Abstract
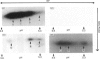
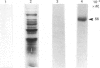
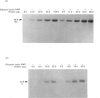
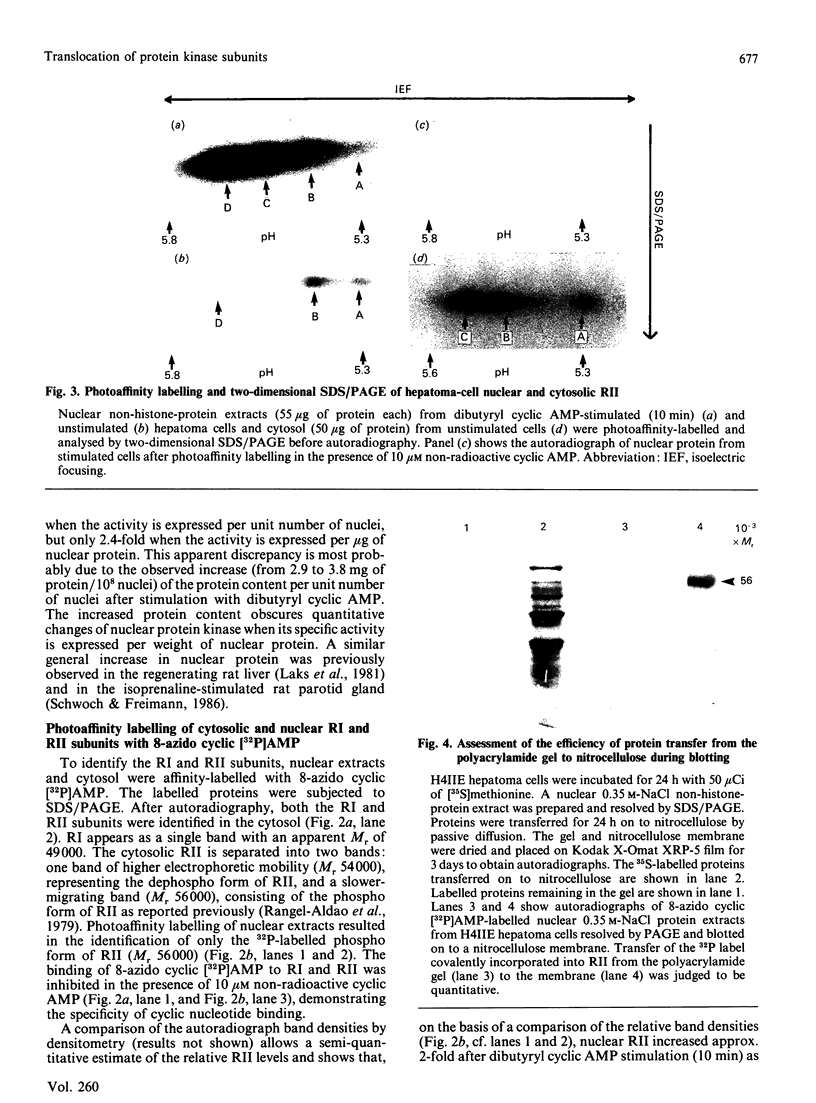
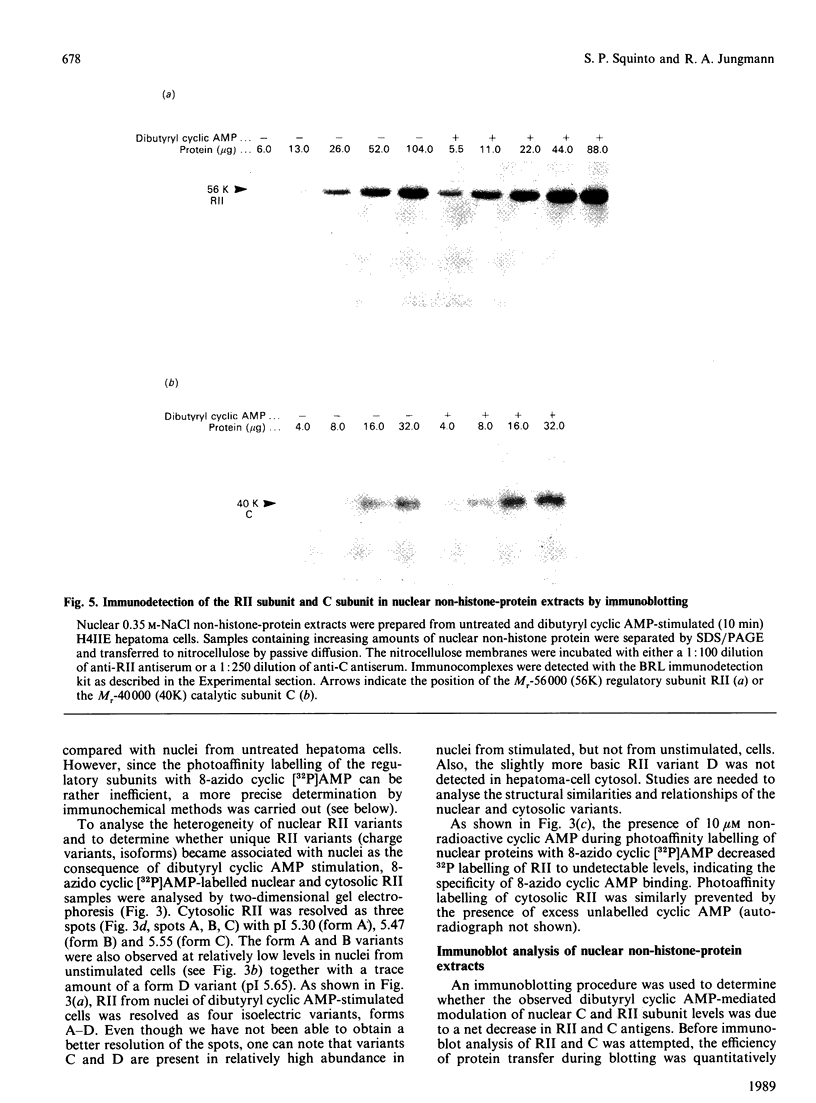
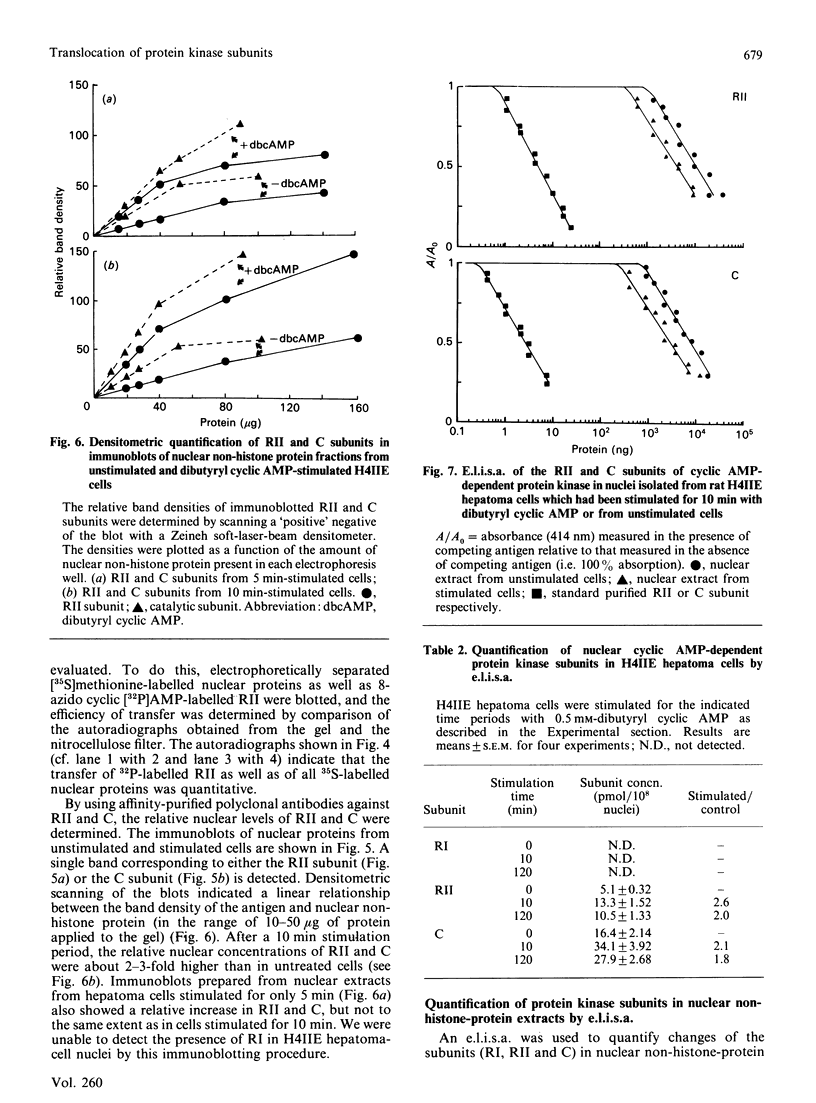
Biochemical and immunochemical studies were undertaken to quantify the effects of cyclic AMP on cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunit levels in nuclei of H4IIE hepatoma cells. Dibutyryl cyclic AMP (10 microM) caused a significant biphasic (10 and 120 min after stimulation) increase in total nuclear protein kinase activity. The increase observed 10 min after dibutyryl cyclic AMP stimulation was primarily due to an approx. 3-fold increase of catalytic (C) subunit activity, whereas the change observed 120 min after stimulation consisted of an increase in both C subunit and cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase activities. Analysis of nuclear protein extracts by photoaffinity labelling with 8-azido cyclic [32P]AMP identified only the type II regulatory subunit (RII), but not the type I regulatory subunit (RI). Analysis of nuclear RII variants by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis demonstrated that dibutyryl cyclic AMP caused the appearance of two RII variant forms which were not present in the nuclei of unstimulated cells. Using affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies and immunoblotting procedures, we identified an approx. 2-fold increase in the RII and C subunits in nuclear extracts of dibutyryl cyclic AMP-treated hepatoma cells. Finally, the RI, RII and C subunits were quantified by an e.l.i.s.a. which indicated that dibutyryl cyclic AMP increased nuclear RII and C subunits levels biphasically, reaching peak values 10 and 120 min after the initial stimulation. Nuclear RI subunit levels were not affected. These results provide qualitative as well as quantitative evidence for a modulation by cyclic AMP of the nuclear RII and C subunit levels in rat H4IIE hepatoma cells, and indicate a relatively rapid but temporarily limited dibutyryl cyclic AMP-induced translocation of the RII and C subunits to nuclear sites.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby C. D., Walsh D. A. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor protein of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:350–358. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boney C., Fink D., Schlichter D., Carr K., Wicks W. D. Direct evidence that the protein kinase catalytic subunit mediates the effects of cAMP on tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4911–4918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho-Chung Y. S., Archibald D., Clair T. Cyclic AMP receptor triggers nuclear protein phosphorylation in a hormone-dependent mammary tumor cell-free system. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1390–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.224463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho-Chung Y. S., Clair T., Bodwin J. S., Berghoffer B. Growth arrest and morphological change of human breast cancer cells by dibutyryl cyclic AMP and L-arginine. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.6269181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho-Chung Y. S. Hypothesis. Cyclic AMP and its receptor protein in tumor growth regulation in vivo. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(3):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou A. I., Squinto S. P., Jungmann R. A. The phosphoform of the regulatory subunit RII of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase possesses intrinsic topoisomerase activity. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., Lincoln T. M., Keely S. L. Compartmentalization of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in heart tissue. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3854–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culpepper J. A., Liu A. Y. Pretranslational control of tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis by 8-bromo-cyclic AMP in H-4 rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13812–13819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derda D. F., Miles M. F., Schweppe J. S., Jungmann R. A. Cyclic AMP regulation of lactate dehydrogenase. Isoproterenol and N6,O2'-dibutyryl cyclic AMP increase the levels of lactate dehydrogenase-5 isozyme and its messenger RNA in rat C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11112–11121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dills W. L., Goodwin C. D., Lincoln T. M., Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Corbin J. D., Krebs E. G. Purification of cyclic nucleotide receptor proteins by cyclic nucleotide affinity chromatography. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:199–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., Andreone T., Sasaki K., Beale E. Inhibition of transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene by insulin. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):549–551. doi: 10.1038/305549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Price D. J., Goodman H. M., Avruch J. Recombinant fragment of protein kinase inhibitor blocks cyclic AMP-dependent gene transcription. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):530–533. doi: 10.1126/science.2821622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn J. M., Ballard F. J., Hanson R. W. Infulence of hormones and medium composition on the degradation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) and total protein in Reuber H35 cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3586–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. J., Schwoch G., Schweppe J. S., Jungmann R. A. Phosphorylative modification of histone H1 subspecies following isoproterenol and N6,O2'-dibutyryl cyclic AMP stimulation of rat C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13602–13609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A., Kelley D. C., Miles M. F., Milkowski D. M. Cyclic AMP regulation of lactate dehydrogenase. Isoproterenol and N6,O2-dibutyryl cyclic amp increase the rate of transcription and change the stability of lactate dehydrogenase a subunit messenger RNA in rat C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5312–5318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A., Kuettel M. R., Squinto S. P., Kwast-Welfeld J. Using immunocolloidal gold electron microscopy to investigate cAMP-dependent protein kinase cellular compartmentalization. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:225–235. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keely S. L., Jr, Corbin J. D., Park C. R. On the question of translocation of heart cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1501–1504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettel M. R., Schwoch G., Jungmann R. A. Localization of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in rat hepatocyte nuclei by immunogold electron microscopy. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1984 Nov;8(11):949–957. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(84)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettel M. R., Squinto S. P., Kwast-Welfeld J., Schwoch G., Schweppe J. S., Jungmann R. A. Localization of nuclear subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by the immunocolloidal gold method. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):965–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwast-Welfeld J., Jungmann R. A. Hormonal regulation of nuclear cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunit levels in rat ovaries. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14343–14350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laks M. S., Harrison J. J., Schwoch G., Jungmann R. A. Modulation of nuclear protein kinase activity and phosphorylation of histone H1 subspecies during the prereplicative phase of rat liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8775–8785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers W. H., Hanson R. W., Meisner H. M. cAMP stimulates transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5137–5141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A. Action of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent histone kinase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5763–5765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. K., Schweppe J. S., Jungmann R. A. Phosphorylation of rat C6 glioma cell DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II in vivo. Identification of phosphorylated subunits and modulation of phosphorylation by isoproterenol and N6,O2'-dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14695–14701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mednieks M. I., Jungmann R. A. Selective expression of type I and type II cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases in subcellular fractions of concanavalin A-stimulated rat thymocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jan;213(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray S. A., Byus C. V., Fletcher W. H. Intracellular kinetics of free catalytic units dissociated from adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in adrenocortical tumor cells (Y-1). Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):364–374. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesterova M. V., Ulmasov K. A., Abdukarimov A., Aripdzhanov A. A., Severin E. S. Nuclear translocation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Apr;132(2):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M., Dutly F. Rapid and reversible translocation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II from the Golgi complex to the nucleus. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2801–2806. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Schäfer G., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M. Cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase type II is associated with the Golgi complex and with centrosomes. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangel-Aldao R., Kupiec J. W., Rosen O. M. Resolution of the phosphorylated and dephosphorylated cAMP-binding proteins of bovine cardiac muscle by affinity labeling and two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2499–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisine T., Rougon G., Barbet J., Affolter H. U. Corticotropin-releasing factor-induced adrenocorticotropin hormone release and synthesis is blocked by incorporation of the inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase into anterior pituitary tumor cells by liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8261–8265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Cripe T. P., Koch S. R., Andreone T. L., Petersen D. D., Beale E. G., Granner D. K. Multihormonal regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene transcription. The dominant role of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15242–15251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. P., Costa E. Protein kinase translocation following beta-adrenergic receptor activation in C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2943–2948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Freimann A. Quantitative changes in the catalytic and regulatory subunits of nuclear cAMP-dependent protein kinases type I and type II during isoproterenol-induced growth of the rat parotid gland. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Hamann A. Determination and comparative analysis of the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate-dependent protein kinase by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):109–117. doi: 10.1042/bj2080109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Hamann A., Hilz H. Antiserum against the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Reactivity towards various protein kinases. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj1920223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Hilz H. Time-dependent translocation of protein kinase in liver of glucagon-treated rats. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 1;90(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabb J. B., Granner D. K. Separation of topoisomerase I activity from the regulatory subunit of type II cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Apr;2(4):324–331. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-4-324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Kelley-Geraghty D. C., Kuettel M. R., Jungmann R. A. Ultrastructural localization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in regenerating rat hepatocytes using immunogold electron microscopy. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(1):65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M., Murdoch G. H., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Cyclic AMP regulation of eukaryotic gene transcription by two discrete molecular mechanisms. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):267–269. doi: 10.1126/science.2990047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimalasena J., Wicks W. D. Coordinate protein kinase activation and specific enzyme induction by cyclic nucleotide derivatives in intact cultured hepatoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(2):449–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]