Abstract
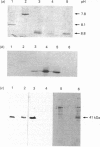
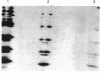
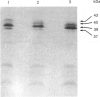
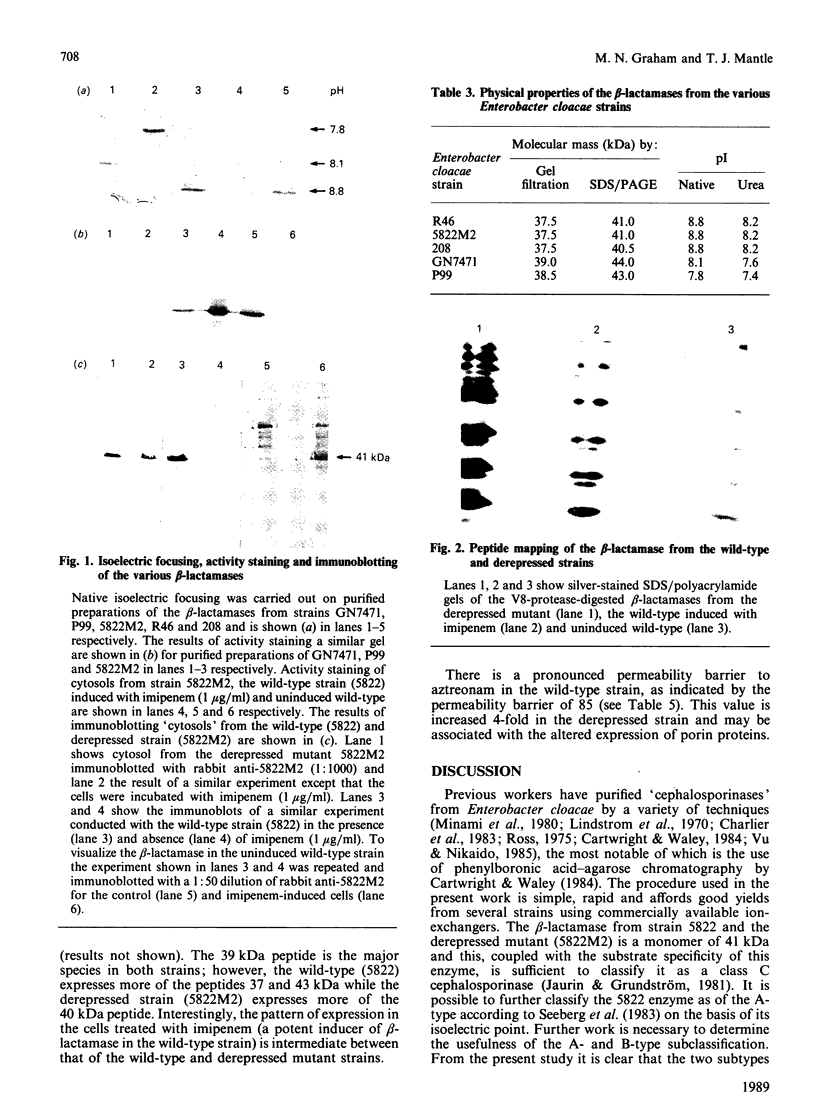
Enterobacter cloacae strain 5822 expresses low levels of a class C beta-lactamase which can be induced 100-fold by imipenem. Mutants that constitutively express high levels of beta-lactamase can be selected on aztreonam or cefotaxime. The beta-lactamase from one such mutant (5822M2) has been purified to homogeneity and compared on the basis of subunit Mr, pI, substrate specificity, inhibitor sensitivity and immunological cross-reactivity with the enzyme from strains P99, GN7471 and 208, which have been studied previously. The enzyme from strain 5822M2 is clearly related to these other forms and is of the A-type according to the criteria of Seeberg, Tolxdorff-Neutzling & Wiedemann [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. (1983) 23, 918-925]. The enzyme from the wild-type strain (5822) is shown to be identical to that found in the depressed strain (5822M2), indicating that the mutation is in a regulatory gene. A detailed analysis of the kinetics of the enzyme from strain 5822M2 shows that all of the beta-lactams studied are substrates and that a mechanism involving the formation of an acyl-enzyme is probably applicable in every case. The substrates however can clearly be grouped into two classes, i.e. 'good' substrates with kcat. values of 80-1200 s-1 and 'poor' substrates/good inhibitors with kcat. values of 0.009-0.00007 s-1. The permeability barrier to aztreonam is 4-fold less in the derepressed strain when compared with the wild-type strain. This is associated with significant changes in the expression of outer membrane porins. The observed resistance in the derepressed mutant appears to be linked to the elevated levels of beta-lactamase (3000-fold) rather than to the modest changes in the permeability barrier.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bush K., Freudenberger J. S., Sykes R. B. Interaction of azthreonam and related monobactams with beta-lactamases from gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Tanaka S. K., Bonner D. P., Sykes R. B. Resistance caused by decreased penetration of beta-lactam antibiotics into Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):555–560. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright S. J., Waley S. G. Purification of beta-lactamases by affinity chromatography on phenylboronic acid-agarose. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):505–512. doi: 10.1042/bj2210505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlier P., Dideberg O., Frère J. M., Moews P. C., Knox J. R. Crystallographic data for the beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae P99. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 5;171(2):237–238. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., East S. J., Cornford R. J., Walker L. A. Properties of spontaneous Enterobacter cloacae mutants with temperature-conditional derepression of type I beta-lactamase synthesis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Apr;19(4):417–427. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEMING P. C., GOLDNER M., GLASS D. G. Observations on the nature, distribution, and significance of cephalosporinase. Lancet. 1963 Jun 29;1(7296):1399–1401. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Comeau D., Norioka S., Inouye M. Localization and membrane topology of EnvZ, a protein involved in osmoregulation of OmpF and OmpC in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16433–16438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. The comparative beta-lactamase resistance and inhibitory activity of 1-oxa cephalosporin, cefoxitin and cefotaxime. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979 Sep;32(9):909–914. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.32.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galleni M., Frère J. M. A survey of the kinetic parameters of class C beta-lactamases. Penicillins. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):119–122. doi: 10.1042/bj2550119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galleni M., Lindberg F., Normark S., Cole S., Honore N., Joris B., Frere J. M. Sequence and comparative analysis of three Enterobacter cloacae ampC beta-lactamase genes and their products. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):753–760. doi: 10.1042/bj2500753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gootz T. D., Sanders C. C., Goering R. V. Resistance to cefamandole: derepression of beta-lactamases by cefoxitin and mutation in Enterobacter cloacae. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jul;146(1):34–42. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T. ampC cephalosporinase of Escherichia coli K-12 has a different evolutionary origin from that of beta-lactamases of the penicillinase type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojo H., Shigi Y., Nishida M. A novel method for evaluating the outer membrane permeability to beta-lactamase-stable beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Mar;33(3):310–316. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojo H., Shigi Y., Nishida M. Enterobacter cloacae outer membrane permeability to ceftizoxime (FK 749) and five other new cephalosporin derivatives. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Mar;33(3):317–321. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. F., Allan B. J., Minshew B. H., Sherris J. C. Mutational enzymatic resistance of Enterobacter species to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):655–660. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Normark S. Common mechanism of ampC beta-lactamase induction in enterobacteria: regulation of the cloned Enterobacter cloacae P99 beta-lactamase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):758–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.758-763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linström E. B., Boman H. G., Steele B. B. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. VI. Purification and characterization of the chromosomally mediated penicillinase present in ampA-containing strains. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):218–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.218-231.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Bronstein H., van Selm N., Peters R. Peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane proteins in gammegatine bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):571–578. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura M., Nakazawa H., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and biochemical properties of beta-lactamase produced by Proteus rettgeri. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):687–690. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of a cephalosporinase from Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):853–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okonogi K., Kuno M., Kida M., Mitsuhashi S. Beta-lactamase stability and antibacterial activity of cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a novel cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):171–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. The beta-lactamase stability of a novel beta-lactam antibiotic containing a 7 alpha-methoxyoxacephem nucleus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jul;6(4):445–453. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.4.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. W. Beta-lactamase (Enterobacter species). Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:678–687. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance during therapy with the newer beta-lactam antibiotics: role of inducible beta-lactamases and implications for the future. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):639–648. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Microbial resistance to newer generation beta-lactam antibiotics: clinical and laboratory implications. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):399–406. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L., Angehrn P. Trapping of nonhydrolyzable cephalosporins by cephalosporinases in Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a possible resistance mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):711–717. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen R. T., Kreike J., Groot G. S. Protein transfer to nitrocellulose filters. A simple method for quantitation of single proteins in complex mixtures. FEBS Lett. 1981 Feb 23;124(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu H., Nikaido H. Role of beta-lactam hydrolysis in the mechanism of resistance of a beta-lactamase-constitutive Enterobacter cloacae strain to expanded-spectrum beta-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):393–398. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner V., Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V. Role of beta-lactamases and outer membrane proteins in multiple beta-lactam resistance of Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):455–459. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Rosselet A. Function of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a permeability barrier to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]