Abstract
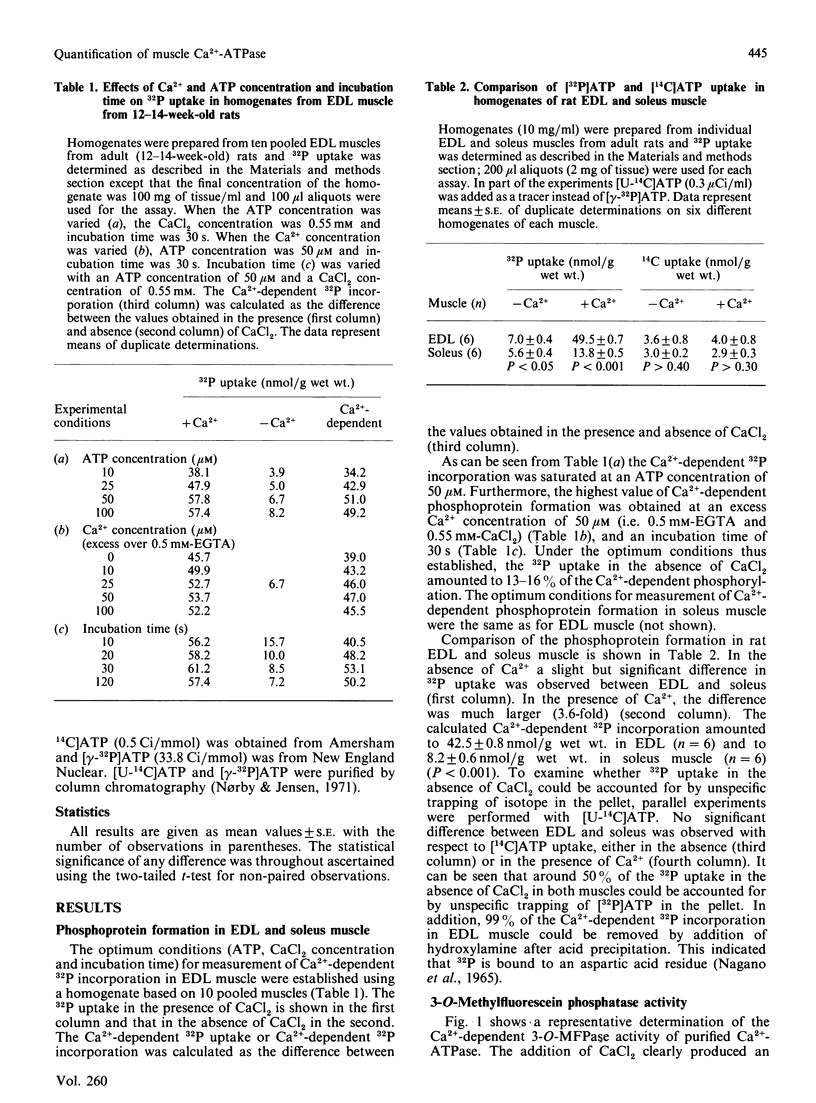
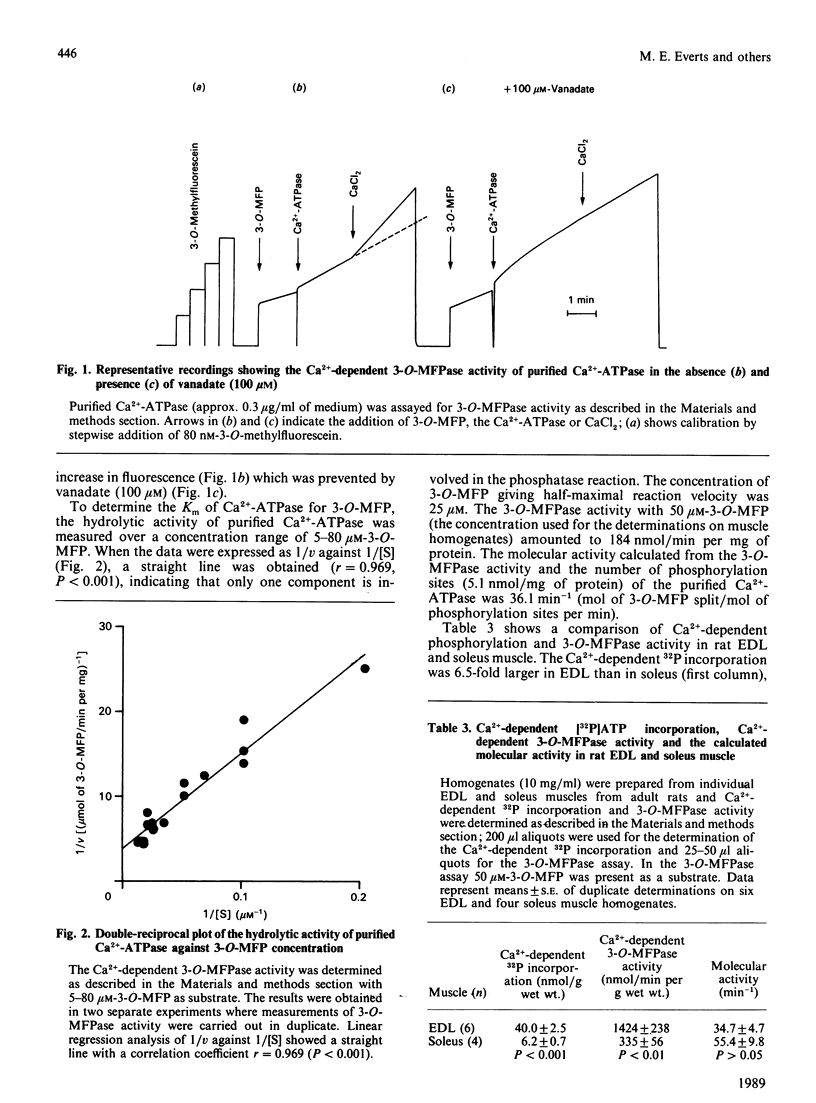
The possibility of quantifying the total concentration of Ca2+-dependent Mg2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum was investigated by measurement of the Ca2+-dependent steady-state phosphorylation from [gamma-32P]ATP and the Ca2+-dependent 3-O-methylfluorescein phosphatase (3-O-MFPase) activity in crude muscle homogenates. The Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation at 0 degree C (mean +/- S.E.) was 40.0 +/- 2.5 (n = 6) and 6.2 +/- 0.7 (n = 4) nmol/g wet wt. in rat extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and soleus muscle, respectively (P less than 0.001). The Ca2+-dependent 3-O-MFPase activity at 37 degrees C was 1424 +/- 238 (n = 6) and 335 +/- 56 (n = 4) nmol/min per g wet wt. in rat EDL and soleus muscle, respectively (P less than 0.01). The molecular activity calculated from these measurements amounted to 35 +/- 5 min-1 (n = 6) and 55 +/- 10 min-1 (n = 4) for EDL and soleus muscle respectively. These values were not different from the molecular activity calculated for purified Ca2+-ATPase (36 min-1). The Ca2+-dependent 32P incorporation in soleus muscle decreased in the order mice greater than rats greater than guinea pigs. In EDL muscles from hypothyroid rats at a 30% reduction of the Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation was observed. The Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation in vastus lateralis muscle from three human subjects amounted to 4.5 +/- 0.8 nmol/g wet wt. It is concluded that measurement of the Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation allows rapid and reproducible quantification of the concentration of Ca2+-dependent Mg2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Since only 20-60 mg of tissue is required for the measurements, the method can also be used for biopsies obtained in clinical studies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. P., Møller J. V., Jørgensen P. L. The functional unit of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Active site titration and fluorescence measurements. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8300–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron R., Burger A., Chinet A., Clausen T., Dubois-Ferrière R. Thyroid hormones and the energetics of active sodium-potassium transport in mammalian skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):47–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOSE R. DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLES OF THE RAT DURING DEVELOPMENT. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:74–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Everts M. E., Kjeldsen K. Quantification of the maximum capacity for active sodium-potassium transport in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:163–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Banyard M. R., Medveczky C. J. Distribution of calcium ATPase in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of fast- and slow-twitch muscles determined with monoclonal antibodies. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(2):79–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01871228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everts M. E., Clausen T. Effects of thyroid hormones on calcium contents and 45Ca exchange in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):E258–E265. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.3.E258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everts M. E., van Hardeveld C. Effects of dantrolene on force development in slow- and fast-twitch muscle of euthyroid, hypothyroid, and hyperthyroid rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):47–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen K., Leberer E., Lømo T., Pette D., Staron R. S. Fibre types, calcium-sequestering proteins and metabolic enzymes in denervated and chronically stimulated muscles of the rat. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:177–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O., Skou J. C. A study on the influence of the concentration of Mg 2+ , P i , K + , Na + , and Tris on (Mg 2+ + P i )-supported g-strophanthin binding to (Na + = K + )activated ATPase from ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 7;311(1):51–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbach W., Oetliker H. Energetics and electrogenicity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:325–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. D., Summer G. K., Waters M. D. An automated fluorometric assay for alkaline phosphatase using 3-O-methylfluorescein phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jul;24(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsher E., Mommaerts W. F., Ricchiuti N. V., Wallner A. Activation heat, activation metabolism and tension-related heat in frog semitendinosus muscles. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;220(3):601–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G. p-nitrophenyl phosphate hydrolysis and calcium ion transport in fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum. Science. 1971 Mar 5;171(3974):901–903. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3974.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Andersen J. P. Structural basis for E1-E2 conformational transitions in Na,K-pump and Ca-pump proteins. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(2):95–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01870942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. H., Witzmann F. A., Fitts R. H. A comparison of sarcoplasmic reticulum function in fast and slow skeletal muscle using crude homogenate and isolated vesicles. Life Sci. 1981 May 18;28(20):2223–2229. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90573-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. H., Witzmann F. A., Fitts R. H. Effect of thyrotoxicosis on sarcoplasmic reticulum in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):C151–C155. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.3.C151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Roufa D., Boland R., Reyes E., Tillack T. W. Development of sarcoplasmic reticulum in cultured chicken muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):318–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Conner G. E., Fleischer S. Isolation of sarcoplasmic reticulum by zonal centrifugation and purification of Ca 2+ -pump and Ca 2+ -binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):246–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano K., Kanazawa T., Mizuno N., Tashima Y., Nakao T., Nakao M. Some acyl phosphate-like properties of P32-labeled sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):759–764. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicol C. J., Bruce D. S. Effect of hyperthyroidism on the contractile and histochemical properties of fast and slow twitch skeletal muscle in the rat. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Apr;390(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00582715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norby J. G., Jensen J. Binding of ATP to brain microsomal ATPase. Determination of the ATP-binding capacity and the dissociation constant of the enzyme-ATP complex as a function of K+ concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):104–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørgaard A., Kjeldsen K., Clausen T. A method for the determination of the total number of 3H-ouabain binding sites in biopsies of human skeletal muscle. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1984 Oct;44(6):509–518. doi: 10.3109/00365518409083604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørgaard A., Kjeldsen K., Hansen O., Clausen T. A simple and rapid method for the determination of the number of 3H-ouabain binding sites in biopsies of skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 28;111(1):319–325. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall J. A. Energetics of Ca2+ cycling during skeletal muscle contraction. Fed Proc. 1982 Feb;41(2):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonides W. S., van Hardeveld C. The effect of hypothyroidism on sarcoplasmic reticulum in fast-twitch muscle of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 21;844(2):129–141. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hardeveld C., Clausen T. Effect of thyroid status on K+-stimulated metabolism and 45Ca exchange in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 1):E421–E430. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.4.E421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Grassi de Gende A. O., Schwartz A. Kinetic properties of calcium adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum isolated from cat skeletal muscles. A comparison of caudofemoralis (fast), tibialis (mixed), and soleus (slow). J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10675–10678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


