Fig 1.
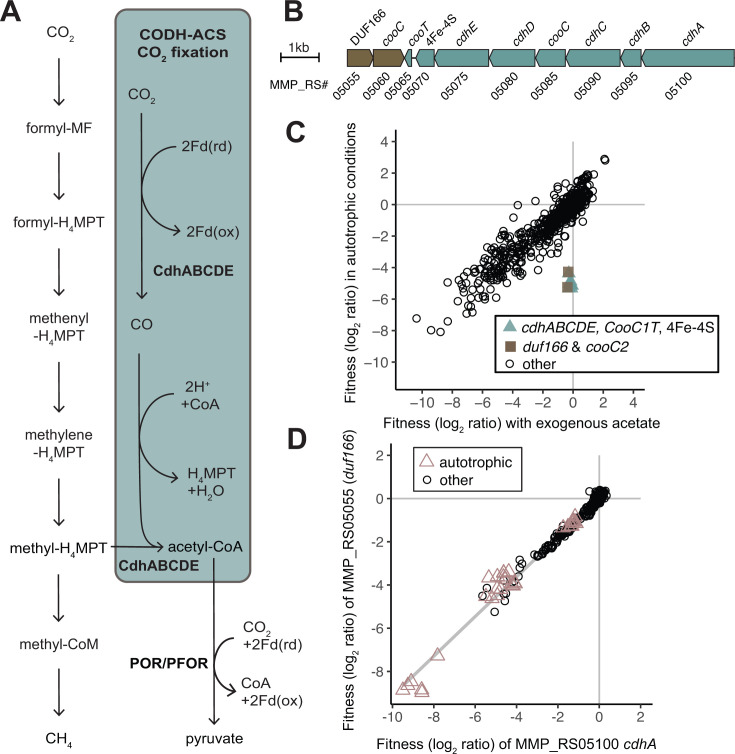
DUF166 encoded by MMP_RS05055 is important for fitness during autotrophic growth. (A) The Wood-Ljungdahl pathway for CO2 fixation, highlighted in blue, uses methyl-H4MPT from the methanogenic pathway (left) for the methyl group of acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA can be further reduced to pyruvate by pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase (POR/PFOR) and reduced ferredoxin (Fd). (B) Gene neighborhood of the CODH-ACS operon. (C) Comparison of gene fitness values for growth with exogenous acetate (10 mM) compared to autotrophic growth in H2 oxidizing conditions. Each value is the average of six autotrophic (Mc defined media) replicates and three replicates with exogenous acetate (Mc defined media + 10 mM acetate). (D) Cofitness of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase/acetyl-coenzyme synthase (CODH-ACS) subunit alpha (cdhA, MMP_RS05100) and DUF166 encoded by MMP_RS05055. Experiments identified as autotrophic conditions were performed in defined minimal media both with and without vitamins and either H2 or formate as the electron donor.