Abstract
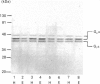
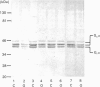
In human adipocyte plasma membranes, pertussis toxin catalysed the ADP-ribosylation of an apparently single 40 kDa protein. The same protein was also observed in Western blots by using an antibody which identifies the C-terminal decapeptide of Gi alpha (alpha subunit of Gi). In analogous experiments, cholera toxin and an antibody raised against the C-terminal decapeptide of Gs alpha (alpha subunit of Gs) were used to identify two proteins of 42 and 45 kDa, the former of which was more prominent. A method was developed to estimate the relative amounts of Gi and Gs in crude adipocyte plasma membranes in a single immunoblot by using the two antisera. In animal models, changes in the amounts of G-proteins have been suggested to explain alterations in hormone-responsiveness in hypothyroidism and obesity. However, the amounts of Gi and Gs were unaltered in thyroidectomized papillary-carcinoma patients who had been without hormone substitution for 4 weeks. In adipocyte plasma membranes prepared from markedly obese subjects, the amounts of both Gi alpha and Gs alpha as calculated per mg of protein were decreased, but the Gi/Gs ratio remained unaltered in comparison with control subjects.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong K. J., Stouffer J. E., Van Inwegen R. G., Thompson W. J., Robison G. A. Effects of thyroid hormone deficiency on cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and control of lipolysis in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4226–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Carter A., Simons C., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8893–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chohan P., Carpenter C., Saggerson E. D. Changes in the anti-lipolytic action and binding to plasma membranes of N6-L-phenylisopropyladenosine in adipocytes from starved and hypothyroid rats. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2230053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correze C., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Nunez J. Hormone-dependent lipolysis in fat-cells from thyroidectomized rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1974 Oct;1(5):309–327. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(74)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Vernet L. Accumulation and inactivation of adenosine by fat cells from hypothyroid rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Jun;121(2):155–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Milligan G., Pines M., Goldsmith P., Codina J., Klee W., Spiegel A. Use of specific antibodies to quantitate the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. Expression of cDNAs for G proteins in Escherichia coli. Two forms of Gs alpha stimulate adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11375–11381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Gawler D. J., Milligan G., Wilson A. Multiple defects occur in the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein system in liver plasma membranes of obese (fa/fa) but not lean (Fa/Fa) Zucker rats: loss of functional Gi and abnormal Gs function. Cell Signal. 1989;1(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Rapiejko P. J., Mangano T. J. Fat cell adenylate cyclase system. Enhanced inhibition by adenosine and GTP in the hypothyroid rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2558–2564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., McKenzie F. R. Opioid peptides promote cholera-toxin-catalysed ADP-ribosylation of the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gi) in membranes of neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):369–373. doi: 10.1042/bj2520369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Saggerson E. D. Chemically induced hypothyroidism produces elevated amounts of the alpha subunit of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein (Gi) and the beta subunit common to all G-proteins. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):223–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2470223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Techniques used in the identification and analysis of function of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2550001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills I., García-Sainz J. A., Fain J. N. Pertussis toxin effects on adenylate cyclase activity, cyclic AMP accumulation and lipolysis in adipocytes from hypothyroid, euthyroid and hyperthyroid rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 21;876(3):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohisalo J. J., Ranta S., Huhtaniemi I. T. Attenuated adenosine R-site effect in adipocytes in obesity. Metabolism. 1986 Feb;35(2):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohisalo J. J., Stoneham S., Keso L. Thyroid status and adenosine content of adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):555–557. doi: 10.1042/bj2460555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohisalo J. J., Stouffer J. E. Adenosine, thyroid status and regulation of lipolysis. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):249–251. doi: 10.1042/bj1780249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelsen B., Pedersen O., Sørensen N. S. Reduced binding and antilipolytic effect of prostaglandin E2 in adipocytes from patients with hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Feb;62(2):258–262. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-2-258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelsen B. Prostaglandin E2 action and binding in human adipocytes: effects of sex, age, and obesity. Metabolism. 1988 Mar;37(3):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros M., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Steady-state levels of G-proteins and beta-adrenergic receptors in rat fat cells. Permissive effects of thyroid hormones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4362–4368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist U., Efendić S., Jereb B., Ostman J. Influence of the hypothyroid state on lipolysis in human adipose tissue in vitro. Hypothyroid state and lipolysis. Acta Med Scand. 1971 May;189(5):381–384. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1971.tb04394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D. Sensitivity of adipocyte lipolysis to stimulatory and inhibitory agonists in hypothyroidism and starvation. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):387–394. doi: 10.1042/bj2380387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahrenberg H., Engfeldt P., Arner P., Wennlund A., Ostman J. Adrenergic regulation of lipolysis in human adipocytes: findings in hyper- and hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Sep;63(3):631–638. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-3-631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward J. A., Saggerson E. D. Effect of adenosine deaminase, N6-phenylisopropyladenosine and hypothyroidism on the responsiveness of rat brown adipocytes to noradrenaline. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):395–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2380395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Imoto Y., Codina J., Hamilton S. L., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The stimulatory G protein of adenylyl cyclase, Gs, also stimulates dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Evidence for direct regulation independent of phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase or stimulation by a dihydropyridine agonist. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9887–9895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]