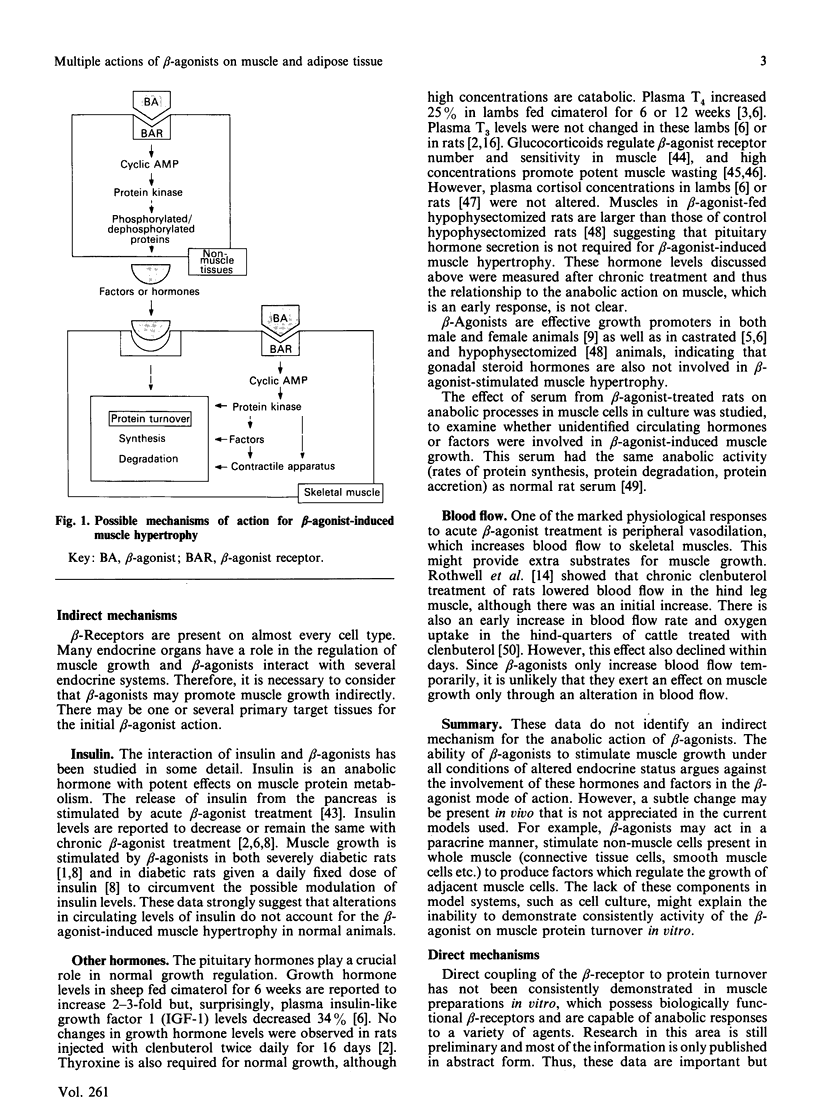
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apperley G. H., Daly M. J., Levy G. P. Selectivity of beta-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on bronchial, skeletal, vascular and cardiac muscle in the anaesthetized cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;57(2):235–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Ainsworth A. T., Cawthorne M. A., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Thody V. E., Wilson C., Wilson S. Atypical beta-adrenoceptor on brown adipocytes as target for anti-obesity drugs. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):163–165. doi: 10.1038/309163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Ainsworth A. T. Thermogenic and antiobesity activity of a novel beta-adrenoceptor agonist (BRL 26830A) in mice and rats. Am J Clin Nutr. 1983 Oct;38(4):549–558. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/38.4.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrup A., Bülow J., Madsen J., Christensen N. J. Contribution of BAT and skeletal muscle to thermogenesis induced by ephedrine in man. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E507–E515. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett J. M. Metabolic effects of catecholamines in sheep. Aust J Biol Sci. 1970 Aug;23(4):903–914. doi: 10.1071/bi9700903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beermann D. H., Butler W. R., Hogue D. E., Fishell V. K., Dalrymple R. H., Ricks C. A., Scanes C. G. Cimaterol-induced muscle hypertrophy and altered endocrine status in lambs. J Anim Sci. 1987 Dec;65(6):1514–1524. doi: 10.2527/jas1987.6561514x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Nemenoff R. A., Bonventre J. V., Cheung J. Y., Avruch J. Hormonal regulation of protein phosphorylation in isolated rat heart cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):C439–C449. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.5.C439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohorov O., Buttery P. J., Correia J. H., Soar J. B. The effect of the beta-2-adrenergic agonist clenbuterol or implantation with oestradiol plus trenbolone acetate on protein metabolism in wether lambs. Br J Nutr. 1987 Jan;57(1):99–107. doi: 10.1079/bjn19870013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojanic D., Nahorski S. R. Identification and subclassification of rat adipocyte beta-adrenoceptors using (+/-)-[125I]cyanopindolol. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 30;93(3-4):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman W. C., Nott M. W. Actions of sympathomimetic amines and their antagonists on skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1969 Mar;21(1):27–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockway J. M., MacRae J. C., Williams P. E. Side effects of clenbuterol as a repartitioning agent. Vet Rec. 1987 Apr 18;120(16):381–383. doi: 10.1136/vr.120.16.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L., Folléa N., Paradis A., Collet A. Stereospecific stimulation of brown adipocyte respiration by catecholamines via beta 1-adrenoreceptors. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):E552–E563. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.6.E552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buur T., Clausen T., Holmberg E., Johansson U., Waldeck B. Desensitization by terbutaline of beta-adrenoceptors in the guinea-pig soleus muscle: biochemical alterations associated with functional changes. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;76(2):313–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. J., Lister C. A., Sennitt M. V., Stewart-Long N., Cawthorne M. A. Improved glycemic control in C57Bl/KsJ (db/db) mice after treatment with the thermogenic beta-adrenoceptor agonist, BRL 26830. Diabetes. 1985 Nov;34(11):1198–1204. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.11.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Leighton B., Wilson S., Thurlby P. L., Arch J. R. An investigation of the beta-adrenoceptor that mediates metabolic responses to the novel agonist BRL28410 in rat soleus muscle. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;37(5):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wiley K. S., Bemis K. G. Analysis of the beta 1 and beta 2 adrenoceptor interactions of the partial agonist, clenbuterol (NAB365), in the rat jugular vein and atria. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;320(2):145–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00506314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramb G., Langslow D. R., Phillips J. H. Hormonal effects on cyclic nucleotides and carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in isolated chicken hepatocytes. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1982 Mar;46(3):310–321. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(82)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham S., Leslie P., Hopwood D., Illingworth P., Jung R. T., Nicholls D. G., Peden N., Rafael J., Rial E. The characterization and energetic potential of brown adipose tissue in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Sep;69(3):343–348. doi: 10.1042/cs0690343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies Y., Willemot J., Leblanc J. Protein synthesis, amino acid uptake, and pools during isoproterenol-induced hypertrophy of the rat heart and tibialis muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;59(2):113–121. doi: 10.1139/y81-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S. Excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:293–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P. W., Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J., Winter P. D. Chronic effects of beta 2-adrenergic agonists on body composition and protein synthesis in the rat. Biosci Rep. 1984 Jan;4(1):83–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01120827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellenius E., Hedberg R., Holmberg E., Waldeck B. Functional and metabolic effects of terbutaline and propranolol in fast- and slow-contracting skeletal muscle in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 May;109(1):89–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frielle T., Collins S., Daniel K. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning of the cDNA for the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7920–7924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandemer G., Durand G., Pascal G. Relative contribution of the main tissues and organs to body fatty acid synthesis in the rat. Lipids. 1983 Mar;18(3):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF02534552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Karl I. E., Kipnis D. M. Alanine and glutamine synthesis and release from skeletal muscle. I. Glycolysis and amino acid release. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):826–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Cyclic AMP-modulated phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins in cultured avian myogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Géloën A., Collet A. J., Guay G., Bukowiecki L. J. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of brown adipocyte proliferation. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):C175–C182. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.1.C175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. W., Ballard F. J. The relative significance of acetate and glucose as precursors for lipid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue from ruminants. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):529–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1050529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. H., Moore L. A., Yamashiro S. The receptors responsible for heat production in brown adipose tissue in the young rabbit. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;64(2):133–137. doi: 10.1139/y86-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton G. M., Wagenvoord R. J., Kemp A., Jr, Nicholls D. G. Brown-adipose-tissue mitochondria: photoaffinity labelling of the regulatory site of energy dissipation. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 16;82(2):515–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg A., Mattsson H., Nerme V., Carlsson E. Effects of in vivo treatment with isoprenaline or prenalterol on beta-adrenoceptor mechanisms in the heart and soleus muscle of the cat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;325(3):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00495952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himms-Hagen J. Brown adipose tissue metabolism and thermogenesis. Annu Rev Nutr. 1985;5:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.05.070185.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg E., Waldeck B. Analysis of the beta-receptor mediated effect on fast-contracting skeletal muscle in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;301(2):109–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00501424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring H., Kirsch D., Obermaier B., Ermel B., Machicao F. Decreased tyrosine kinase activity of insulin receptor isolated from rat adipocytes rendered insulin-resistant by catecholamine treatment in vitro. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):59–66. doi: 10.1042/bj2340059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle D. L., Bauman D. E., Garrigus U. S. Lipogenesis in the ruminant: in vivo site of fatty acid synthesis in sheep. J Nutr. 1972 May;102(5):617–623. doi: 10.1093/jn/102.5.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. W., Easter R. A., McKeith F. K., Dalrymple R. H., Maddock H. M., Bechtel P. J. Effect of the beta-adrenergic agonist cimaterol (CL 263,780) on the growth and carcass characteristics of finishing swine. J Anim Sci. 1985 Oct;61(4):905–913. doi: 10.2527/jas1985.614905x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagen L. J., Freedman A. Studies on the effects of acetylcholine, epinephrine, dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate, theophylline, and calcium on the synthesis of myoglobin in muscle cell cultures estimated by radioimmunoassay. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Sep;88(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90627-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama T., Etlinger J. D. Calcium-dependent regulation of protein synthesis and degradation in muscle. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):344–346. doi: 10.1038/279344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Lee Y. B., Dalrymple R. H. Effect of the repartitioning agent cimaterol on growth, carcass and skeletal muscle characteristics in lambs. J Anim Sci. 1987 Nov;65(5):1392–1399. doi: 10.2527/jas1987.6551392x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langslow D. R., Hales C. N. Lipolysis in chicken adipose tissue in vitro. J Endocrinol. 1969 Feb;43(2):285–294. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0430285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J. Heterogeneity of adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Mar 1;24(5):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. E., Anderson P., Goldspink D. F. The effects of calcium on protein turnover in skeletal muscles of the rat. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):257–264. doi: 10.1042/bj2040257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. B., Jefferson L. S. Effect of isoproterenol on amino acid levels and protein turnover in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1977 Feb;232(2):E243–E249. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.232.2.E243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Characterization of beta-adrenergic receptors of human skeletal muscle obtained by needle biopsy. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 1):E795–E798. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.6.E795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières A., Mariani M. M., Sorel G., Savi L. The action of beta-adrenergic blocking and stimulating agents on insulin secretion. Characterization of the type of beta receptor. Diabetologia. 1971 Jun;7(3):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01212541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltin C. A., Delday M. I., Hay S. M., Smith F. G., Reeds P. J. Propranolol apparently separates the physical and compositional characteristics of muscle growth induced by clenbuterol. Biosci Rep. 1987 Jan;7(1):51–57. doi: 10.1007/BF01122727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltin C. A., Delday M. I., Reeds P. J. The effect of a growth promoting drug, clenbuterol, on fibre frequency and area in hind limb muscles from young male rats. Biosci Rep. 1986 Mar;6(3):293–299. doi: 10.1007/BF01115158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltin C. A., Hay S. M., Delday M. I., Smith F. G., Lobley G. E., Reeds P. J. Clenbuterol, a beta agonist, induces growth in innervated and denervated rat soleus muscle via apparently different mechanisms. Biosci Rep. 1987 Jun;7(6):525–532. doi: 10.1007/BF01116510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElligott M. A., Barreto A., Jr, Chaung L. Y. Effect of continuous and intermittent clenbuterol feeding on rat growth rate and muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1989;92(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(89)90215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElligott M. A., Mulder J. E., Chaung L. Y., Barreto A., Jr Clenbuterol-induced muscle growth: investigation of possible mediation by insulin. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):E370–E375. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.4.E370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. A., Goldspink D. F. Glucocorticoid action on protein synthesis and protein breakdown in isolated skeletal muscles. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):641–645. doi: 10.1042/bj2060641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Locke R. M. Thermogenic mechanisms in brown fat. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):1–64. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutting D. F. Anabolic effects of catecholamines in diaphragm muscle from hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):307–317. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hea E. K., Leveille G. A. Lipid biosynthesis and transport in the domestic chick (Gallus domesticus). Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Jul 1;30(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)91309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hea E. K., Leveille G. A. Significance of adipose tissue and liver as sites of fatty acid synthesis in the pig and the efficiency of utilization of various substrates for lipogenesis. J Nutr. 1969 Nov;99(3):338–344. doi: 10.1093/jn/99.3.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odedra B. R., Bates P. C., Millward D. J. Time course of the effect of catabolic doses of corticosterone on protein turnover in rat skeletal muscle and liver. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):617–627. doi: 10.1042/bj2140617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pires E., Perry S. V., Thomas M. A. Myosin light-chain kinase, a new enzyme from striated muscle. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogátsa G., Tamás J., Jr, Dubecz E. Effect of catecholamines on insulin secretion and liver glycogenolysis in the rat. Horm Metab Res. 1978 Sep;10(5):378–381. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Goodman D. B. Relationships between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):421–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeds P. J., Hay S. M., Dorwood P. M., Palmer R. M. Stimulation of muscle growth by clenbuterol: lack of effect on muscle protein biosynthesis. Br J Nutr. 1986 Jul;56(1):249–258. doi: 10.1079/bjn19860104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr A role for alpha-adrenergic receptors in abnormal insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):791–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI108338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochet N., Tanti J. F., Grémeaux T., Van Obberghen E., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Effect of a thermogenic agent, BRL 26830A, on insulin receptors in obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 1):E101–E109. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.2.E101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodemann H. P., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. The stimulation of protein degradation in muscle by Ca2+ is mediated by prostaglandin E2 and does not require the calcium-activated protease. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8716–8723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Beaudoin J. Phosphorylation of purified insulin receptor by cAMP kinase. Diabetes. 1987 Jan;36(1):123–126. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J., Sudera D. K. Beta-adrenoreceptors in rat brown adipose tissue: proportions of beta 1- and beta 2-subtypes. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 1):E397–E402. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.4.E397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J., Sudera D. K. Changes in tissue blood flow and beta-receptor density of skeletal muscle in rats treated with the beta2-adrenoceptor agonist clenbuterol. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;90(3):601–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D. The regulation of glyceride synthesis in isolated white-fat cells. The effects of palmitate and lipolytic agents. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1057–1067. doi: 10.1042/bj1281057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salleo A., Anastasi G., La Spada G., Falzea G., Denaro M. G. New muscle fiber production during compensatory hypertrophy. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1980;12(4):268–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidegger K., O'Connell M., Robbins D. C., Danforth E., Jr Effects of chronic beta-receptor stimulation on sympathetic nervous system activity, energy expenditure, and thyroid hormones. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 May;58(5):895–903. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-5-895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid A., Renaud J. F., Lazdunski M. Short term and long term effects of beta-adrenergic effectors and cyclic AMP on nitrendipine-sensitive voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13041–13046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schudt C., Pette D. Ca2+ -ions as coupling agents in enzymatic differentiation and carbohydrate metabolism of cultured muscle cells. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1977 Oct 3;16:121–139. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(78)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver G., Etlinger J. D. Regulation of myofibrillar accumulation in chick muscle cultures: evidence for the involvement of calcium and lysosomes in non-uniform turnover of contractile proteins. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2383–2391. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Levy A. L., Sennitt M. V., Simson D. L., Cawthorne M. A. Effects of BRL 26830, a novel beta-adrenoceptor agonist, on glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and glucose turnover in Zucker (fa/fa) rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 15;34(14):2425–2429. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Dana R., Krichevsky A., Bilezikian J. P., Schonberg M. Inhibition of beta-adrenergic responsiveness in muscle cell cultures by dexamethasone. Endocrinology. 1981 Dec;109(6):2110–2116. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-6-2110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanti J. F., Grémeaux T., Rochet N., Van Obberghen E., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Effect of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase on insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):19–26. doi: 10.1042/bj2450019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro N. Effects of isoprenaline on contractions of directly stimulated fast and slow skeletal muscles of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 May;48(1):121–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlby P. L., Ellis R. D. Differences between the effects of noradrenaline and the beta-adrenoceptor agonist BRL 28410 in brown adipose tissue and hind limb of the anaesthetized rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;64(8):1111–1114. doi: 10.1139/y86-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck B., Jeppsson A. B., Widmark E. Partial agonism and functional selectivity: a study on beta-adrenoceptor mediated effects in tracheal, cardiac and skeletal muscle. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1986 Mar;58(3):209–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1986.tb00096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Beermann D. H. Reduced calcium-dependent proteinase activity in cimaterol-induced muscle hypertrophy in lambs. J Anim Sci. 1988 Oct;66(10):2545–2550. doi: 10.2527/jas1988.66102545x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson-Wright W. M., Wilkinson M. The muscle slice--a new preparation for the characterization of beta-adrenergic binding in fast- and slow-twitch skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve. 1986 Jun;9(5):416–422. doi: 10.1002/mus.880090506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. E., Pagliani L., Innes G. M., Pennie K., Harris C. I., Garthwaite P. Effects of a beta-agonist (clenbuterol) on growth, carcass composition, protein and energy metabolism of veal calves. Br J Nutr. 1987 May;57(3):417–428. doi: 10.1079/bjn19870049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Wilson S., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Arch J. R. The rat lipolytic beta-adrenoceptor: studies using novel beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 May 4;100(3-4):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman R. J., Kameyama T., Matsumoto K., Bernstein P., Etlinger J. D. Regulation of protein degradation in muscle by calcium. Evidence for enhanced nonlysosomal proteolysis associated with elevated cytosolic calcium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13619–13624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman R. J., Ludemann R., Easton T. G., Etlinger J. D. Slow to fast alterations in skeletal muscle fibers caused by clenbuterol, a beta 2-receptor agonist. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 1):E726–E732. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.6.E726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman R. J., Ludemann R., Etlinger J. D. Clenbuterol, a beta 2-agonist, retards atrophy in denervated muscles. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 1):E152–E155. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.1.E152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]