Abstract
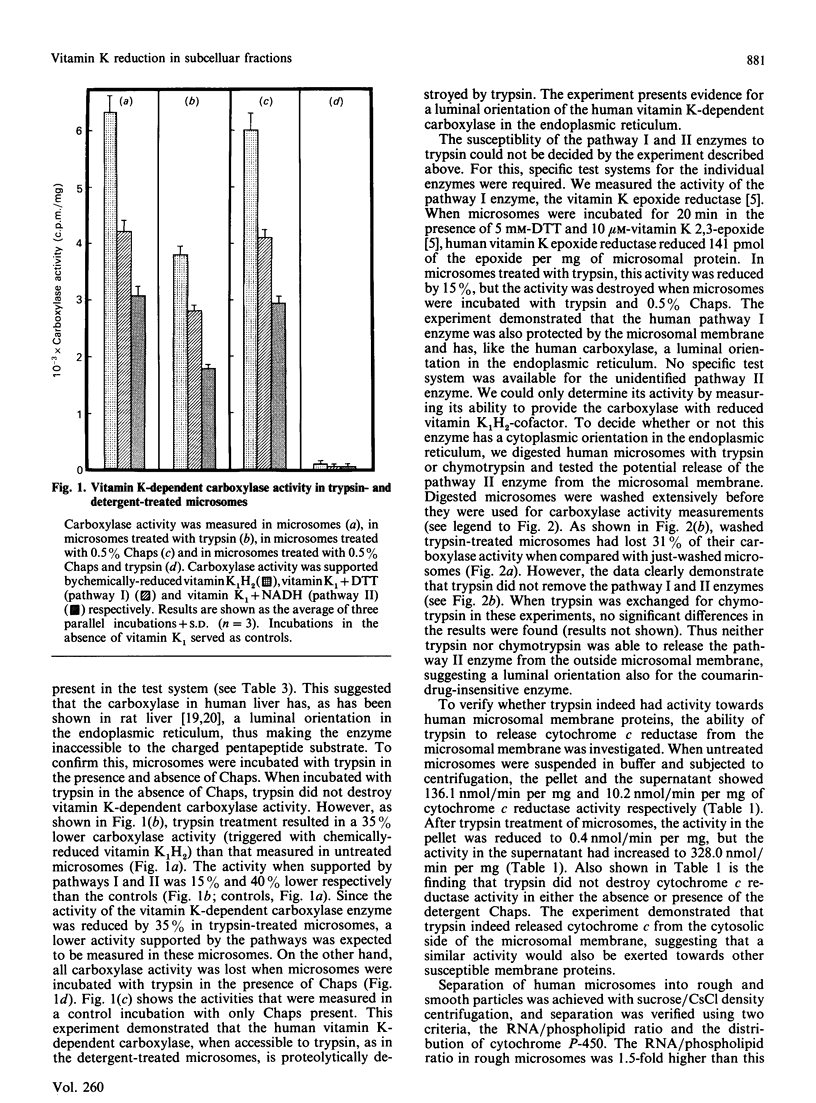
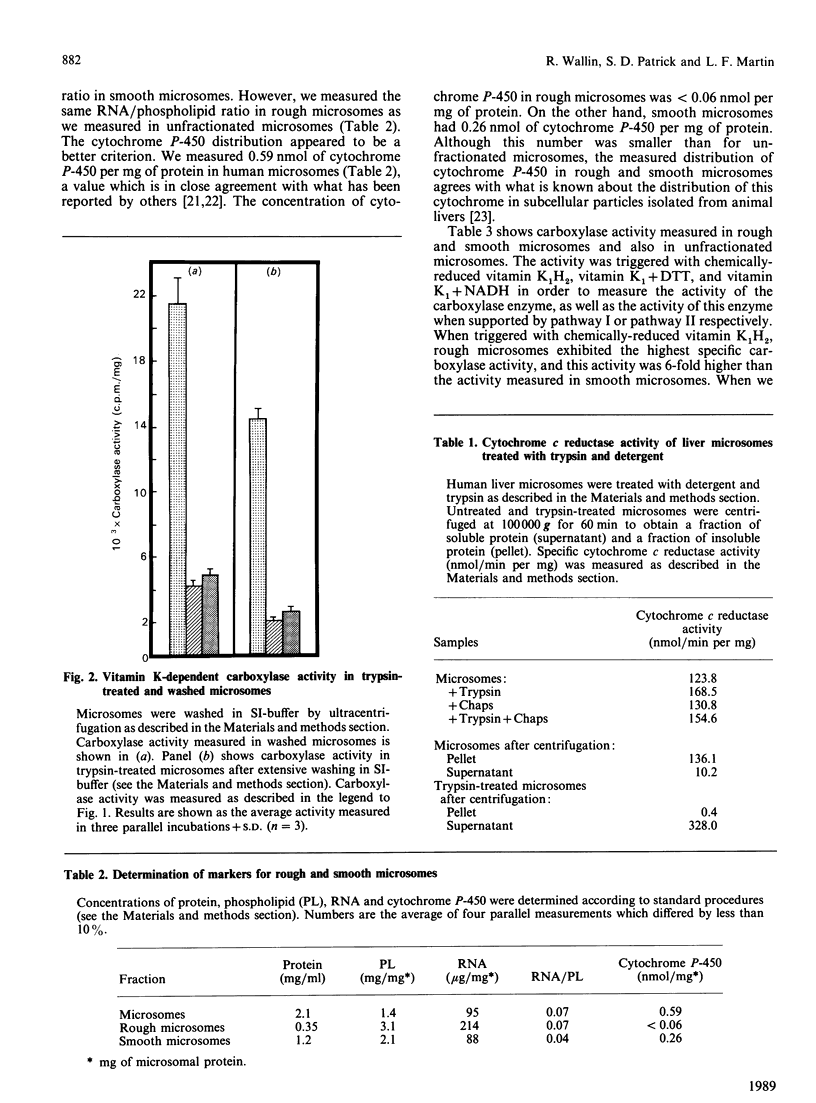
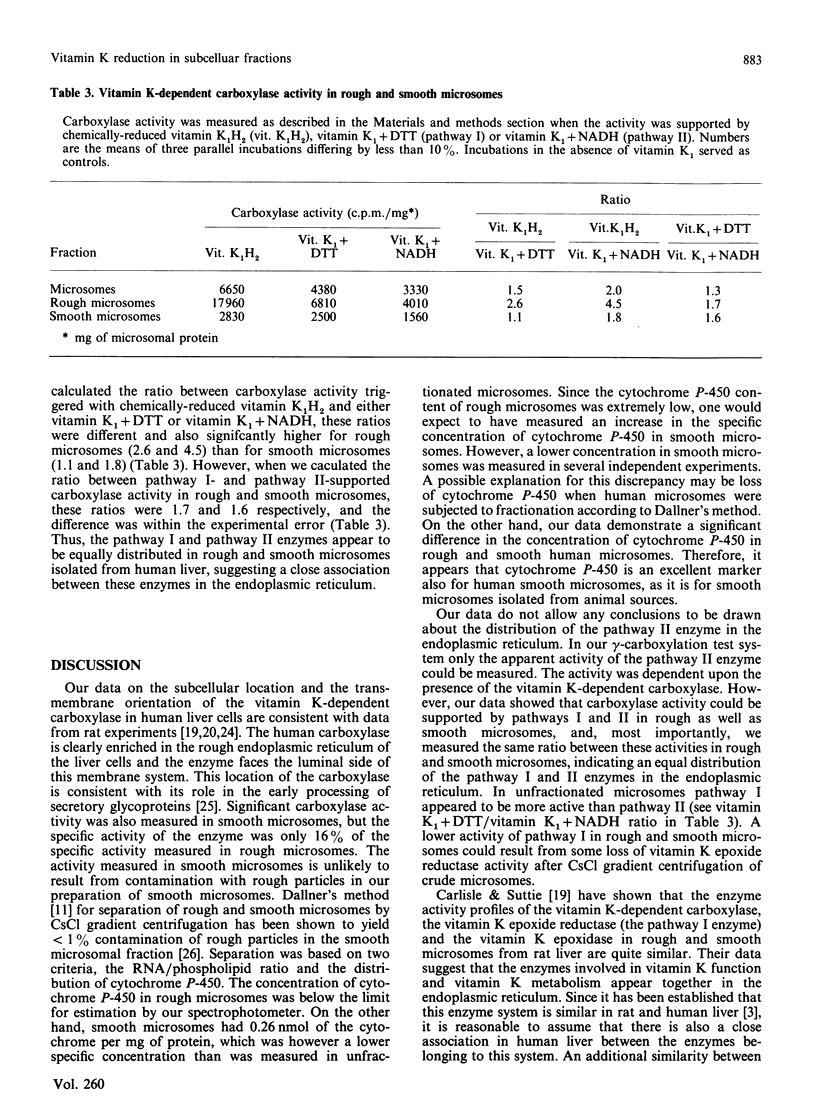
The antidotal effect of vitamin K in overcoming poisoning by coumarin anticoagulant drugs is mediated by a vitamin K-reducing enzyme of the endoplasmic reticulum [Wallin & Martin (1987) Biochem. J. 241, 389-396]. With microsomes obtained from human liver biopsies, we have investigated the localization and the transverse orientation of this enzyme in the endoplasmic reticulum and compared its orientation to that of the other enzymes of the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation system. All enzymes were protected by the microsomal membrane and thus appear to have a luminal orientation in the endoplasmic reticulum, consistent with their role in the vitamin K-dependent modification of secretory glycoproteins. Separation of rough and smooth microsomes showed that vitamin K-dependent carboxylase activity was 6-fold higher in rough than in smooth microsomes. Vitamin K1 reduction by the coumarin-drug-sensitive (pathway I) and -insensitive (pathway II) enzymes of the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation system was the same in rough and smooth microsomes. The data suggest a close association between the pathway I and II enzymes in the endoplasmic reticulum. These pathways may be partial reactions of multienzyme complex which carries out the various activities associated with the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford A. J., Pain V. M. Effect of diabetes on the rates of synthesis and degradation of ribosomes in rat muscle and liver in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4059–4065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlisle T. L., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K dependent carboxylase: subcellular location of the carboxylase and enzymes involved in vitamin K metabolism in rat liver. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1161–1167. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G. Isolation of rough and smooth microsomes--general. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:191–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Solubilization and properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6238–6243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram T. E. Separation of hepatic smooth and rough microsomes associated with drug-metabolizing enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:225–237. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland L. The submicrosomal site for the conversion of prothrombin precursor to biologically active prothrombin in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 29;499(2):181–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. F., Patrick S. D., Wallin R. DT-diaphorase in morbidly obese patients. Cancer Lett. 1987 Sep;36(3):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(87)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura S., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Tashiro Y. Immunoelectron microscope localization of cytochrome P-450 on microsomes and other membrane structures of rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):503–519. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus M. E., Boobis A. R., Pacifici G. M., Frempong R. Y., Brodie M. J., Kahn G. C., Whyte C., Davies D. S. Xenobiotic metabolism in the human lung. Life Sci. 1980 Feb 11;26(6):481–487. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Mueller H. K., Dick B., Meyer U. A. Hepatic monooxygenase activities in subjects with a genetic defect in drug oxidation. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):682–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. II. SOLUBILIZATION, PURIFICATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski J. A., Esmon C. T., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Requirements of the rat liver microsomal enzyme system. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2770–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W. Mechanism of action of vitamin K: synthesis of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(2):191–223. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Hutson S. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. Evidence that at least two microsomal dehydrogenases reduce vitamin K1 to support carboxylation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1583–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Martin L. F. Early processing of prothrombin and factor X by the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9994–10001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Martin L. F. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation and vitamin K metabolism in liver. Effects of warfarin. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1879–1884. doi: 10.1172/JCI112182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Martin L. F. Warfarin poisoning and vitamin K antagonism in rat and human liver. Design of a system in vitro that mimics the situation in vivo. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):389–396. doi: 10.1042/bj2410389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Patrick S. D., Ballard J. O. Vitamin K antagonism of coumarin intoxication in the rat. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):235–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Prydz H. Studies on a subcellular system for vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. Thromb Haemost. 1979 May 25;41(3):529–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R. Vitamin K antagonism of coumarin anticoagulation. A dehydrogenase pathway in rat liver is responsible for the antagonistic effect. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):685–693. doi: 10.1042/bj2360685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




