Abstract
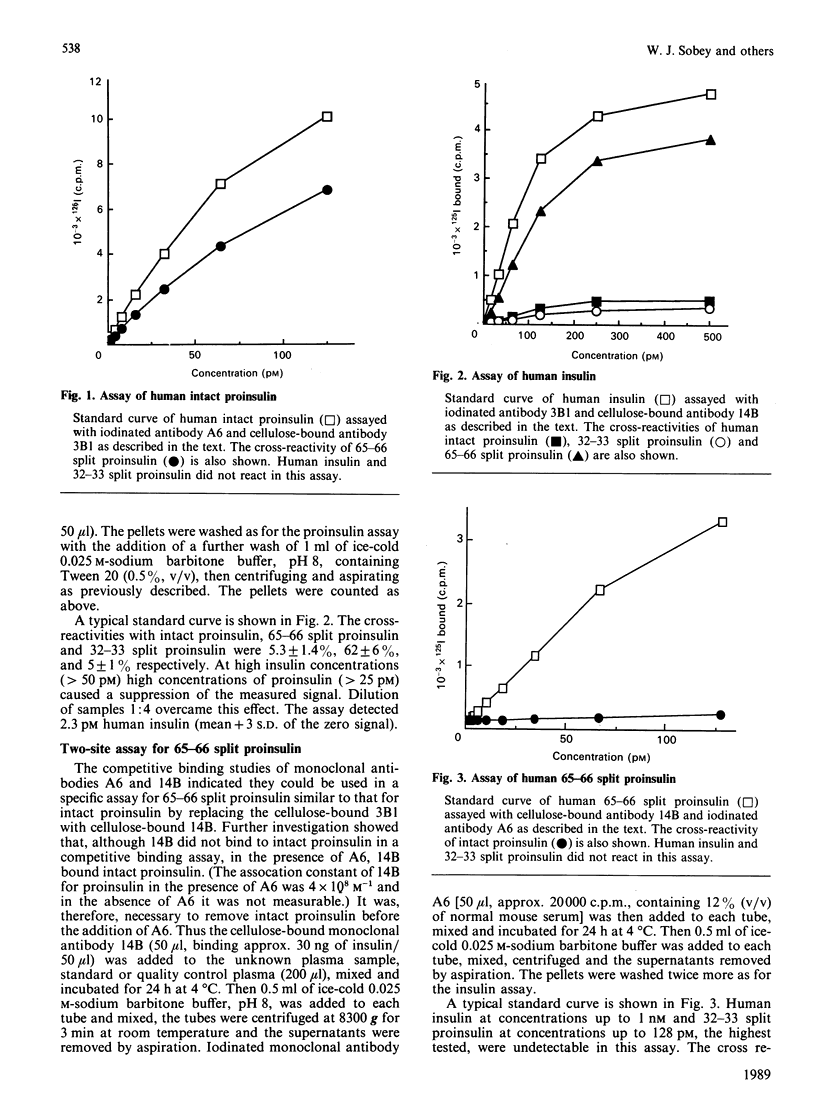
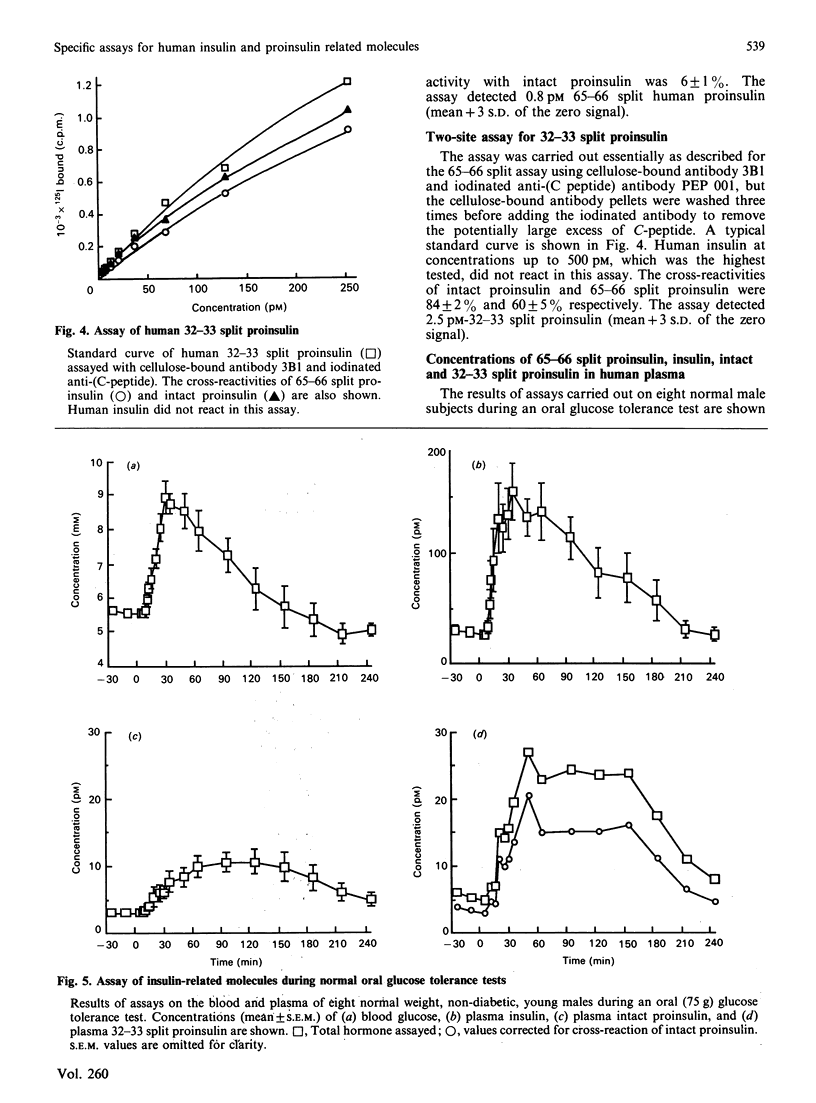
Monoclonal antibody-based two-site immunoradiometric assays are described for human insulin, proinsulin, 65-66 split and 32-33 split proinsulin. The detection limits of the assays lie in the range 0.8-2.5 pM. The assays for 65-66 and 32-33 split proinsulins do not distinguish between these substances and their respective C-terminal di-desamino derivatives. The assay of 65-66 split proinsulin does not cross-react with insulin, proinsulin or 32-33 split proinsulin. This material was undetectable (less than 1.0 pM) in plasma taken after an overnight fast in eight normal male subjects and the maximum individual concentration reached in plasma taken during an oral glucose tolerance test of these subjects was 3.8 pM. The proinsulin assay cross-reacted 66% with 65-66 split proinsulin but not with insulin or 32-33 split proinsulin. The 32-33 split proinsulin assay cross-reacted 84 and 60% with proinsulin and 65-66 split proinsulin respectively. The insulin assay cross-reacted 5.3, 62 and 5.0% with intact proinsulin, 65-66 split proinsulin and 32-33 split proinsulin respectively. The very low concentration of 65-66 split proinsulin meant that this derivative did not interfere significantly with the specificity of the assays of proinsulin and insulin. The concentration of 32-33 split proinsulin could be calculated by subtracting the cross-reactivity of the measured proinsulin. The mean concentrations of insulin, proinsulin and 32-33 split proinsulin in eight young male subjects in the fasting state were (pM +/- S.E.M.) 20 +/- 0.3, 2.3 +/- 0.3 and 2.1 +/- 0.7 and at the maximum reached during an oral glucose tolerance test, 150 +/- 26, 9.9 +/- 1.4 and 19.7 +/- 6.0 respectively.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck P., Nicholas H. Immunoassay of serum polypeptide hormones by using 125I-labelled anti(-immunoglobulin G) antibodies. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):607–616. doi: 10.1042/bj1450607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruck C., Portetelle D., Glineur C., Bollen A. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid by DEAE Affi-Gel blue chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. M., Nakabayashi T., Blix P. M., Rue P. A., Shoelson S. E., Root M. A., Frank B. H., Revers R. R., Rubenstein A. H. A radioimmunoassay for circulating human proinsulin. Diabetes. 1985 Jan;34(1):84–91. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comitti R., Racchetti G., Gnocchi P., Morandi E., Galante Y. M. A monoclonal-based, two-site enzyme immunoassay of human insulin. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 4;99(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Hutton J. C. The insulin-secretory-granule carboxypeptidase H. Purification and demonstration of involvement in proinsulin processing. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):575–582. doi: 10.1042/bj2450575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon C. F., Conlon J. M. Measurement of circulating human proinsulin concentrations using a proinsulin-specific antiserum. Diabetes. 1985 May;34(5):491–497. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.5.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Given B. D., Cohen R. M., Shoelson S. E., Frank B. H., Rubenstein A. H., Tager H. S. Biochemical and clinical implications of proinsulin conversion intermediates. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1398–1405. doi: 10.1172/JCI112116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray I. P., Siddle K., Docherty K., Frank B. H., Hales C. N. Proinsulin in human serum: problems in measurement and interpretation. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1984 Jul;21(1):43–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1984.tb00134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray I. P., Siddle K., Frank B. H., Hales C. N. Characterization and use in immunoradiometric assay of monoclonal antibodies directed against human proinsulin. Diabetes. 1987 Jun;36(6):684–688. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.6.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Woodhead J. S. Labeled antibodies and their use in the immunoradiometric assay. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):334–355. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartling S. G., Dinesen B., Kappelgård A. M., Faber O. K., Binder C. ELISA for human proinsulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1986 May 15;156(3):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(86)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heding L. G. Determination of total serum insulin (IRI) in insulin-treated diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1972 Aug;8(4):260–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01225569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mako M. E., Starr J. I., Rubenstein A. H. Circulating proinsulin in patients with maturity onset diabetes. Am J Med. 1977 Dec;63(6):865–869. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. E., Hales C. N. Labelled antibodies and immunological assay systems. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):186–189. doi: 10.1038/219186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Anderson D. M., Ehrlich P. H. A circular antibody-antigen complex is responsible for increased affinity shown by mixtures of monoclonal antibodies to human chorionic gonadotropin. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1900–1905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rahilly S., Turner R. C., Matthews D. R. Impaired pulsatile secretion of insulin in relatives of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 12;318(19):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805123181902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. E., Brunner M. R., Duckworth W. C., Hooker C. S., Frank B. H. Receptor binding and biological potency of several split forms (conversion intermediates) of human proinsulin. Studies in cultured IM-9 lymphocytes and in vivo and in vitro in rats. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):13989–13994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainbow S. J., Woodhead J. S., Yue D. K., Luzio S. D., Hales C. N. Measurement of human proinsulin by an indirect two-site immunoradiometric assay. Diabetologia. 1979 Oct;17(4):229–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01235859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Gorden P., Pastan I. "Big insulin": a new component of plasma insulin detected by immunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):138–145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan K., Hashida S., Yoshitake S., Ishikawa E., Wakisaka O., Yamamoto Y., Ichioka T., Nakajima K. A more sensitive and less time-consuming sandwich enzyme immunoassay for insulin in human serum with less serum interference. Ann Clin Biochem. 1986 Jan;23(Pt 1):54–58. doi: 10.1177/000456328602300106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M., Siddle K. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against human thyroid stimulating hormone. J Immunol Methods. 1982;51(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Oyer P. E. The biosynthesis of insulin and a probable precursor of insulin by a human islet cell adenoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):473–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple R. C., Carrington C. A., Luzio S. D., Owens D. R., Schneider A. E., Sobey W. J., Hales C. N. Insulin deficiency in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1989 Feb 11;1(8633):293–295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivonen E., Hemmilä I., Marniemi J., Jørgensen P. N., Zeuthen J., Lövgren T. Two-site time-resolved immunofluorometric assay of human insulin. Clin Chem. 1986 Apr;32(4):637–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward W. K., Paquette T. L., Frank B. H., Porte D., Jr A sensitive radioimmunoassay for human proinsulin, with sequential use of antisera to C-peptide and insulin. Clin Chem. 1986 May;32(5):728–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead J. S., Addison G. M., Hales C. N. Radioimmunoassay and saturation analysis. The immunoradiometric assay and related techniques. Br Med Bull. 1974 Jan;30(1):44–49. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Assay of plasma insulin in human subjects by immunological methods. Nature. 1959 Nov 21;184(Suppl 21):1648–1649. doi: 10.1038/1841648b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka M., Taniguchi H., Kawaguchi A., Kobayashi T., Murakami K., Seki M., Tsutou A., Tamagawa M., Minoda H., Baba S. Evaluation of a commercial enzyme immunoassay for insulin in human serum, and its clinical application. Clin Chem. 1979 Jan;25(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


