Abstract
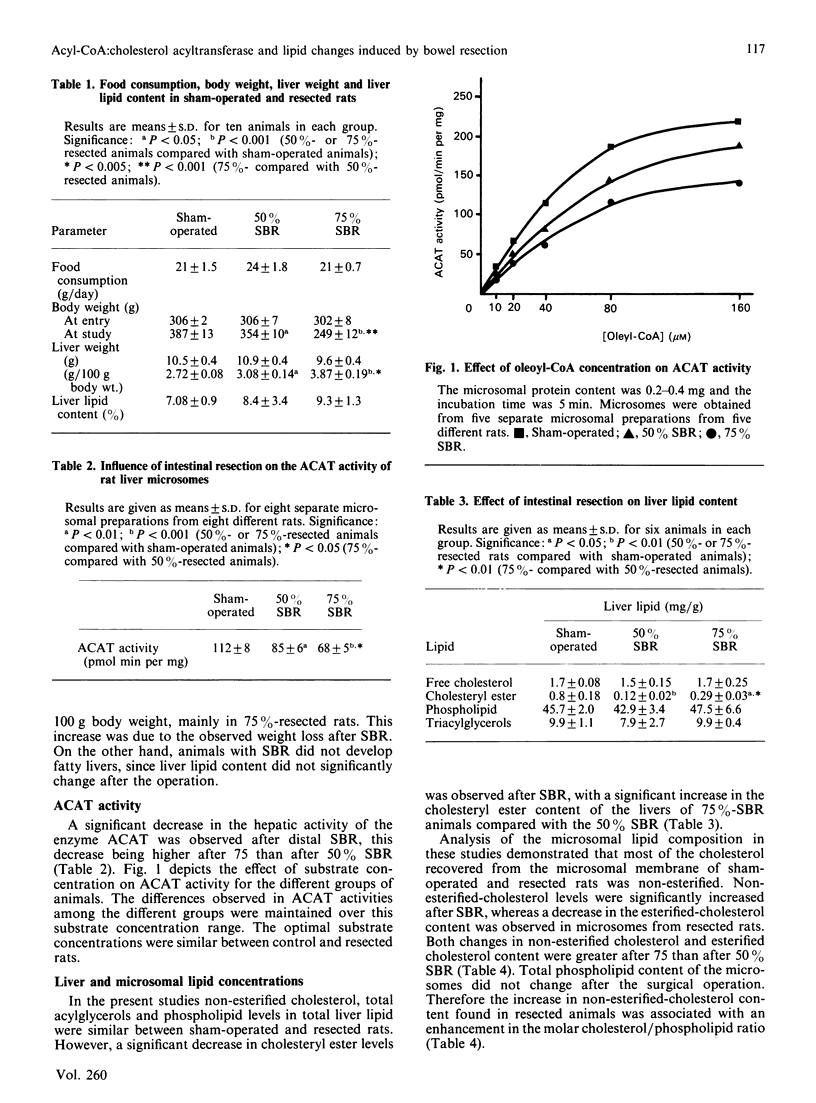
The acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) activity and lipid composition of hepatic microsomal membrane were investigated 6 weeks after both 50 and 75% distal-small-bowel resection (SBR). A significant decrease in hepatic cholesteryl ester levels was observed after SBR, with a significant increase in the cholesteryl ester content of the livers of 75% SBR compared with the 50% SBR. Hepatic total acylglycerols, free cholesterol and phospholipid levels were not modified after the surgical operation. Microsomal free cholesterol was increased after both 50 and 75% SBR. However, a decrease in both microsomal ACAT activity and cholesteryl ester levels were found in microsomes (microsomal fractions) of resected rats, both changes being higher after 75 than after 50% resection. The total phospholipid content of the microsomes did not change after the surgical operation. The microsomal phospholipid fatty acid composition indicated higher changes after 75 than after 50% SBR. These results demonstrated that, in resected animals: (1) the activity of the enzyme responsible for catalysing cholesterol esterification (ACAT) is decreased, and (2) hepatic microsomal free cholesterol does not appear to influence the activity of ACAT.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akesson B., Nilsson A. Intestinal absorption of phosphatidylcholine and triglyceride after ileal resection. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Mar;23(2):251–256. doi: 10.3109/00365528809103976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfin-Slater R. B., Aftergood L. Essential fatty acids reinvestigated. Physiol Rev. 1968 Oct;48(4):758–784. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.4.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomstrand R., Diczfalusy U., Sisfontes L., Svensson L. Influence of dietary partially hydrogenated vegetable and marine oils on membrane composition and function of liver microsomes and platelets in the rat. Lipids. 1985 May;20(5):283–295. doi: 10.1007/BF02534261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drevon C. A., Engelhorn S. C., Steinberg D. Secretion of very low density lipoproteins enriched in cholesteryl esters by cultured rat hepatocytes during simulation of intracellular cholesterol esterification. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):1065–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson S. K., Shrewsbury M. A., Brooks C., Meyer D. J. Rat liver acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase: its regulation in vivo and some of its properties in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1980 Sep;21(7):930–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field F. J., Salome R. G. Effect of dietary fat saturation, cholesterol and cholestyramine on acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase activity in rabbit intestinal microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 14;712(3):557–570. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis S. M. The activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase and acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase in hepatic microsomes from male, female and pregnant rats. The effect of cholestyramine treatment and the relationship of enzyme activity to microsomal lipid composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 12;875(2):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers F., Havinga R., Bosschieter H., Toorop G. P., Hindriks F. R., Vonk R. J. Enterohepatic circulation in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Feb;88(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur S. N., Armstrong M. L., Alber C. A., Spector A. A. Hepatic acylcoenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase activity during diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in cynomolgus monkeys. J Lipid Res. 1981 May;22(4):659–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitropoulos K. A., Balasubramaniam S., Venkatesan S., Reeves B. E. On the mechanism for the regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase and of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase by free cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 25;530(1):99–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murillo M. L., Campos M. S., Mataix F. J., Varela G. Influencia de las resecciones intestinales en la rata sobre algunos aspectos de las secreciones digestivas. Rev Esp Fisiol. 1978 Dec;34(4):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nervi F., Bronfman M., Allalón W., Depiereux E., Del Pozo R. Regulation of biliary cholesterol secretion in the rat. Role of hepatic cholesterol esterification. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2226–2237. doi: 10.1172/JCI111649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Kaduce T. L., Dane R. W. Effect of dietary fat saturation on acylcoenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase activity of rat liver microsomes. J Lipid Res. 1980 Feb;21(2):169–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synouri-Vrettakou S., Mitropoulos K. A. Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase. Transfer of cholesterol to its substrate pool and modulation of activity. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):299–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


