Abstract
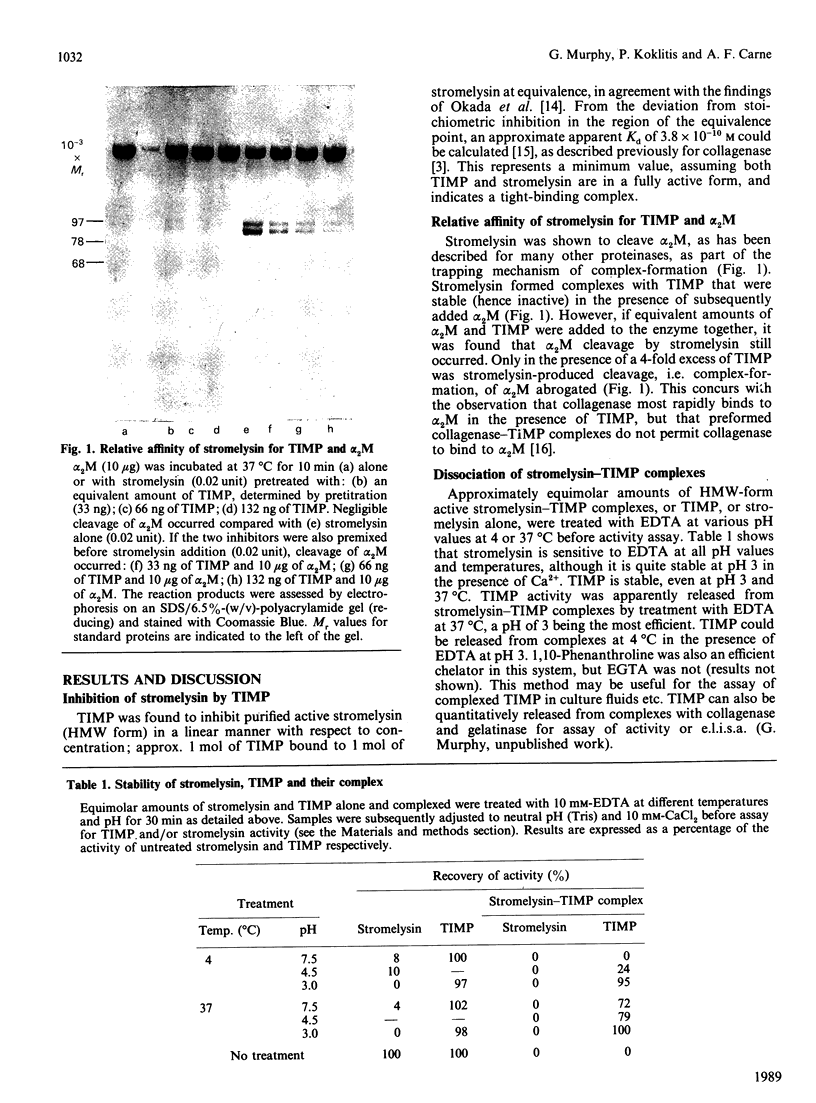
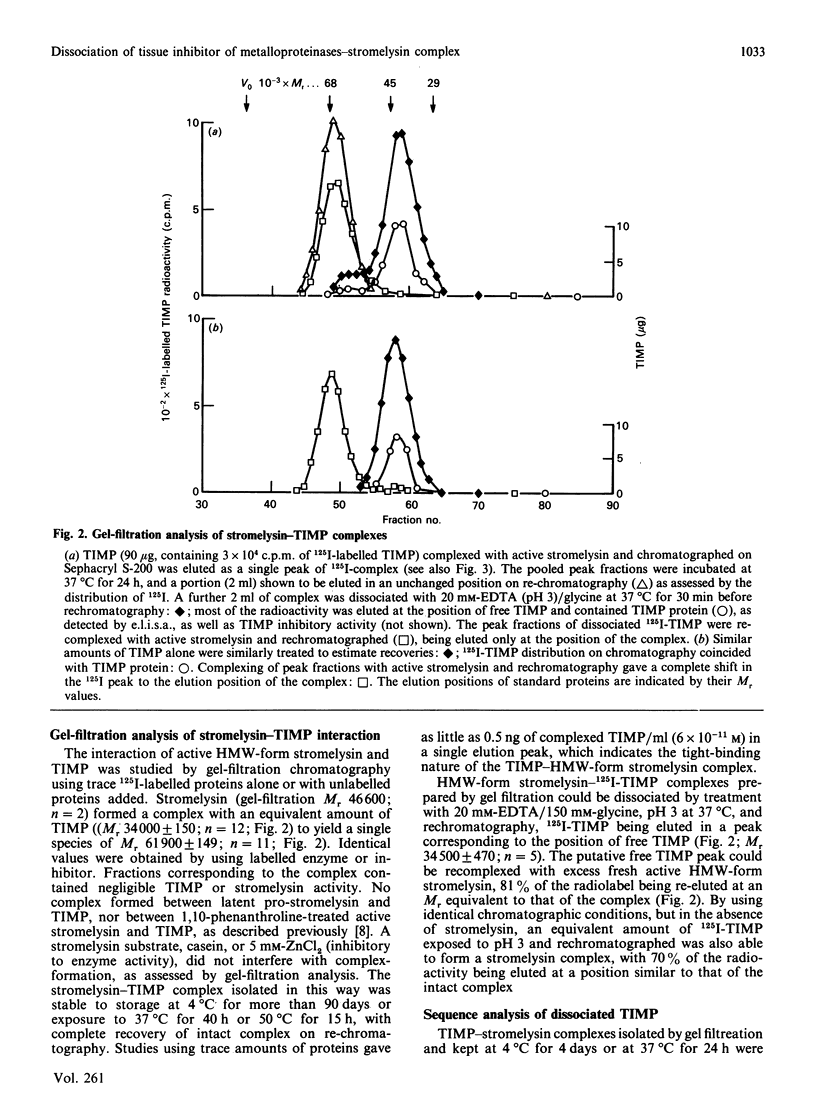
Recombinant human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) forms complexes with high-Mr active recombinant stromelysin that are stable over long periods under physiological conditions. TIMP-stromelysin complexes could be dissociated in the presence of EDTA at pH 3, releasing free TIMP and destroying stromelysin activity. The dissociated TIMP was apparently unmodified, in contrast with other known protein inhibitors of metalloproteinases and many classes of serine-proteinase inhibitor, which are slowly cleaved.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Mercer E. Preferential binding of collagenase to alpha 2-macroglobulin in the presence of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Murphy G., Mercer E., Galloway W. A., Hazleman B. L., Reynolds J. J. The interaction of purified rabbit bone collagenase with purified rabbit bone metalloproteinase inhibitor. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):313–318. doi: 10.1042/bj2110313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty A. J., Lyons A., Smith B. J., Wright E. M., Stephens P. E., Harris T. J., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. Sequence of human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and its identity to erythroid-potentiating activity. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):66–69. doi: 10.1038/318066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M., WORK E. Pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. II. Reaction with trypsin. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):347–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0540347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway W. A., Murphy G., Sandy J. D., Gavrilovic J., Cawston T. E., Reynolds J. J. Purification and characterization of a rabbit bone metalloproteinase that degrades proteoglycan and other connective-tissue components. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):741–752. doi: 10.1042/bj2090741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai H., Hara S., Ikenaka T., Oda K., Murao S. Amino acid sequence of Streptomyces metallo-proteinase inhibitor from Streptomyces nigrescens TK-23. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):173–180. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cawston T. E., Reynolds J. J. An inhibitor of collagenase from human amniotic fluid. Purification, characterization and action on metalloproteinases. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):167–170. doi: 10.1042/bj1950167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cockett M. I., Stephens P. E., Smith B. J., Docherty A. J. Stromelysin is an activator of procollagenase. A study with natural and recombinant enzymes. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):265–268. doi: 10.1042/bj2480265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Harris E. D., Jr, Nagase H. The precursor of a metalloendopeptidase from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Purification and mechanisms of activation by endopeptidases and 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):731–741. doi: 10.1042/bj2540731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. C., Lipscomb W. N. Structure of the potato inhibitor complex of carboxypeptidase A at 2.5-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4633–4637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z., Roswit W. T., Stricklin G. P. Human skin fibroblast collagenase: interaction with substrate and inhibitor. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Mar;5(2):167–179. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]