Abstract
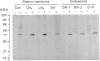
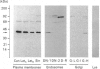
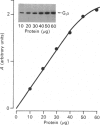
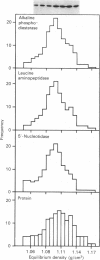
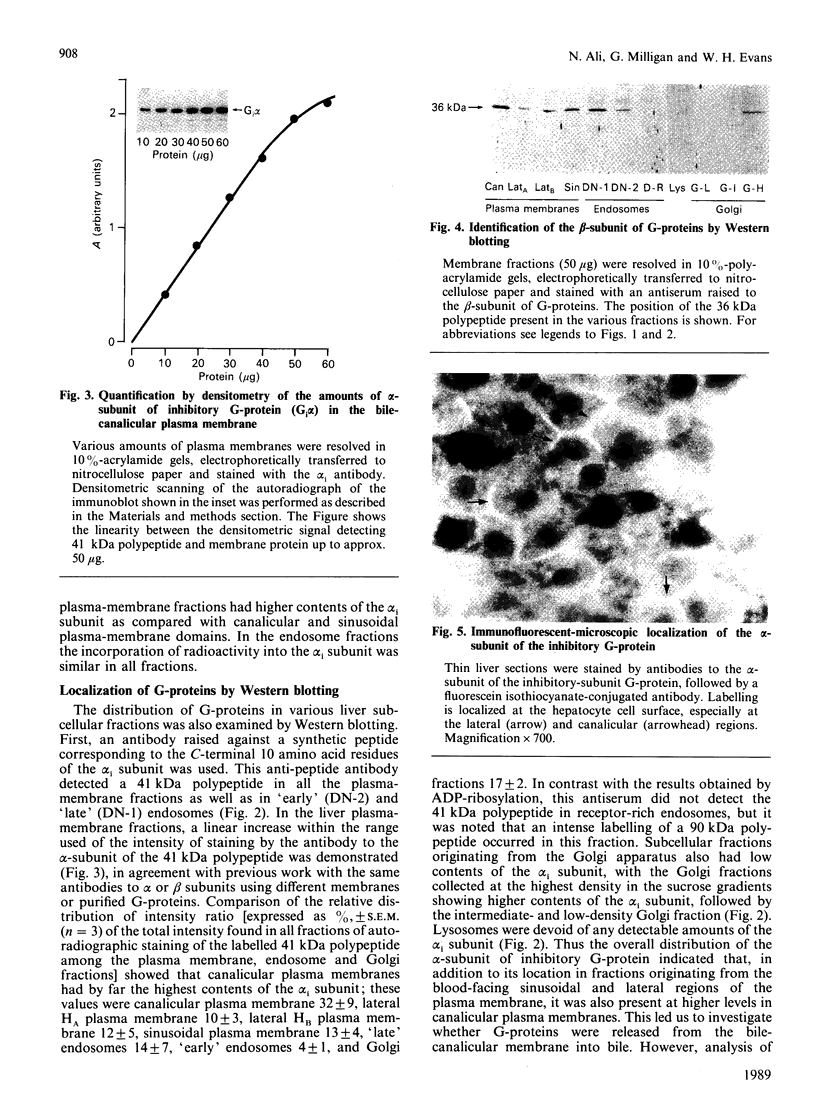
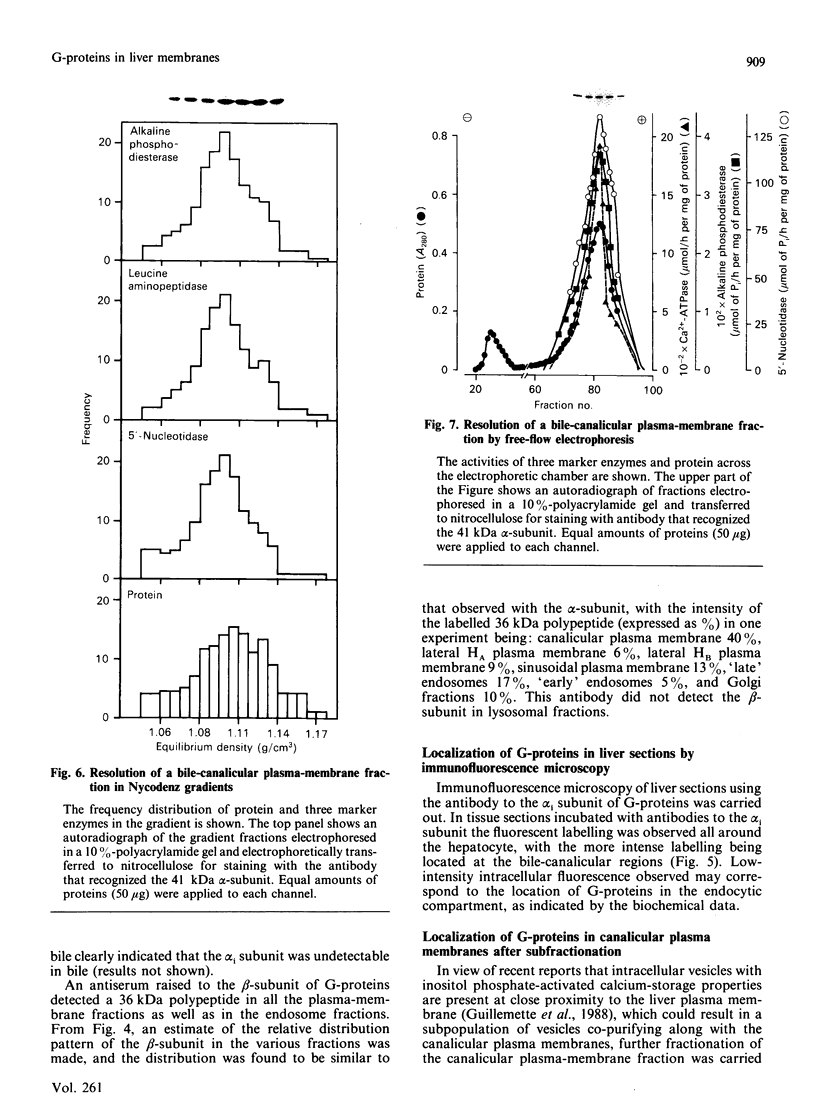
1. The distribution of the alpha- and beta-subunits of nucleotide-binding G-proteins among rat liver sinusoidal, lateral and canalicular plasma membranes, endosomes, Golgi membranes and lysosomes was investigated. 2. Pertussis-toxin-catalysed ADP-ribosylation identified a 41 kDa inhibitory alpha-subunit in all liver plasma-membrane functional domains as well as in endosomes. An antibody to a synthetic peptide corresponding to a C-terminal sequence of the inhibitory alpha-subunit also identified the 41 kDa polypeptide in all plasma-membrane domains, in 'early' and 'late' endosomes and in Golgi membranes; this polypeptide was not detected in lysosomes. The antibody-binding studies showed that bile-canalicular plasma membranes had the highest content of the inhibitory alpha-subunit. 3. Immunofluorescent microscopy confirmed the presence of the inhibitory alpha-subunit in all regions of the hepatocyte's cell surface. 4. An antibody recognizing the beta-subunit showed that a 36 kDa polypeptide was present in all plasma membranes and in 'early' and 'late' endosomes; it was not detected in lysosomes. The relative distribution among the fractions of this polypeptide was similar to the distribution of the inhibitory alpha-subunit. 5. The presence of high levels of the G-protein inhibitory alpha-subunit in bile-canalicular plasma membranes was confirmed by demonstration of its co-fractionation with marker enzymes in Nycodenz gradients and by free-flow electrophoresis. The significance of this location is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachs O., Famulski K. S., Mirabelli F., Carafoli E. ATP-dependent Ca2+ transport in vesicles isolated from the bile canalicular region of the hepatocyte plasma membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Bickford K., Bohl B. P. Subcellular localization and quantitation of the major neutrophil pertussis toxin substrate, Gn. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1927–1936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H. A biochemical dissection of the functional polarity of the plasma membrane of the hepatocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 27;604(1):27–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90584-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Flint N. A., Vischer P. Biogenesis of hepatocyte plasma-membrane domains. Incorporation of (3H)fucose into plasma-membrane and golgi-apparatus glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):903–910. doi: 10.1042/bj1920903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Flint N. Subfractionation of hepatic endosomes in Nycodenz gradients and by free-flow electrophoresis. Separation of ligand-transporting and receptor-enriched membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):25–32. doi: 10.1042/bj2320025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H. Preparation of low-density "endosome" and "endosome"-depleted Golgi fractions from rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:246–257. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBARG J. A., RUTENBURG A. M. The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer. 1958 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–291. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195803/04)11:2<283::aid-cncr2820110209>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Milligan G., Pines M., Goldsmith P., Codina J., Klee W., Spiegel A. Use of specific antibodies to quantitate the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Sidiropoulos D., Spiegel A., Jakobs K. H. Purification and immunochemical characterization of the major pertussis-toxin-sensitive guanine-nucleotide-binding protein of bovine-neutrophil membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 15;165(1):185–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Balla T., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors and calcium mobilization in a hepatic plasma membrane fraction. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4541–4548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. Structure, biochemistry, and assembly of epithelial tight junctions. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C749–C758. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiivanova N., Flint N., Evans W. H., Dix C., Cooke B. A. Endocytosis of beta-adrenergic ligands by rat liver. Comparison of beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase distribution in endosome and plasma-membrane fractions. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):749–754. doi: 10.1042/bj2220749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Kusakabe K., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in brain tissues serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Simon M. I. G protein multiplicity in eukaryotic signal transduction systems. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4957–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luetje C. W., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C., Spiegel A., Nathanson N. M. Tissue-specific regulation of GTP-binding protein and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor levels during cardiac development. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4876–4884. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Kelly E. C., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M., Milligan G. Antibodies which recognize the C-terminus of the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gi) demonstrate that opioid peptides and foetal-calf serum stimulate the high-affinity GTPase activity of two separate pertussis-toxin substrates. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):653–659. doi: 10.1042/bj2490653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. The site of diphosphoinositide synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M., Klee W. A. The GTP-binding regulatory proteins of neuroblastoma x glioma, NG108-15, and glioma, C6, cells. Immunochemical evidence of a pertussis toxin substrate that is neither Ni nor No. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M. The use of specific antibodies to identify and quantify guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):42–45. doi: 10.1042/bst0150042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Klee W. A. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Ni) purified from bovine brain is a high affinity GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2057–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Techniques used in the identification and analysis of function of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2550001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Simister N. E. Transcytosis. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):389–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution, activity, and properties of the 35,000-dalton (beta) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11361–11368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I., Spiegel A. M., Malech H. L. Subcellular localization of Gi alpha in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10958–10964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saermark T., Flint N., Evans W. H. Hepatic endosome fractions contain an ATP-driven proton pump. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):51–58. doi: 10.1042/bj2250051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer N. M., Toro M. J., Entman M. L., Birnbaumer L. G-protein distribution in canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and sarcolemma: comparison to rabbit skeletal muscle membranes and to brain and erythrocyte G-proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Dec;259(2):431–440. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90509-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff J. M., Fisher M. M., Jones A. L., Underdown B. J. Human IgA as a heterovalent ligand: switching from the asialoglycoprotein receptor to secretory component during transport across the rat hepatocyte. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):920–931. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Evans W. H., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Preferential localization of rat liver D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate/1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate 5-phosphatase in bile-canalicular plasma membrane and 'late' endosomal vesicles. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):363–369. doi: 10.1042/bj2560363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant M., Barhanin J., Bockaert J., Rouot B. G-proteins in skeletal muscle. Evidence for a 40 kDa pertussis-toxin substrate in purified transverse tubules. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 1;254(2):405–409. doi: 10.1042/bj2540405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reconstitution of a calcium pump using defined membrane components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):622–626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattiaux R., Wattiaux-De Coninck S., Ronveaux-dupal M. F., Dubois F. Isolation of rat liver lysosomes by isopycnic centrifugation in a metrizamide gradient. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):349–368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisher M. H., Evans W. H. Functional polarity of the rat hepatocyte surface membrane. Isolation and characterization of plasma-membrane subfractions from the blood-sinusoidal, bile-Canalicular and contiguous surfaces of the hepatocyte. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):375–388. doi: 10.1042/bj1460375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct activation of mammalian atrial muscarinic potassium channels by GTP regulatory protein Gk. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2432660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]