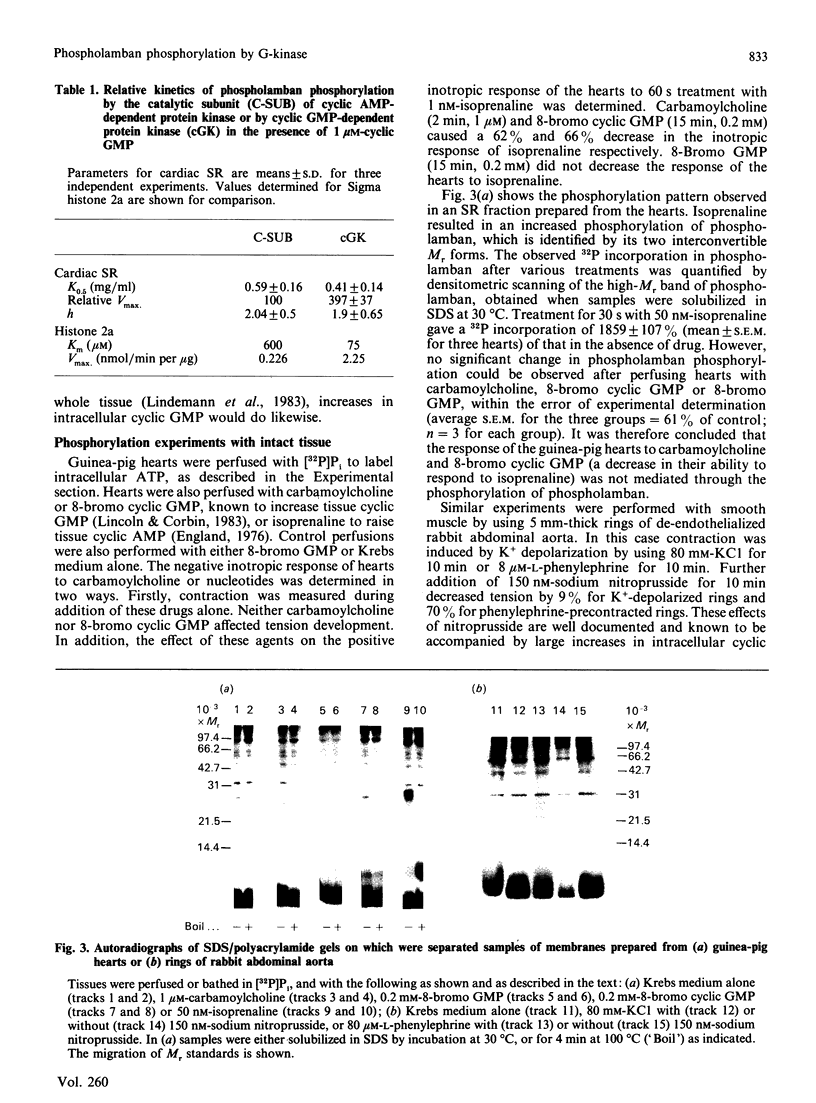
Abstract
1. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates purified phospholamban. It also phosphorylates phospholamban present in vesicles of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and smooth muscle microsomal fractions, and in transformants of Escherichia coli which contain a plasmid into which a gene encoding phospholamban has been inserted. 2. In vitro the phospholamban present in cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes is a better substrate for cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase than for cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. 3. Studies using [32P]Pi to label the cellular ATP in intact cardiac or smooth muscle failed to demonstrate that phosphorylation of phospholamban occurs in response to stimuli which increase intracellular cyclic GMP. Possible reasons for this functional separation between increased cyclic GMP and phosphorylation of phospholamban are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltensperger K., Carafoli E., Chiesi M. The Ca2+-pumping ATPase and the major substrates of the cGMP-dependent protein kinase in smooth muscle sarcolemma are distinct entities. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 15;172(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J. Correlation between contraction and phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin in perfused rat heart. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J. Studies on the phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin during modification of contraction in perfused rat heart. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):295–304. doi: 10.1042/bj1600295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiscus R. R., Rapoport R. M., Waldman S. A., Murad F. Atriopeptin II elevates cyclic GMP, activates cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase and causes relaxation in rat thoracic aorta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 30;846(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores R. A rapid and reproducible assay for quantitative estimation of proteins using bromophenol blue. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):605–611. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii J., Ueno A., Kitano K., Tanaka S., Kadoma M., Tada M. Complete complementary DNA-derived amino acid sequence of canine cardiac phospholamban. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):301–304. doi: 10.1172/JCI112799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Nakamura H. Cyclic GMP regulation of the plasma membrane (Ca2+-Mg2+)ATPase in vascular smooth muscle. J Biochem. 1987 Jan;101(1):287–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation by guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of synthetic peptide analogs of a site phosphorylated in histone H2B. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1196–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T. EDRF and cyclic GMP control gating of receptor-operated calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul 31;126(3):341–343. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Sweet R. W., Sathe G., Yokoyama S., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Wigler M., Rosenberg M. Purification and characterization of human H-ras proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1015–1024. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggins J. P., England P. J. Evidence for a phosphorylation-induced conformational change in phospholamban from the effects of three proteases. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 8;217(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kanmura Y., Kuriyama H., Sasaguri T. Nitroglycerine- and isoprenaline-induced vasodilatation: assessment from the actions of cyclic nucleotides. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):393–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. R., Simmerman H. K., Wilson W. W., Gurd F. R., Wegener A. D. Purification and characterization of phospholamban from canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7721–7730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai H., Kanaide H., Matsumoto T., Nakamura M. 8-Bromoguanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate decreases intracellular free calcium concentrations in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells from rat aorta. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchberger M. A., Antonetz T. Phospholamban: dissociation of the 22,000 molecular weight protein of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum into 11,000 and 5,500 molecular weight forms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 15;105(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranias E. G., Di Salvo J. A phospholamban protein phosphatase activity associated with cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10029–10032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M., Hall C. L., Park C. R., Corbin J. D. Guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate binding proteins in rat tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M. cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:62–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann J. P., Jones L. R., Hathaway D. R., Henry B. G., Watanabe A. M. beta-Adrenergic stimulation of phospholamban phosphorylation and Ca2+-ATPase activity in guinea pig ventricles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malencik D. A., Anderson S. R. Characterization of a fluorescent substrate for the adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):34–40. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90422-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel N., Wibo M., Godfraind T. A calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+ pump in rat aorta plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 9;644(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Alteration of cytoplasmic ionized calcium levels in smooth muscle by vasodilators in the ferret. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:539–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ousterhout J. M., Sperelakis N. Cyclic nucleotides depress action potentials in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 24;144(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks T. P., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Jamieson J. D. The cyclic nucleotide-dependent phosphorylation of aortic smooth muscle membrane proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jun;255(2):361–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini A., Hartshorne D. J. Ordered phosphorylation of the two 20 000 molecular weight light chains of smooth muscle myosin. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):470–476. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu L. M., Panoiu C., Hinescu M., Nutu O. The mechanism of cGMP-induced relaxation in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 8;107(3):393–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers L., Hofmann F., Casteels R. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates phospholamban in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum from cardiac and smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):269–273. doi: 10.1042/bj2520269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers L., Jones L. R. Evidence for the presence of phospholamban in the endoplasmic reticulum of smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 19;882(2):258–265. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Draznin M. B., Murad F. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat aorta may be mediated through cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):174–176. doi: 10.1038/306174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Waldman S. A., Schwartz K., Winquist R. J., Murad F. Effects of atrial natriuretic factor, sodium nitroprusside, and acetylcholine on cyclic GMP levels and relaxation in rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 24;115(2-3):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90694-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashatwar S. S., Cornwell T. L., Lincoln T. M. Effects of 8-bromo-cGMP on Ca2+ levels in vascular smooth muscle cells: possible regulation of Ca2+-ATPase by cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5685–5689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Beham R. A. Catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:51–55. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Beham R. A. Catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:51–55. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suematsu E., Hirata M., Kuriyama H. Effects of cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases, and calmodulin on Ca2+ uptake by highly purified sarcolemmal vesicles of vascular smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90552-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Kirchberger M. A., Repke D. I., Katz A. M. The stimulation of calcium transport in cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum by adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6174–6180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener A. D., Jones L. R. Phosphorylation-induced mobility shift in phospholamban in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Evidence for a protein structure consisting of multiple identical phosphorylatable subunits. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1834–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. F., Desselberger U., Palese P., Ferguson B., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Efficient expression of influenza virus NS1 nonstructural proteins in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6105–6109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]