Abstract
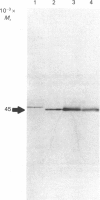
Renal dipeptidase (EC 3.4.13.11) has been solubilized from pig kidney microvillar membranes with n-octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside and then purified by affinity chromatography on cilastatin-Sepharose. The enzyme exists as a disulphide-linked dimer of two identical subunits of Mr 45,000 each. The purified dipeptidase partitioned into the detergent-rich phase upon phase separation in Triton X-114 and reconstituted into liposomes consistent with the presence of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of the amphipathic, detergent-solubilized, form of renal dipeptidase was identical with that of the hydrophilic, phospholipase-solubilized, form, locating the membrane anchor at the C-terminus of the protein. The glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of both purified and microvillar membrane renal dipeptidase was a substrate for an activity in pig plasma which displayed properties similar to those of a previously described phospholipase D. The cross-reacting determinant of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor was generated by incubation of purified renal dipeptidase with bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase c, whereas the anchor-degrading activity in plasma failed to generate this determinant.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D. J., Mukhopadhyay S. K., Campbell B. J. Physicochemical characterization of renal dipeptidase. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1745–1750. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon R. J., Shannon J. D., Bond J. S. Purification and characterization of a metallo-endoproteinase from mouse kidney. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):591–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1990591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. J., Forrester L. J., Zahler W. L., Burks M. Beta-lactamase activity of purified and partially characterized human renal dipeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14586–14590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Hereld D., Shak S., Krakow J., Englund P. T., Nussenzweig V. A glycan-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D in human serum. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.2443973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier D., Bergé J. B., Cardoso de Almeida M. L., Bordier C. Acetylcholinesterases from Musca domestica and Drosophila melanogaster brain are linked to membranes by a glycophospholipid anchor sensitive to an endogenous phospholipase. J Neurochem. 1988 Apr;50(4):1158–1163. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock M. J., Farrell C. A., Huybensz S., Luh B. Y., Phelps D. J. Affinity purification of renal dipeptidase solubilized with detergent. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Keen J., Pappin D. J., Turner A. J. Pig kidney angiotensin converting enzyme. Purification and characterization of amphipathic and hydrophilic forms of the enzyme establishes C-terminal anchorage to the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):85–93. doi: 10.1042/bj2470085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Low M. G., Turner A. J. Renal dipeptidase is one of the membrane proteins released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2440465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Differential solubilization by detergents can predict a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):865–869. doi: 10.1042/bj2500865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Isolation of two differentially glycosylated forms of peptidyl-dipeptidase A (angiotensin converting enzyme) from pig brain: a re-evaluation of their role in neuropeptide metabolism. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2410625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Ingram J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Purification and properties of the phosphoramidon-insensitive endopeptidase ('endopeptidase-2') from rat kidney. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):515–524. doi: 10.1042/bj2450515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Campbell B. J. Association of renal dipeptidase with the Triton-insoluble fraction of kidney microvilli. J Membr Biol. 1983;75(2):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01995631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood G. M., Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Affinity purification, characterization and localization of the phospholipase C-solubilized form of renal dipeptidase. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2570361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol: an anchor for eukaryotic membrane proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1988 Jun;16(3):271–272. doi: 10.1042/bst0160271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Prasad A. R. A phospholipase D specific for the phosphatidylinositol anchor of cell-surface proteins is abundant in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto A. W., Zakim D. Reconstitution of membrane proteins. Spontaneous association of integral membrane proteins with preformed unilamellar lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4066–4075. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterchi E. E., Naim H. Y., Lentze M. J., Hauri H. P., Fransen J. A. N-benzoyl-L-tyrosyl-p-aminobenzoic acid hydrolase: a metalloendopeptidase of the human intestinal microvillus membrane which degrades biologically active peptides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Aug 15;265(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch C. L., Campbell B. J. Uptake of glycine from L-alanylglycine into renal brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1980;54(1):39–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01875375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamze S. E., Ferguson M. A., Collins R., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Characterization of the cross-reacting determinant (CRD) of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):527–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida M. L., Turner M. J., Stambuk B. B., Schenkman S. Identification of an acid-lipase in human serum which is capable of solubilizing glycophosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):476–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]