Abstract
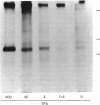
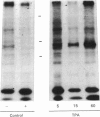
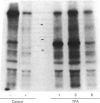
As a means of determining the role of protein kinase C in the signal transduction from novel growth factors and hormones, we investigated the effects of well-characterized agents on the phosphorylation state of protein kinase C itself. These studies show that agents that stimulate protein kinase C either directly (phorbol esters) or indirectly through phosphatidylinositol breakdown (platelet-derived growth factor) induce an increase in the phosphorylation state of the kinase. By contrast, epidermal growth factor, which does not stimulate protein kinase C in fibroblasts, does not increase the phosphorylation state of protein kinase C, but leads to a decrease. The data suggest that the phosphorylation state of protein kinase C is dynamically controlled and can be used to provide evidence of protein kinase C activation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashendel C. L. The phorbol ester receptor: a phospholipid-regulated protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 9;822(2):219–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Watson S. P., Cuatrecasas P. Lack of association of epidermal growth factor-, insulin-, and serum-induced mitogenesis with stimulation of phosphoinositide degradation in BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):723–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Witters L. A., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Quamo S. N. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13304–13315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey D. L., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Blackshear P. J. Protein kinase C in fibroblasts. Characteristics of its intracellular location during growth and after exposure to phorbol esters and other mitogens. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2234–2243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa-Sasaki H. Early changes in inositol lipids and their metabolites induced by platelet-derived growth factor in quiescent Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):99–109. doi: 10.1042/bj2320099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Chan K. F., Singh T. J., Nakabayashi H., Huang F. L. Autophosphorylation of rat brain Ca2+-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12134–12140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Nakabayashi H., Huang F. L. Isozymic forms of rat brain Ca2+-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan L. C., Aitken A., Heath J., Foulkes J. G. Embryonal carcinoma-derived growth factor activates protein kinase C in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):921–926. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Koshland D. E., Jr Domain structure and phosphorylation of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2291–2297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Walaas S. I., Greengard P. Neuronal phosphoproteins: physiological and clinical implications. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1357–1364. doi: 10.1126/science.6474180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Goris J., Merlevede W. Specificity of protein phosphatases in the dephosphorylation of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):63–67. doi: 10.1042/bj2400063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena M., Smith K. A. Phorbol esters, phospholipase C, and growth factors rapidly stimulate the phosphorylation of a Mr 80,000 protein in intact quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7244–7248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Rodriguez-Pena A., Young S., Rozengurt E., Parker P. J. Quantitation of protein kinase C by immunoblot--expression in different cell lines and response to phorbol esters. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jan;130(1):111–117. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Parker P. J., Ullrich A., Stabel S. Down-regulation of protein kinase C is due to an increased rate of degradation. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):775–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2440775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Rothbard J., Parker P. J. A monoclonal antibody recognising the site of limited proteolysis of protein kinase C. Inhibition of down-regulation in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]