Abstract
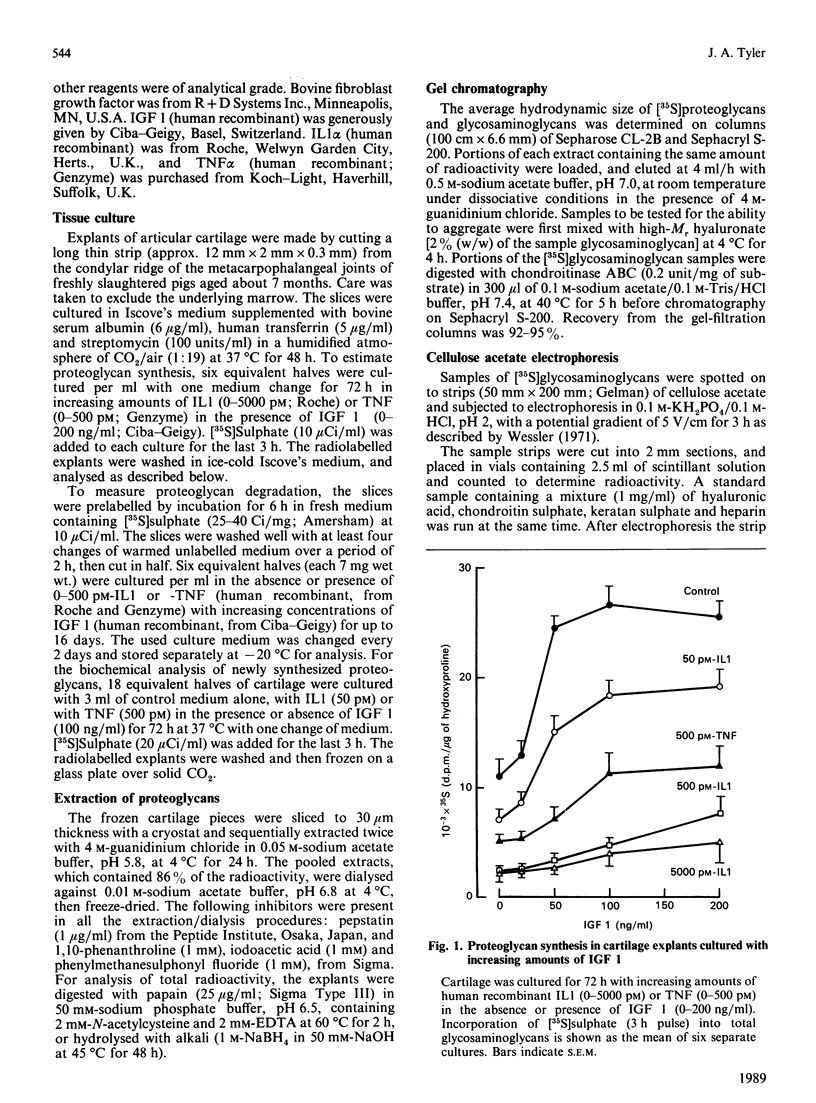
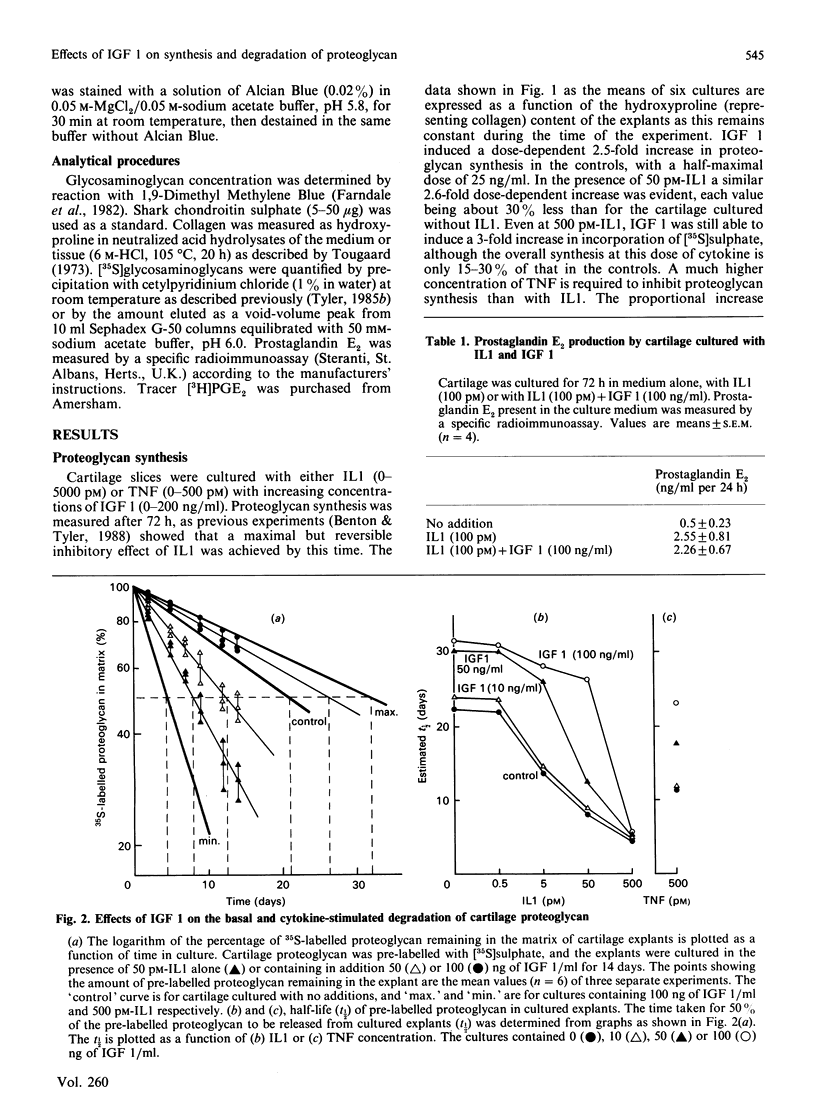
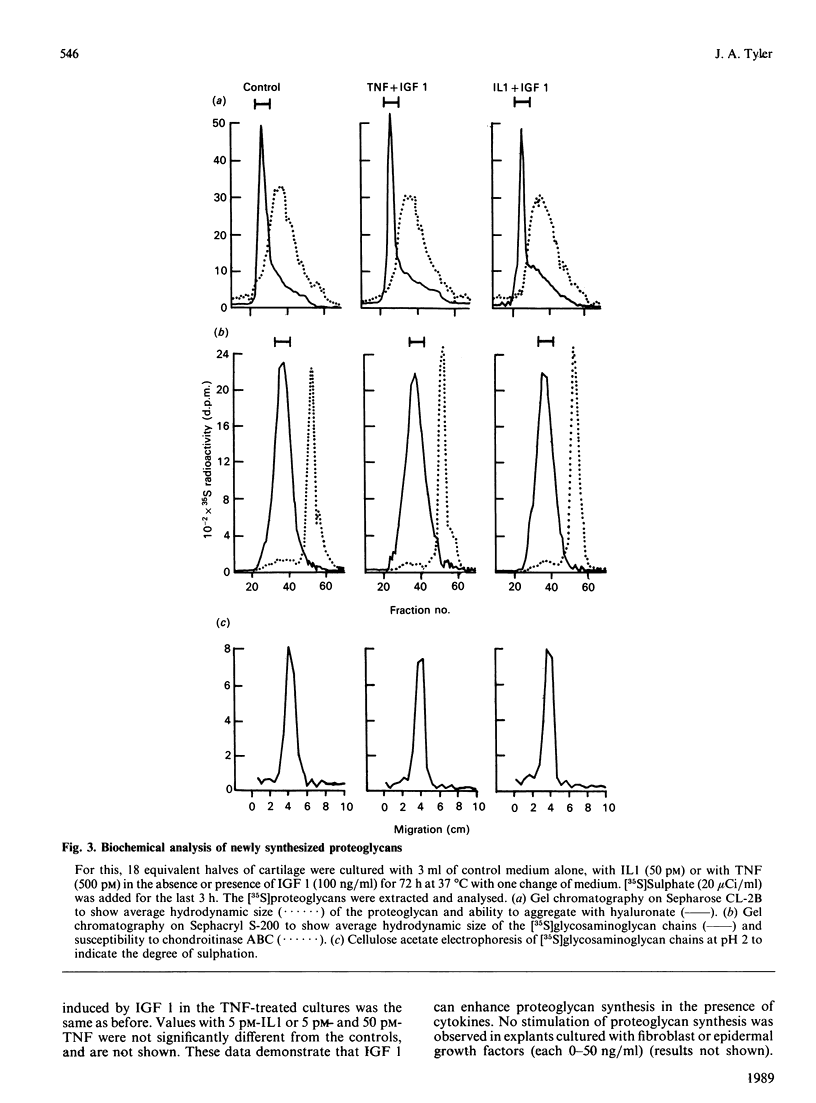
A model system of explanted cartilage has been used in vitro to determine whether insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF 1), which promotes matrix formation is effective in the presence of cytokines such as interleukin 1 (IL1) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF), which induce net matrix depletion. IGF 1 induced a dose-dependent 2.5-fold stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis, with a half-maximal dose of 25 ng/ml. A similar relative increase occurred in response to IGF 1 (10-100 ng/ml) in cartilage cultured also with IL1 or TNF (5-500 pM). There was no detectable qualitative change in the average molecular size or charge of the aggregating proteoglycan synthesized by explants exposed to IGF 1 alone or with IL1 or TNF. The increased production of prostaglandin E2, which is initiated when IL1 or TNF bind to the chondrocytes, was the same in the presence or absence of IGF 1. The time taken for 50% of pre-labelled proteoglycan to be released from the explants (t1/2) increased in the presence of IGF 1 (100 ng/ml) from 21 to 32 days in control cultures and from 8 to 26 days in cartilage cultured with IL1 (50 pM). It is concluded that IGF 1 enhances the synthesis of aggregating proteoglycan in cartilage exposed to cytokines and can directly decrease both the basal and the cytokine-stimulated degradation of proteoglycan in cartilage.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard F. J., Read L. C., Francis G. L., Bagley C. J., Wallace J. C. Binding properties and biological potencies of insulin-like growth factors in L6 myoblasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj2330223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton H. P., Tyler J. A. Inhibition of cartilage proteoglycan synthesis by interleukin I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90703-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D., Nimni M. E. The stability of the collagen phenotype during stimulated collagen, glycosaminoglycan, and DNA synthesis by articular cartilage organ cultures. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Feb;192(2):327–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farndale R. W., Sayers C. A., Barrett A. J. A direct spectrophotometric microassay for sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cartilage cultures. Connect Tissue Res. 1982;9(4):247–248. doi: 10.3109/03008208209160269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenther H. L., Guenther H. E., Froesch E. R., Fleisch H. Effect of insulin-like growth factor on collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis by rabbit articular chondrocytes in culture. Experientia. 1982 Aug 15;38(8):979–981. doi: 10.1007/BF01953688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Handley C. J., McQuillan D. J., Hascall G. K., Robinson H. C., Lowther D. A. The effect of serum on biosynthesis of proteoglycans by bovine articular cartilage in culture. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 1;224(1):206–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraki Y., Inoue H., Hirai R., Kato Y., Suzuki F. Effect of transforming growth factor beta on cell proliferation and glycosaminoglycan synthesis by rabbit growth-plate chondrocytes in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 2;969(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson G. E., Tuke M. A., Dingle J. T., Barrett A. J., Horsfield P. H. The effects of proteolytic enzymes on the mechanical properties of adult human articular cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 28;428(3):741–760. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer T., Oppenheim J. J., Jasin H. E. Human interleukin 1 mediates cartilage matrix degradation. Cell Immunol. 1985 Mar;91(1):92–99. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas A., Bannon C. Measurement of swelling pressure in cartilage and comparison with the osmotic pressure of constituent proteoglycans. Biorheology. 1981;18(3-6):619–632. doi: 10.3233/bir-1981-183-624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillan D. J., Handley C. J., Campbell M. A., Bolis S., Milway V. E., Herington A. C. Stimulation of proteoglycan biosynthesis by serum and insulin-like growth factor-I in cultured bovine articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):423–430. doi: 10.1042/bj2400423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillan D. J., Handley C. J., Robinson H. C. Control of proteoglycan biosynthesis. Further studies on the effect of serum on cultured bovine articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):741–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2370741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri A. M., Panayi G. S., Goodman S. M. Cytokines and the chronic inflammation of rheumatic disease. I. The presence of interleukin-1 in synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):295–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettipher E. R., Higgs G. A., Henderson B. Interleukin 1 induces leukocyte infiltration and cartilage proteoglycan degradation in the synovial joint. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8749–8753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Sarsfield S. J., Townsend Y. Pig interleukin 1. Purification of two immunologically different leukocyte proteins that cause cartilage resorption, lymphocyte activation, and fever. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1208–1222. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J. Tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulates resorption and inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan in cartilage. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):547–549. doi: 10.1038/322547a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. D., Brown H. L., Lowther D. A. Control of proteoglycan synthesis. Studies on the activation of synthesis observed during culture of articular cartilages. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):119–130. doi: 10.1042/bj1880119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth in hypophysectomized rats. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):252–253. doi: 10.1038/296252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. Reversible collapse of rabbit ears after intravenous papain, and prevention of recovery by cortisone. J Exp Med. 1956 Aug 1;104(2):245–252. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tougaard L. The degree of mineralization in bone tissue. The phosphorus-hydroxyproline ratio determined on small amounts of bone tissue. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1973 Dec;32(4):351–355. doi: 10.3109/00365517309084358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. A. Articular cartilage cultured with catabolin (pig interleukin 1) synthesizes a decreased number of normal proteoglycan molecules. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):869–878. doi: 10.1042/bj2270869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. A. Chondrocyte-mediated depletion of articular cartilage proteoglycans in vitro. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):493–507. doi: 10.1042/bj2250493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. P., Maroudas A., Bayliss M. T., Dillon J. Swelling pressures of proteoglycans at the concentrations found in cartilaginous tissues. Biorheology. 1979;16(6):447–464. doi: 10.3233/bir-1979-16609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler E. Electrophoresis of acidic glycosaminoglycans in hydrochloric acid: a micro method for sulfate determination. Anal Biochem. 1971 May;41(1):67–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumstein P., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences that are regulated by insulin-like growth factor I. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11252–11260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


