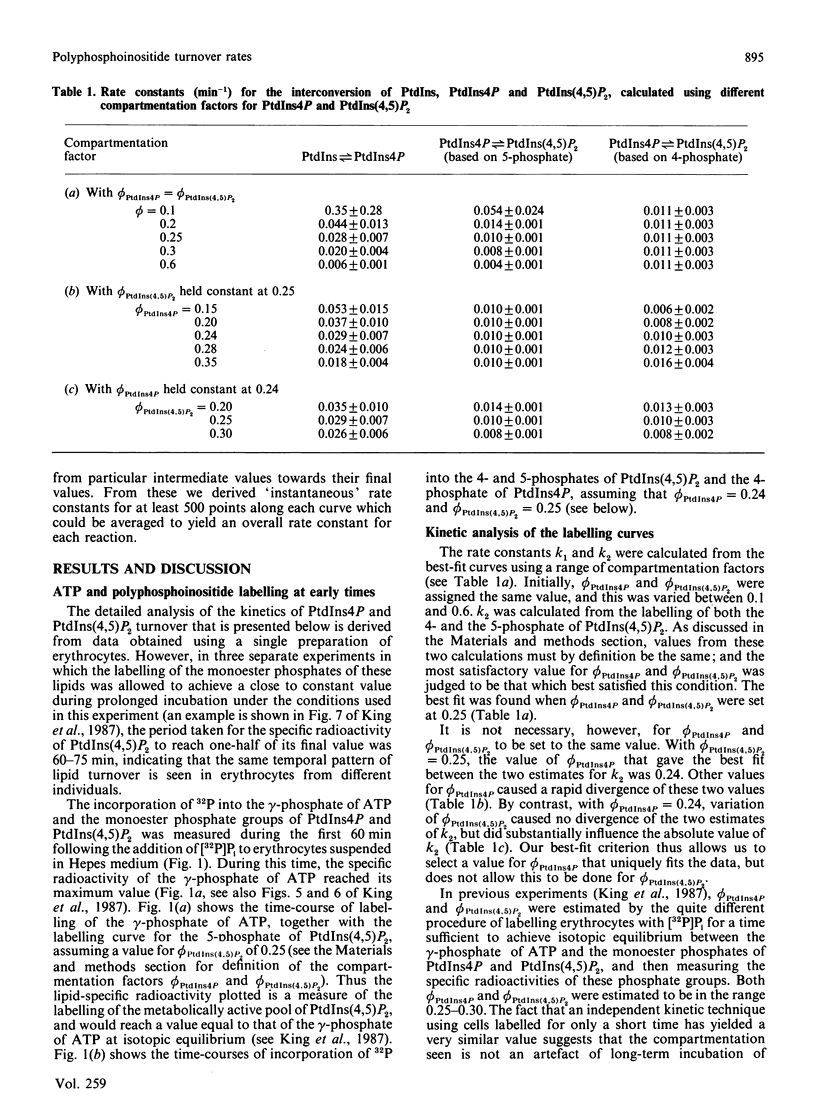
When intact human erythrocytes are incubated at metabolic steady state in a chloride-free medium containing [32P]Pi, there is rapid labelling of the gamma-phosphate of ATP, followed by a slower labelling of the monoester phosphate groups of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] [King, Stephens, Hawkins, Guy & Michell (1987) Biochem. J. 244, 209-217]. We have analysed the early kinetics of the labelling of these phosphate groups, in order to determine: (a) the steady-state rates of the interconversions of phosphatidylinositol, PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2; and (b) the fractions of the total cellular complement of PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2 that participate in this steady-state turnover. The experimental data most closely fit a pattern of PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2 turnover in which one-quarter of the total cellular complement of each lipid is in the metabolic pool that participates in rapid metabolic turnover, with rate constants of 0.028 min-1 for the interconversion of PtdIns and PtdIns4P, and of 0.010 min-1 for the PtdIns4P/PtdIns(4,5)P2 cycle. These rate constants represent metabolic fluxes of approx. 2.1 nmol of lipid/h per ml of packed erythrocytes between PtdIns and PtdIns4P and of approx. 5.7 nmol/h per ml of cells between PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan D. Inositol lipids and membrane function in erythrocytes. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):451–465. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G. L. Quantitation of adenosine-5'-triphosphate used for phosphoinositide metabolism in human erythrocytes. Blood. 1985 Nov;66(5):1133–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. E., Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Guy G. R., Michell R. H. Multiple metabolic pools of phosphoinositides and phosphatidate in human erythrocytes incubated in a medium that permits rapid transmembrane exchange of phosphate. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):209–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2440209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maretzki D., Klatt D., Reimann B., Rapoport S. ATP utilizing reactions of human erythrocyte membranes and the influence of modulator proteins. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(4-5):479–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momsen G., Vestergaard-Bogind B. Human erythrocyte 2,3-diphosphoglycerate metabolism. Influence of 1,3-diphosphoglycerate and Pi. In vitro studies at low pH with computer simulations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller E., Hegewald H., Jaroszewicz K., Cumme G. A., Hoppe H., Frunder H. Turnover of phosphomonoester groups and compartmentation of polyphosphoinositides in human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):775–783. doi: 10.1042/bj2350775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


