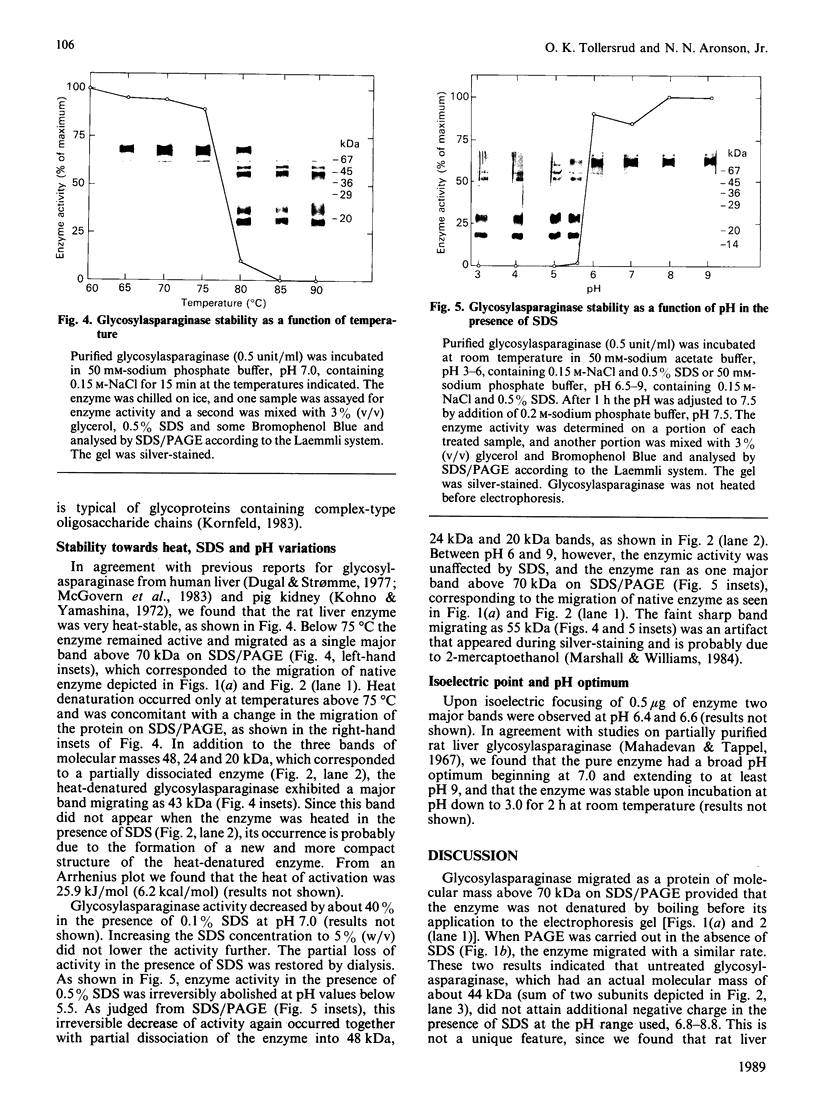
Abstract
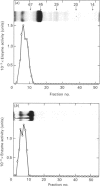
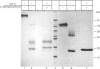
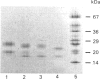
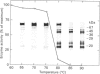
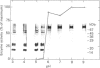
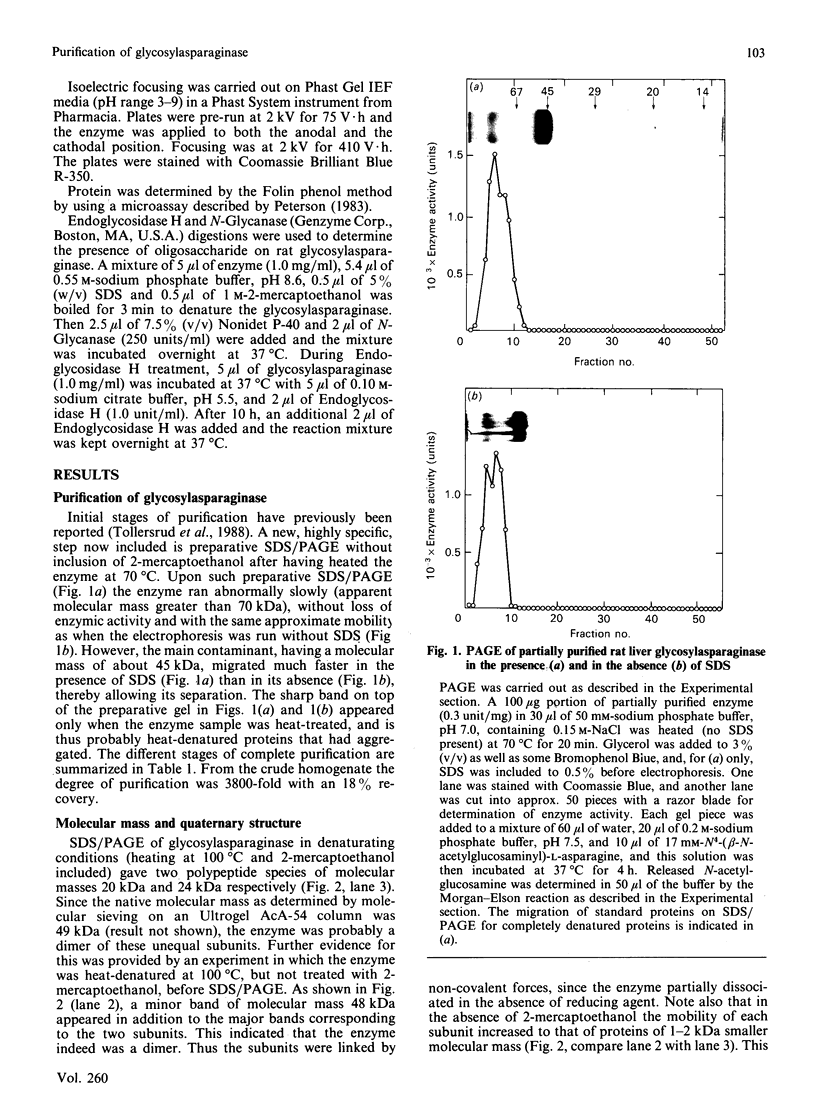
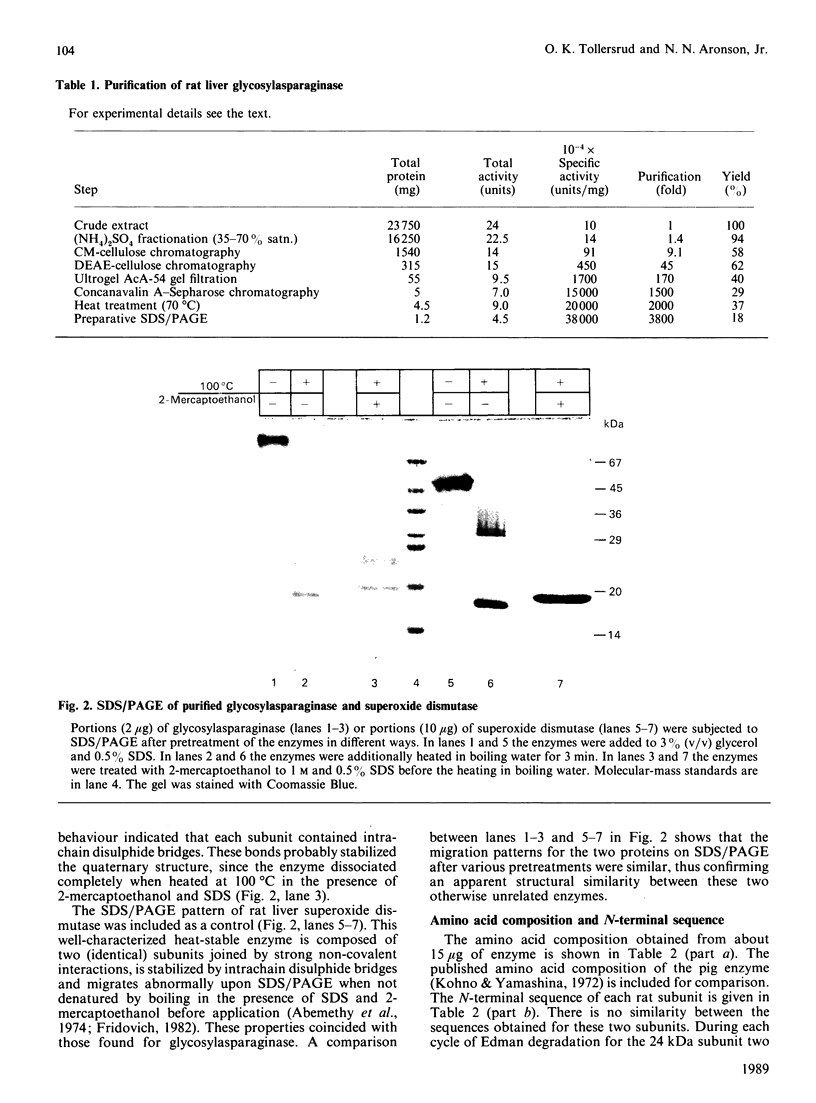
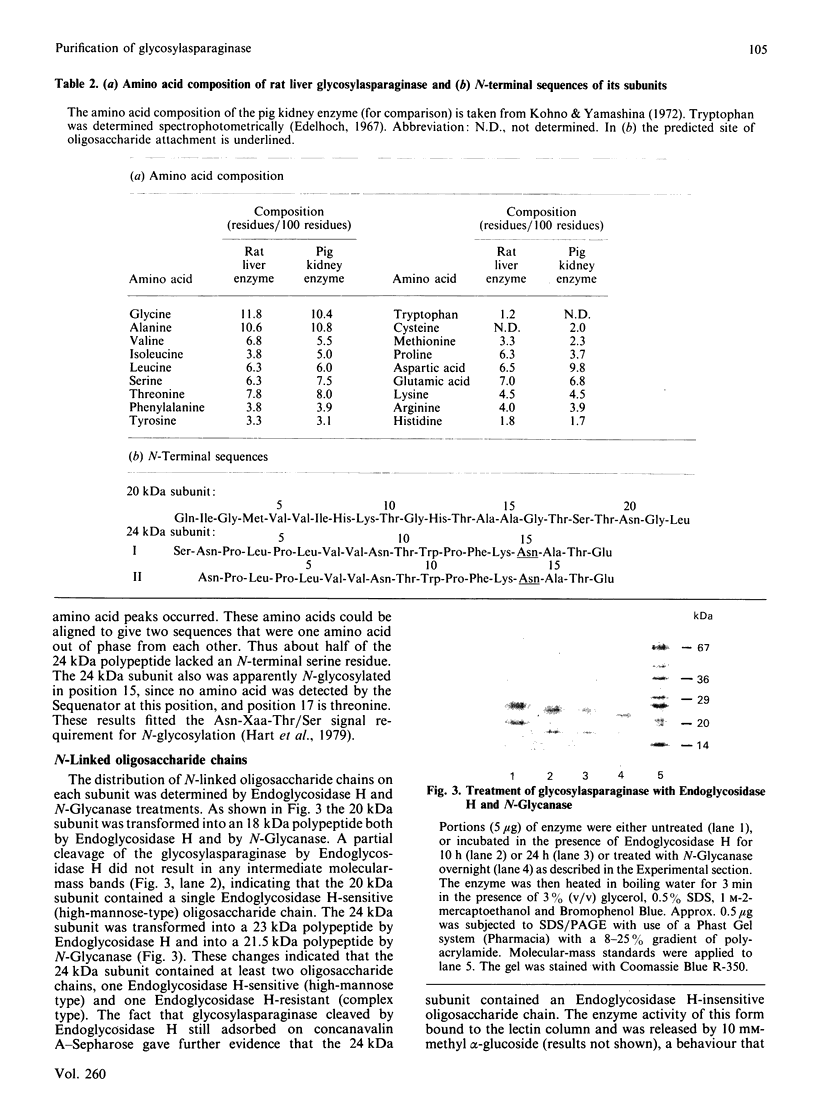
1. Rat liver glycosylasparaginase [N4-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparaginase, EC 3.5.1.26] was purified to homogeneity by using salt fractionation, CM-cellulose and DEAE-cellulose chromatography, gel filtration on Ultrogel AcA-54, concanavalin A-Sepharose affinity chromatography, heat treatment at 70 degrees C and preparative SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. The purified enzyme had a specific activity of 3.8 mumol of N-acetylglucosamine/min per mg with N4-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparagine as substrate. 2. The native enzyme had a molecular mass of 49 kDa and was composed of two non-identical subunits joined by strong non-covalent forces and having molecular masses of 24 and 20 kDa as determined by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. 3. The 20 kDa subunit contained one high-mannose-type oligosaccharide chain, and the 24 kDa subunit had one high-mannose-type and one complex-type oligosaccharide chain. 4. N-Terminal sequence analysis of each subunit revealed a frayed N-terminus of the 24 kDa subunit and an apparent N-glycosylation of Asn-15 in the same subunit. 5. The enzyme exhibited a broad pH maximum above 7. Two major isoelectric forms were found at pH 6.4 and 6.6. 6. Glycosylasparaginase was stable at 75 degrees C and in 5% (w/v) SDS at pH 7.0.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abernethy J. L., Steinman H. M., Hill R. L. Bovine erythrocyte superoxide dismutase. Subunit structure and sequence location of the intrasubunit disulfide bond. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7339–7347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amelunxen R. E., Murdock A. L. Mechanisms of thermophily. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;6(4):343–393. doi: 10.3109/10408417809090626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baussant T., Strecker G., Wieruszeski J. M., Montreuil J., Michalski J. C. Catabolism of glycoprotein glycans. Characterization of a lysosomal endo-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase specific for glycans with a terminal chitobiose residue. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):381–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., McCord J. M. Oxygen-induced changes in pulmonary superoxide dismutase assayed by antibody titrations. Am J Physiol. 1976 Oct;231(4):1196–1203. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.4.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diment S., Leech M. S., Stahl P. D. Cathepsin D is membrane-associated in macrophage endosomes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6901–6907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugal B., Stromme J. Purification and some properties of 1-aspartamido-beta-N-acetylglucosamine amidohydrolase from human liver. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):497–502. doi: 10.1042/bj1650497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstone A., Koenig H. Synthesis and turnover of lysosomal glycoproteins. Relation to the molecular heterogeneity of the lysosomal enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):176–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. W., Brew K., Grant G. A., Bradshaw R. A., Lennarz W. J. Primary structural requirements for the enzymatic formation of the N-glycosidic bond in glycoproteins. Studies with natural and synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9747–9753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono M., Yamashina I. Purification and properties of 4-L-aspartylglycosylamine amidohydrolase from hog kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):600–617. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuranda M. J., Aronson N. N., Jr A di-N-acetylchitobiase activity is involved in the lysosomal catabolism of asparagine-linked glycoproteins in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5803–5809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVVY G. A., MCALLAN A. The N-acetylation and estimation of hexosamines. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:127–132. doi: 10.1042/bj0730127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little L. E., Lau M. M., Quon D. V., Fowler A. V., Neufeld E. F. Proteolytic processing of the alpha-chain of the lysosomal enzyme, beta-hexosaminidase, in normal human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4288–4292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Tappel A. L. Beta-aspartylglucosylamine amido hydrolase of rat liver and kidney. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4568–4576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino M., Kojima T., Ohgushi T., Yamashina I. Studies on enzymes acting on glycopeptides. J Biochem. 1968 Feb;63(2):186–192. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino M., Kojima T., Yamashina I. Enzymatic cleavage of glycopeptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):961–966. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall T., Williams K. M. Artifacts associated with 2-mercaptoethanol upon high resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jun;139(2):502–505. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P. Aspartylglycosaminuria: an inborn error of glycoprotein catabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1982;5(4):192–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02179139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern M. M., Aula P., Desnick R. J. Purification and properties of human hepatic aspartylglucosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10743–10747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. A. The binding of detergents to proteins. I. The maximum amount of dodecyl sulfate bound to proteins and the resistance to binding of several proteins. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3895–3901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgushi T., Yamashina I. Distribution of a glycopeptide-degrading enzyme in tissue and cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 11;156(2):417–419. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Z. W., Li S. C., Li Y. T. Absence of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity in the kidneys of sheep, cattle and pig. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):145–149. doi: 10.1042/bj2480145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. The purification and properties of a beta-aspartyl N-acetylglucosylamine amidohydrolase from hen oviduct. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. The isolation and structure of the core oligosaccharide sequences of IgM. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5516–5523. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollersrud O. K., Hofmann S. H., Aronson N. N., Jr The turnover of lysosomal glycosylasparaginase in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 14;953(3):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomazic S. J., Klibanov A. M. Why is one Bacillus alpha-amylase more resistant against irreversible thermoinactivation than another? J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3092–3096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Tachibana Y., Takada S., Matsuda I., Arashima S., Kobata A. Urinary glycopeptides of fucosidosis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4820–4827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]