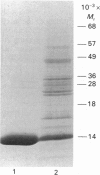
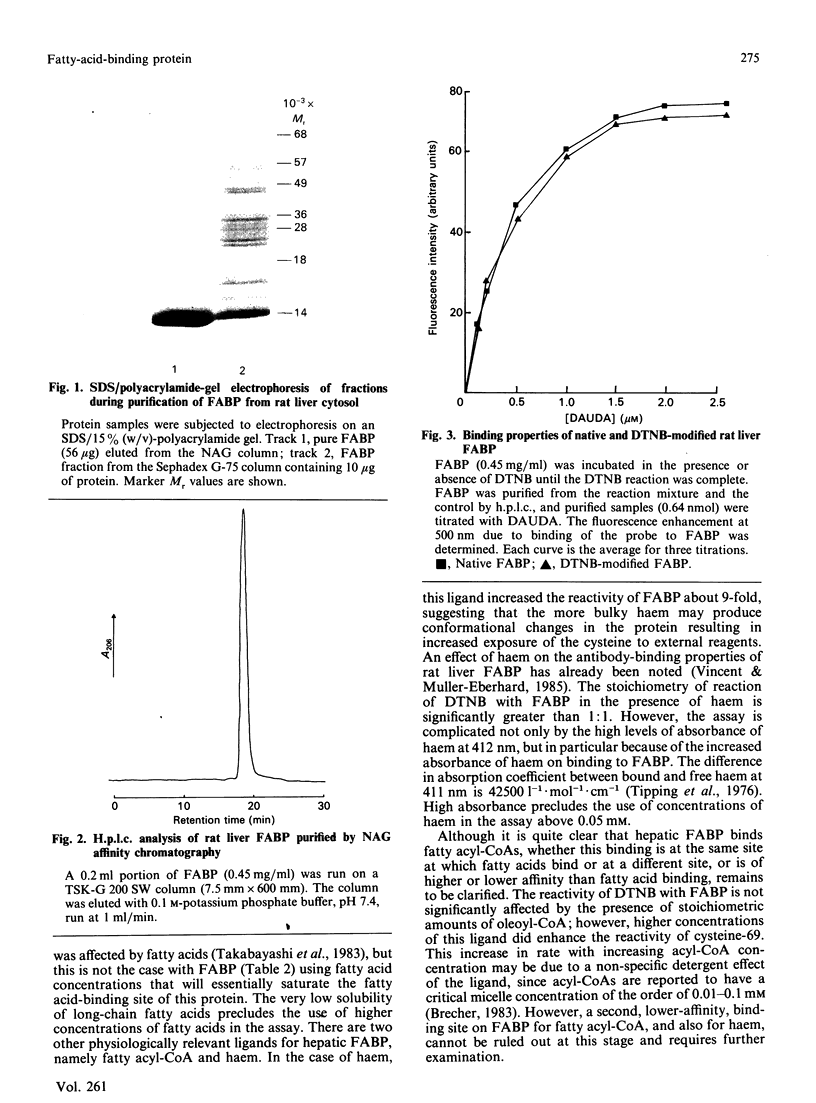
Abstract
1. A new, simple and high-yield procedure is described for the purification of hepatic fatty-acid-binding protein from rat liver using naphthylaminodecyl-agarose as an affinity column. 2. Cysteine-69 is shown to react slowly, but quantitatively, with 5,5'-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB), indicating that the thiol group is free, but may be buried within the protein. 3. Fatty acids do not affect the DTNB reactivity of this cysteine residue; however, cysteine reactivity is enhanced in the presence of haem and oleoyl-CoA. 4. Fatty-acid-binding protein that has been modified with DTNB is still able to bind the fluorescent fatty acid 11-(dansylamino)undecanoic acid, indicating that cysteine-69 may be remote from the fatty-acid-binding site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassuk J. A., Tsichlis P. N., Sorof S. Liver fatty acid binding protein is the mitosis-associated polypeptide target of a carcinogen in rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecher P. The interaction of long-chain acyl CoA with membranes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;57(1):3–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00223520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatz J. F., Veerkamp J. H. Intracellular fatty acid-binding proteins. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima Y., Nakagawa S., Tachibana Y., Kozuka H. Effects of peroxisome proliferators on fatty acid-binding protein in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 1;754(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer B., Tipping E., Hackney J. F., Beale D. A low-molecular-weight protein from rat liver that resembles ligandin in its binding properties. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 1;155(3):511–521. doi: 10.1042/bj1550511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. S., Walsh M. P., Nemcek K., Johnson J. D. Biologically active fluorescent derivatives of spinach calmodulin that report calmodulin target protein binding. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):991–996. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel J. K., Hunter M. J. Bovine mercaptalbumin and non-mercaptalbumin monomers. Interconversions and structural differences. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7391–7406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A., Kane J. P. Fatty acid binding protein. Isolation from rat liver, characterization, and immunochemical quantification. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7872–7878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddles P. W., Blakeley R. L., Zerner B. Reassessment of Ellman's reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:49–60. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchettini J. C., Gordon J. I., Banaszak L. J. The structure of crystalline Escherichia coli-derived rat intestinal fatty acid-binding protein at 2.5-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5815–5819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifried S. E., Wang Y., von Hippel P. H. Fluorescent modification of the cysteine 202 residue of Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13511–13514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Heuckeroth R. O., Gordon J. I. The metabolic significance of mammalian fatty-acid-binding proteins: abundant proteins in search of a function. Annu Rev Nutr. 1987;7:337–359. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.07.070187.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabayashi K., Imada T., Saito Y., Inada Y. Coupling between fatty acid binding and sulfhydryl oxidation in bovine serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 2;136(2):291–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping E., Ketterer B., Christodoulides L., Enderby G. The interactions of haem with ligandin and aminoazo-dye-binding protein A. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):461–467. doi: 10.1042/bj1570461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. H., Muller-Eberhard U. A protein of the Z class of liver cytosolic proteins in the rat that preferentially binds heme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14521–14528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson T. C., Wilton D. C. Studies on fatty acid-binding proteins. The binding properties of rat liver fatty acid-binding protein. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):485–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2470485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson T. C., Wilton D. C. Studies on fatty acid-binding proteins. The detection and quantification of the protein from rat liver by using a fluorescent fatty acid analogue. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):419–424. doi: 10.1042/bj2380419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan S. X., Haug A. Ligand-triggered conformational perturbations elicit changes at the single cysteinyl residue of spinach calmodulin. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 15;175(1):119–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]