Abstract
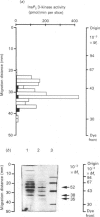
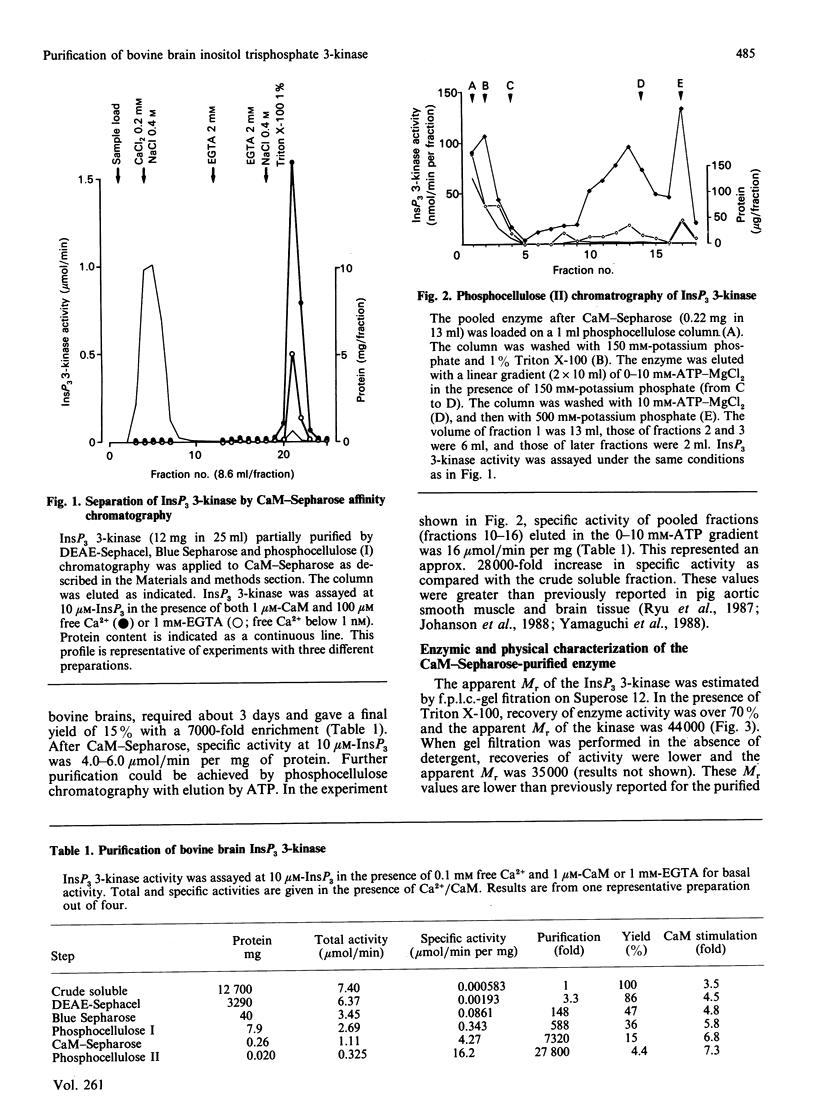
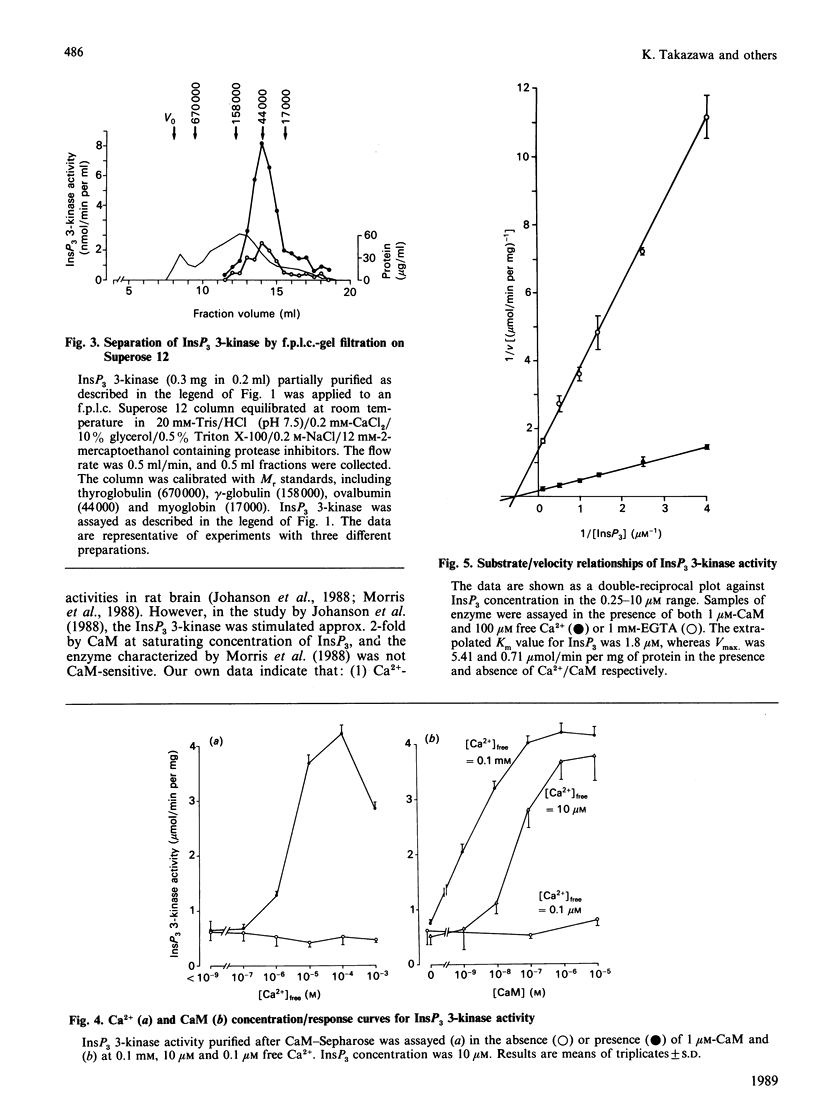
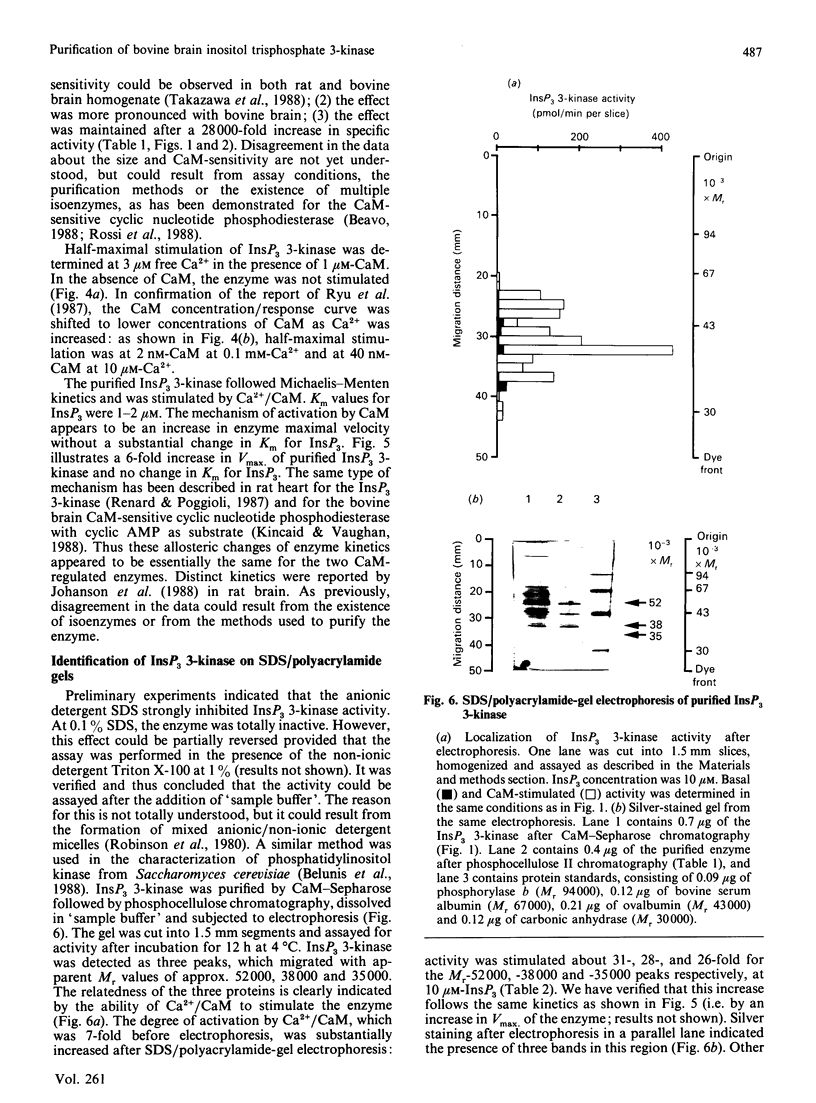
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) 3-kinase catalyses the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of InsP3 to inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (InsP4). A method is presented for the rapid purification of InsP3 3-kinase from bovine brain by calmodulin (CaM)-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Maximal activation of the purified InsP3 3-kinase by Ca2+/CaM was 6-7-fold as compared with the activity measured in the presence of EGTA (1 mM) and 10 microM-InsP3. At 10 microM-InsP3 and 0.1 mM free Ca2+, half-maximal activation required about 2 nM-CaM. The mechanism of activation by CaM appeared to be an increase in the maximal velocity of the enzyme without a substantial change in the Km for InsP3. Further purification was achieved by phosphocellulose chromatography eluted with ATP. Specific activity of the purified enzyme at 37 degrees C and 10 microM-InsP3 was 10-20 mumol/min per mg. The apparent Mr of the enzyme, determined by f.p.l.c.-gel filtration, was estimated as about 44,000. The purified InsP3 3-kinase was subjected to SDS/10%-polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. InsP3 3-kinase activity was associated with three silver-stained bands, which migrated with apparent Mr values of approx. 52,000, 38,000 and 35,000.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belunis C. J., Bae-Lee M., Kelley M. J., Carman G. M. Purification and characterization of phosphatidylinositol kinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18897–18903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. A simple method for the accurate determination of free [Ca] in Ca-EGTA solutions. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):C404–C408. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.5.C404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erneux C., Delvaux A., Moreau C., Dumont J. E. The dephosphorylation pathway of D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in rat brain. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):635–639. doi: 10.1042/bj2470635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen R. S., Beavo J. A. Differential recognition of calmodulin-enzyme complexes by a conformation-specific anti-calmodulin monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14636–14645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. R., Takemura H., Putney J. W., Jr Kinetics of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol cyclic 1:2,4,5-trisphosphate metabolism in intact rat parotid acinar cells. Relationship to calcium signalling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M., Pollock W. K., Smith P. M., Wreggett K. A. Inositol phosphates: proliferation, metabolism and function. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):281–298. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson R. A., Hansen C. A., Williamson J. R. Purification of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7465–7471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid R. L., Vaughan M. Purification and properties of calmodulin-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from mammalian brain. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:557–573. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H. Purification of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitory protein by affinity chromatography on activator protein coupled to Sepharose. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):120–126. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinks M. H., Haiech J., Rhoads A., Klee C. B. Reversible and irreversible activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase: separation of the regulatory and catalytic domains by limited proteolysis. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;16:31–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Murray K. J., England P. J., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Partial purification and some properties of rat brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):157–163. doi: 10.1042/bj2510157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renard D., Poggioli J. Does the inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway exist in rat heart? FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 8;217(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. B., Jr, Strottmann J. M., Wick D. G., Stellwagen E. Affinity chromatography in nonionic detergent solutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5847–5851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., Giorgi M., Geremia R., Kincaid R. L. Testis-specific calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. A distinct high affinity cAMP isoenzyme immunologically related to brain calmodulin-dependent cGMP phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15521–15527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Catalytic properties of inositol trisphosphate kinase: activation by Ca2+ and calmodulin. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):388–393. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.5.2824270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B. Inositol phosphate metabolism: further problems and some solutions. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazawa K., Passareiro H., Dumont J. E., Erneux C. Ca2+/calmodulin-sensitive inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase in rat and bovine brain tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 16;153(2):632–641. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Hirata M., Kuriyama H. Purification and characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from pig aortic smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):129–134. doi: 10.1042/bj2510129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa M., Sakuma M., Yagi K. Calmodulins from muscles of marine invertebrates, scallop and sea anemone. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1313–1320. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberman Y., Howe L. R., Moore J. P., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C. Calcium regulates inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate production in lysed thymocytes and in intact cells stimulated with concanavalin A. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):957–962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04845.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]