Abstract
Background
The relationship between free fatty acids (FFAs) and the risk of mortality remains unclear. There is a scarcity of prospective studies examining the associations between specific FFAs, rather than total concentrations, of their effect on long-term health outcomes.
Objective
To evaluate the correlation between different FFAs and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a large, diverse, nationally representative sample of adults in the US, and examine how different FFAs may mediate this association.
Methods
This cohort study included unsaturated fatty acids (USFA) and saturated fatty acids (SFA) groups in the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2011 to 2014 and provided blood samples for FFAs levels. Multiple model calibration was performed using Cox regression analysis for known risk factors to explore the associations between FFAs and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality.
Results
In the group of USFA, 3719 people were included, median follow-up, 6.7 years (5.8–7.8 years). In the SFA group, we included 3900 people with a median follow-up, 6.9 years (5.9-8 years). In the USFA group, myristoleic acid (14:1 n-5) (hazard ratio (HR) 1.02 [1.006–1.034]; P = 0.004), palmitoleic acid (16:1 n-7) (HR 1.001 [1.001–1.002]; P < 0.001), cis-vaccenic acid (18:1 n-7) (HR 1.006 [1.003–1.009]; P < 0.001), nervonic acid (24:1 n-9) (HR 1.007 [1.002–1.012]; P = 0.003), eicosatrienoic acid (20:3 n-9) (HR 1.027 [1.009–1.046]; P = 0.003), docosatetraenoic acid (22:4 n-6) (HR 1.024 [1.012–1.036]; P < 0.001), and docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-6) (HR 1.019 [1.006–1.032]; P = 0.005) were positively associated with the all-cause mortality, while docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 n-3) had a statistically lower risk of all-cause mortality (HR 0.998 [0.996–0.999]; P = 0.007). Among the SFA group, palmitic acid (16:0) demonstrated a higher risk of all-cause mortality (HR 1.00 [1.00–1.00]; P = 0.022), while tricosanoic acid (23:0) (HR 0.975 [0.959–0.991]; P = 0.002) and lignoceric acid (24:0) (HR 0.992 [0.984–0.999]; P = 0.036) were linked to a lower risk of all-cause mortality. Besides 23:0 and 24:0, the other FFAs mentioned above were linearly associated with the risks of all-cause mortality.
Conclusions
In this nationally representative cohort of US adults, some different FFAs exhibited significant associations with risk of all-cause mortality. Achieving optimal concentrations of specific FFAs may lower this risk of all-cause mortality, but this benefit was not observed in regards to cardiovascular mortality.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12986-024-00844-6.
Keywords: Free fatty acids, All-cause mortality, Cardiovascular mortality, NHANES
Introduction
Fatty acids, structurally, can be categorized as saturated fatty acids (SFA) (no double bonds) and unsaturated fatty acids (USFA); the later are again of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) (one double bond), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) (greater than one double bond) [1]. Functionally, the regulation of fatty acid metabolism is well-established in healthy individuals [2], emphasizing the significance of both specific type and quantity of consumed fatty acid. For over 50 years, reducing intake of SFA was recommended [3] given that SFA increase low-density lipoprotein cholesterol [4], a strong risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, USFA, particularly PUSFA, may play a vital role in disease prevention and contribute to overall health [1]. Considering that essential fatty acids are exclusively obtained from dietary sources, their concentrations in blood, also known as free fatty acids (FFAs), could serve as indicators of dietary intake [5].
Although large quantities of FFAs may be supplied by diet, they may also be indicators of disease risk, morbidity, and mortality [6]. Several studies have displayed an association between FFAs concentrations and coronary artery disease (CAD) [7, 8], and FFAs may independently predict all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in individuals with angiographic CAD [9]. In contrast, findings suggest that FFAs concentrations may not be an absolute risk factor [8] and are not related to the presence of angiographic CAD [9]. The discrepancies in these results could stem from the diverse effects that each individual fatty acid rather than groups of fatty acids may exert on CVD risk factors [10]. A study revealed that only palmitic acid association with increased risk of cardiovascular mortality but not the other SFA or the sum of all SFA [10]. Studies have found that high levels of circulating very long SFA was associated with a lower risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) [11] and heart failure [12]. All these results indicated that each fatty acid individually had different association with CHD [13].
Furthermore, the quality, rather than the quantity, of dietary fatty acids is paramount in influencing the development of cardiometabolic diseases [14]. Besides CAD, FFAs have emerged as a major link among obesity, development of metabolic syndrome, and atherosclerosis [15–17]. Marked elevations of FFAs have been observed in obesity and type 2 diabetes [17–21], as well as in patients with stroke [22]. Nevertheless, additional data elucidate that FFAs are used as an independent risk factor for cancer mortality, but presenting no association with myocardial infarction or overall cardiovascular mortality [23, 24].
Therefore, the relationship between different FFAs and the risk of mortality remains unclear. In this study, we aimed a nationally representative cohort from the US to investigate the association of individual FFAs with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in adults.
Methods
Study population
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a program that conducts health surveys representative of the national civilian, noninstitutionalized population across the US.
Administered by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), NHANES serves as a comprehensive effort to evaluate the health and nutrition status of US citizens. NHANES stands out due to its comprehensive approach, encompassing both questionnaire data collected through in-person interviews and health examinations conducted in the mobile examination center, collecting specimens for laboratory tests. Consequently, strata, sample weights, and primary sampling units were utilized in accordance with the NHANES analytic guidelines [25] to address oversampling of specific subpopulations, the unequal probability of selection, and adjustments for nonresponse. The NHANES protocol received approval from NCHS ethics review board, and written consent was obtained from all participants.
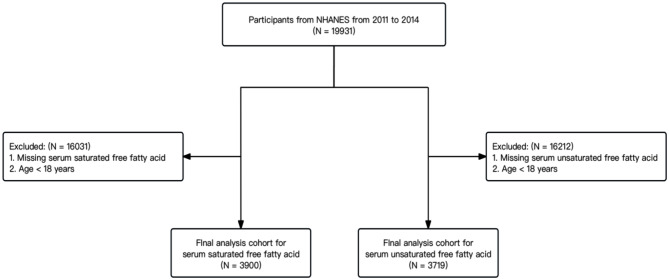
For the present analysis, we included adults aged 18 and older who participated in NHANES during 2011–2014, which had available data on serum FFAs measurements. This study followed the guidelines of strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology for cohort studies. The proportions of missing values for the covariates we included were no more than 10%, so we used the “miceforest” in Python to implement multiple imputation by chained equations [26]. The final analysis was conducted on a cohort consisting of individuals who actively took part in the NHANES survey and had their each FFAs levels measured. The flow chart for this study showed in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Flow chart for study. NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Assessment of serum FFAs
Morning fasting blood samples were collected from NHANES participants, and serum FFAs were measured using a modified of Lagerstedt methods described previously [27]. Specifically, total fatty acids were hexane-extracted from the matrix, along with an internal standard solution containing eighteen stable isotopically-labeled fatty acids, to ensure accurate fatty acids recovery. The resulting extract was then derivatized to form pentafluorobenzyl esters and injected into a capillary gas chromatograph column to resolve individual fatty acids from other matrix constituents. FFAs were expressed as a % of total fatty acids (FFAs/the sum of measured fatty acids). Values of FFAs below the limit of detection divided by the square root of 2 [28]. A total of thirty fatty acids, including eleven SFA and nineteen USFA, were measured.
Ascertainment of mortality outcomes
We utilized the NHANES public-use linked mortality file, linked by the NCHS to the national death index through December 31, 2019, employing a probabilistic matching algorithm to establish mortality status [29]. The US data on the underlying cause of death were utilized for case definition based on the international classification of diseases, 10th Revision [30], which death from heart disease (codes I00-I09, I11, I13, I20-I51, and I60-I69) are classified as cardiovascular mortality. This method has been confirmed by the CDC and has been utilized in previously CDC reports [31, 32].
Assessment of covariates
The baseline information on age, sex, race, educational level, family income to poverty ratio (FIP), alcohol drinking, body mass index (BMI), abdominal obesity, weight loss, increasing exercise, cholesterol and triglycerides, and dietary intake (energy, protein, carbohydrate, sugar, dietary fiber, total fat, total SFA, total MUSFA and total PUSFA), comorbidities (diabetes, CVD, and cancer) were collected using questionnaires.
For all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, we adjusted for different combination of confunders, which were based on univariate logistic regression (Supplementary Table S1 for all-cause mortality, Supplementary Table S2 for cardiovascular mortality). We then utilized the variance inflation factor to address multicollinearity and removed the confunders with values exceeding 10 (Supplementary Table S3 for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality).
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics and distribution of FFAs were compared between survivors and non-survivors. Continuous variables were expressed as median with interquartile range (for non-normal distribution), and the Mann-Whitney test was utilized for analysis. Categorical variables were displayed as counts (percentages) and underwent comparison through the chi-square test. FFAs associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality were based on univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis. We utilized the Cox proportional hazards model to calculate hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). Quartile concentration (Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4) of FFAs related to all-cause and cardiovascular mortality were found through Cox regression. Kaplan–Meier survival curves for all-cause mortality according to FFAs quartiles. To find the interactions with gender, we used subgroup analysis. We employed Restricted Cubic Spline (RCS) analysis to assess the non-linear association between FFAs and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Four knots were placed at the 25th, 50th, 75th, and 95th percentiles to define the spline. The follow-up duration for each individual was determined as the interval between the NHANES examination date and the last known date of being alive or being censored from the linked mortality file. We added a sensitivity analysis to further explore whether homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) would affect the results.
A P-value below 0.05 was considered statistically significant, and all analyses were two-tailed. Kaplan–Meier survival curves and RCS were generated using R software (version 4.3.2, Salzburg, Austria), while statistical analyses were performed with SPSS software (version 29, IBM).
Results
Baseline participant characteristics
As showed in Table 1, in the group of USFA, there were 796 (21.4%) adults aged ≥ 65 years and 1797 (48.3%) male. Between survivors and non-survivors, all social demographic (age, sex, race, education level and FIP) and comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, chronic heart failure (CHF), angina, CHD, heart attack, stroke and cancer) were significantly different. All dietary habits showed statistical significance except for fat reduction and SFA intake. During 3719 person-years of follow-up (median follow-up, 6.7 years (5.8–7.8 years); maximum follow-up, 9.3 years), 321 deaths occurred, comorbid with 99 diabetes, 227 hypertension, 52 CHF, 57 CHD, 29 angina, 48 heart attack, 48 stroke, and 82 cancer.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristic of serum unsaturated fatty acid and saturated fatty acid in the NHANES study, 2011–2014
| Variables | Unsaturated fatty acid (N = 3719) | Saturated fatty acid (N = 3900) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Survivors | Non-survivors | P | All | Survivors | Non-survivors | P | |
| Age ≥ 65 years | 796 (21.4) | 572 (16.8) | 224 (69.8) | < 0.001 | 859 (22.0) | 618 (17.4) | 241 (70.3) | < 0.001 |
| Male | 1797 (48.3) | 1605 (47.2) | 192 (59.8) | < 0.001 | 1880 (48.2) | 1678 (47.2) | 202 (58.9) | < 0.001 |
| Race | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||||
| Mexican American | 423 (11.4) | 401 (11.8) | 22 (6.9) | 446 (11.4) | 424 (11.9) | 22 (6.4) | ||
| Other Hispanic | 407 (10.9) | 391 (11.5) | 16 (5.0) | 396 (10.2) | 381 (10.7) | 15 (4.4) | ||
| Non-Hispanic White | 1599 (43.0) | 1398 (41.1) | 201 (62.6) | 1584 (40.6) | 1379 (38.8) | 205 (59.8) | ||
| Non-Hispanic Black | 753 (20.2) | 689 (20.3) | 64 (19.9) | 881 (22.6) | 807 (22.7) | 74 (21.6) | ||
| Non-Hispanic Asian | 451 (12.1) | 436 (12.8) | 15 (4.7) | 506 (13.0) | 486 (13.7) | 20 (5.8) | ||
| Other Race | 86 (2.3) | 83 (2.4) | 3 (0.9) | 87 (2.2) | 80 (2.2) | 7 (2.0) | ||
| Education level | 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||||
| < High school | 857 (23.0) | 758 (22.3) | 99 (30.8) | 897 (23.0) | 787 (22.1) | 110 (32.1) | ||
| High school | 866 (23.3) | 787 (23.2) | 79 (24.6) | 897 (23.0) | 813 (22.9) | 84 (24.5) | ||
| College or higher | 1996 (53.7) | 1853 (54.5) | 143 (44.5) | 2106 (54.0) | 1957 (55.0) | 149 (43.4) | ||
| FIP | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||||
| < 0.5 | 295 (7.9) | 278 (8.2) | 17 (5.3) | 307 (7.9) | 287 (8.1) | 20 (5.8) | ||
| 0.5-1 | 597 (16.1) | 536 (15.8) | 61 (19.0) | 625 (16.0) | 559 (15.7) | 66 (19.2) | ||
| 1–2 | 962 (25.9) | 850 (25.0) | 112 (34.9) | 1037 (26.6) | 915 (25.7) | 122 (35.6) | ||
| > 2 | 1865 (50.1) | 1734 (51.0) | 131 (40.8) | 1931 (49.5) | 1796 (50.5) | 135 (39.4) | ||
| Alcohol drinking | 0.646 | 0.724 | ||||||
| Never | 1071 (28.8) | 975 (28.7) | 96 (29.9) | 1105 (28.3) | 1005 (28.3) | 100 (29.2) | ||
| Ever | 2648 (71.2) | 2423 (71.3) | 225 (70.1) | 2795 (71.7) | 2552 (71.7) | 243 (70.8) | ||
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.306 | 0.356 | ||||||
| < 25 | 1182 (31.8) | 1069 (31.5) | 113 (35.2) | 1272 (32.6) | 1152 (32.4) | 120 (35.0) | ||
| ≥ 25 < 30 | 1197 (32.2) | 1094 (32.2) | 103 (32.1) | 1242 (31.8) | 1129 (31.7) | 113 (32.9) | ||
| ≥ 30 | 1340 (36.0) | 1235 (36.3) | 105 (32.7) | 1386 (35.5) | 1276 (35.9) | 110 (32.1) | ||
| Abdominal obesity, cm | 0.107 | 0.258 | ||||||
| < 102 (Male) or < 88 (Female) | 1712 (46.0) | 1578 (46.4) | 134 (41.7) | 1819 (46.6) | 1669 (46.9) | 150 (43.7) | ||
| ≥ 102 (Male) or ≥ 88 (Female) | 2007 (54.0) | 1820 (53.6) | 187 (58.3) | 2081 (53.4) | 1888 (53.1) | 193 (56.3) | ||
| Losing weight | 0.256 | 0.156 | ||||||
| Yes | 2242 (60.3) | 2058 (60.6) | 184 (57.3) | 2379 (61.0) | 2182 (61.3) | 197 (57.4) | ||
| Increasing exercise | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||||
| Yes | 2211 (59.5) | 2051 (60.4) | 160 (49.8) | 2322 (59.5) | 2157 (60.6) | 165 (48.1) | ||
| Reducing salt diet | 0.002 | < 0.001 | ||||||
| Yes | 1909 (51.3) | 1716 (50.5) | 193 (60.1) | 2025 (51.9) | 1817 (51.1) | 208 (60.6) | ||
| Reducing fat diet | 0.488 | 0.595 | ||||||
| Yes | 2038 (54.8) | 1868 (55.0) | 170 (53.0) | 2134 (54.7) | 1951 (54.8) | 183 (53.4) | ||
| Daily intake | ||||||||
| Energy, kcal | 1954.0 (1450.0, 2582.0) | 1970.5 (1465.0, 2598.0) | 1754.0 (1301.5, 2382.5) | < 0.001 | 1956.0 (1446.0, 2573.0) | 1971.0 (1458.5, 2595.5) | 1755.0 (1318.0, 2369.0) | < 0.001 |
| Protein, gm | 75.4 (53.8, 102.5) | 76.2 (54.6, 103.3) | 68.1 (49.3, 93.6) | < 0.001 | 75.9 (53.8, 101.5) | 76.6 (54.6, 102.8) | 69.1 (49.0, 93.6) | < 0.001 |
| Carbohydrate, gm | 237.0 (170.3, 315.5) | 239.9 (172.1, 320.0) | 211.0 (155.9, 278.5) | < 0.001 | 235.5 (168.3, 313.3) | 237.7 (170.0, 317.4) | 211.0 (156.9, 279.1) | < 0.001 |
| Sugar, gm | 95.5 (59.0, 142.8) | 96.5 (58.7, 144.1) | 87.8 (59.5, 123.4) | 0.018 | 94.7 (57.7, 140.8) | 95.4 (57.4, 142.2) | 88.9 (61.6, 121.6) | 0.115 |
| Dietary fiber, gm | 14.9 (9.8, 21.9) | 15.0 (9.9, 22.1) | 13.9 (8.6, 19.9) | 0.005 | 14.9 (9.7, 22.2) | 15.1 (9.7, 22.5) | 14.1 (9.2, 19.6) | 0.015 |
| Total fat, gm | 72.5 (48.7, 102.3) | 73.2 (49.1, 102.5) | 64.9 (44.4, 96.4) | 0.008 | 72.2 (48.7, 101.6) | 72.7 (49.2, 102.4) | 64.2 (44.2, 96.1) | 0.007 |
| Total SFA, gm | 22.7 (14.7, 33.7) | 22.8 (14.7, 33.9) | 20.7 (13.9, 31.6) | 0.074 | 22.3 (14.5, 33.6) | 22.5 (14.6, 33.9) | 20.7 (13.6, 31.8) | 0.092 |
| Total MUFA, gm | 25.1 (16.6, 36.5) | 25.3 (16.8, 36.7) | 23.0 (15.0, 33.9) | 0.020 | 25.4 (16.6, 36.5) | 25.5 (16.9, 36.7) | 22.6 (14.7, 34.2) | 0.011 |
| Total PUFA, gm | 16. 2 (10.5, 24.8) | 16.4 (10.7, 24.9) | 14.2 (9.6, 23.4) | 0.007 | 16.4 (10.4, 24.7) | 16.5 (10.6, 24.8) | 14.7(9.3, 23.0) | 0.009 |
| Laboratory indicators | ||||||||
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 187.0 (161.0, 213.0) | 187.0 (162.0, 214.0) | 177.0 (153.0, 210.0) | < 0.001 | 186.0 (160.0, 213.8) | 186.0 (161.0, 214.0) | 178.0 (152.0, 213.0) | 0.005 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 51.0 (43.0, 62.0) | 51.0 (43.0, 62.0) | 50.0 (42.0, 62.0) | 0.185 | 52.0 (43.0, 62.0) | 52.0 (43.0, 62.0) | 51.0 (42.0, 63.0) | 0.576 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 110.0 (87.0, 134.0) | 111.0 (88.0, 135.0) | 98.0 (76.0, 127.0) | < 0.001 | 10.08 (86.0, 133.0) | 109.0 (87.0, 134.0) | 98.0 (76.0, 129.0) | < 0.001 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 97.0 (68.0, 146.0) | 96.0 (68.0, 144.0) | 106.0 (77.5, 160.0) | < 0.001 | 97.0 (68.0, 143.0) | 95.0 (67.0, 141.0) | 105.0 (77.0, 157.0) | < 0.001 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||||
| Diabetes | 432 (11.6) | 333 (9.8) | 99 (30.8) | < 0.001 | 459 (11.8) | 355 (10.0) | 104 (30.3) | < 0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1342 (36.1) | 1115 (32.8) | 227 (70.7) | < 0.001 | 1411 (36.2) | 1165 (32.8) | 246 (71.7) | < 0.001 |
| CHF | 142 (3.8) | 90 (2.6) | 52 (16.2) | < 0.001 | 145 (3.7) | 91 (2.6) | 54 (15.7) | < 0.001 |
| CHD | 147 (4.0) | 90 (2.6) | 57 (17.8) | < 0.001 | 156 (4.0) | 95 (2.7) | 61 (17.8) | < 0.001 |
| Angina | 102 (2.7) | 73 (2.1) | 29 (9.0) | < 0.001 | 107 (2.7) | 75 (2.1) | 32 (9.3) | < 0.001 |
| Heart attack | 145 (3.9) | 97 (2.9) | 48 (15.0) | < 0.001 | 156 (4.0) | 105 (3.0) | 51 (14.9) | < 0.001 |
| Stroke | 149 (4.0) | 101 (3.0) | 48 (15.0) | < 0.001 | 153 (3.9) | 102 (2.9) | 51 (14.9) | < 0.001 |
| Cancer | 339 (9.1) | 257 (7.6) | 82 (25.5) | < 0.001 | 357 (9.2) | 269 (7.6) | 88 (25.7) | < 0.001 |
“losing weight” and “increasing exercise” were assessed by the question “Are you now losing weight” and “Are you now increasing exercise”, respectively, collected by medical conditions recall interviews, “reducing salt diet, reducing fat diet” were assessed by the question “Have you done Dietary information (reducing salt diet and reducing fat diet)” collected by 24-hour dietary recall interviews, from which total energy intake was calculated using the US Department of Agriculture Automated Multiple-Pass Method; the Alternative Healthy Eating Index (AHEI) is based on a comprehensive review of the original Healthy Eating Index and subsequent studies that included food components (energy, protein, carbohydrate, sugar, dietary fiber, total fat, total SFA, total MUFA and total PUFA. Abbreviations: FIP, family income to poverty ratio; BMI, body mass index, SFA, saturated fatty acids; MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acids; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CHF, congestive heart failure; CHD, coronary heart disease
In the SFA group, we included 859 (22.0%) adults aged ≥ 65 and 1880 (48.2%) males. Baseline characteristics in the SFA population were consistent between survivors and non-survivors, except for sugar intake. During 3900 person-years of follow-up (median follow-up, 6.9 years (5.9-8 years), maximum follow-up, 9.3 years), 343 deaths occurred, comorbid with 104 diabetes, 246 hypertension, 54 CHF, 61 CHD, 32 angina, 51 heart attack, 51 stroke, and 88 cancer (Table 1).
Characteristics of FFAs
A total of 30 different FFAs were included in our study, including 19 USFA and 11 SFA. Table 2 showed that in the USFA group, a statistically significant difference was observed between survivors and non-survivors (palmitoleic acid (16:1 n-7), cis-vaccenic acid (18:1 n-7), Oleic acid (18:1 n-9), eicosenoic acid (20:1 n-9), linoleic acid (18:2 n-6), stearidonic acid (18:4 n-3), eicosatrienoic acid (20:3 n-9), arachidonic acid (20:4 n-6), docosatetraenoic acid (22:4 n-6), and docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-3)). In the SFA group, 6 fatty acids were statistically significant between the groups (capric acid (10:0), palmitic acid (16:0), margaric acid (17:0), docosanoic acid (22:0), tricosanoic acid (23:0), and lignoceric acid (24:0)). As shown in Table 2, non-survivors demonstrated higher concentrations of the USFA, 16:1 n-7, 18:1 n-7, 18:1 n-9, 20:1 n-9, 20:3 n-9, 20:4 n-6, 22:4 n-6, 22:5 n-3, docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-6), and docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 n-3). Among SFA, 10:0, 16:0, and 17:0 showed increased concentrations in the non-survivor group, while 22:0, 23:0 and 24:0 were lower compared to survivors.
Table 2.
Distribution of serum fatty acids in the two cohorts
| Name | All | Survivors | Non-survivors | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unsaturated fatty acids (µmol/L) | ||||
| Myristoleic acid (14:1 n-5) | 6.0 (3.3, 10.0) | 6.0 (3.3, 10.0) | 6.0 (3.3, 10.0) | 0.745 |
| Palmitoleic acid (16:1 n-7) | 199.0 (135.0, 298.0) | 197.0 (133.0, 295.3) | 228.0 (151.5, 320.0) | 0.002 |
| cis-Vaccenic acid (18:1 n-7) | 141.0 (11.05, 177.0) | 140.0 (114.0, 175.0) | 156.0 (126.5, 194.0) | < 0.001 |
| Oleic acid (18:1 n-9) | 1930.0 (1550.0, 2500.0) | 1920.0 (1540, 2480) | 2110.0 (168.0, 2670.0) | < 0.001 |
| Eicosenoic acid (20:1 n-9) | 13.0 (10.1, 16.9) | 13.0 (10.0, 16.6) | 14.0 (11.0, 18.1) | < 0.001 |
| Nervonic acid (24:1 n-9) | 86.3 (73.0, 102.0) | 86.0 (73.0, 102.0) | 87.2 (73.0, 104.0) | 0.578 |
| Linoleic acid (18:2 n-6) | 3480.0 (2960.0, 4070.0) | 3500.0 (2970.0, 4080.0) | 3340.0 (2735.0, 3985.0) | 0.002 |
| α-Linolenic acid (18:3 n-3) | 77.0 (56.6, 107.0) | 77.0 (57.0, 106.3) | 76.2 (54.9, 111.0) | 0.701 |
| γ-Linolenic acid (18:3 n-6) | 51.0 (35.8, 73.0) | 51.0 (35.4, 73.0) | 53.0 (38.9, 76.9) | 0.085 |
| Stearidonic acid (18:4 n-3) | 3.0 (2.0, 5.0) | 3.0 (2.0, 5.0) | 3.0 (2.0, 5.0) | 0.035 |
| Eicosadienoic acid (20:2 n-6) | 21.7 (17.6, 27.2) | 21.6 (17.5, 27.0) | 22.0 (18.0, 28.9) | 0.121 |
| Dihomo-γ-Linolenic acid (20:3 n-6) | 151.0 (117.0, 194.0) | 151.0 (117.0, 194.0) | 147.0 (112.5, 190.0) | 0.232 |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (20:3 n-9) | 7.0 (5.0, 9.4) | 6.8 (4.9, 9.1) | 8.0 (5.2,8.0) | < 0.001 |
| Arachidonic acid (20:4 n-6) | 823.0 (673.0, 1010.0) | 820.0 (673.0, 1000.0) | 864.0 (712.0, 1050.0) | 0.004 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5 n-3) | 50.7 (33.9, 79.0) | 50.6 (33.1, 78.8) | 52.5 (36.6, 82.8) | 0.100 |
| Docosatetraenoic acid (22:4 n-6) | 25.3 (20.0, 32.5) | 25.0 (20.0, 32.1) | 27.8 (21.5, 34.4) | < 0.001 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-3) | 48.7 (38.6, 62.0) | 48.2 (38.2, 61.0) | 52.0 (41.5, 65.6) | < 0.001 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-6) | 19.7 (15.0, 25.9) | 19.5 (14.9, 25.6) | 20.2 (15.0, 26.7) | 0.059 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 n-3) | 144.0 (109.0, 199.0) | 143.0 (109.0, 198.3) | 149.0 (107.5, 199.5) | 0.537 |
| Saturated fatty acids (µmol/L) | ||||
| Capric acid (10:0) | 1.7 (1.1, 2.9) | 1.7 (1.1, 2.8) | 1.9 (1.1, 3.0) | 0.009 |
| Lauric acid (12:0) | 7.3 (4.8, 13.0) | 7.3 (4.8, 12.8) | 7.9 (5.0, 14.7) | 0.295 |
| Myristic acid (14:0) | 105.0 (72.0, 157.0) | 105.0 (72.0, 157.0) | 104.0 (73.7, 153.0) | 0.790 |
| Pentadecanoic acid (15:0) | 21.0 (16.0, 27.7) | 21.0 (16.0, 27.5) | 22.0 (16.0, 28.3) | 0.358 |
| Palmitic acid (16:0) | 2630.0 (2160.0, 3230.0) | 2620.0 (2160.0, 3220.0) | 2730.0 (2240.0, 3360.0) | 0.020 |
| Margaric acid (17:0) | 29.0 (24.0, 35.3) | 29.0 (24.0, 35.1) | 31.0 (25.4, 37.3) | 0.003 |
| Stearic acid (18:0) | 644.0 (550.0, 760.0) | 643.0 (549.0, 760.0) | 653.0 (552.0, 769.0) | 0.353 |
| Arachidic acid (20:0) | 23.0 (19.8, 26.6) | 23.0 (19.9, 26.6) | 22.0 (19.3, 26.6) | 0.120 |
| Docosanoic acid (22:0) | 64.8 (55.0, 76.0) | 65.0 (55.1, 76.0) | 61.2 (49.3, 73.1) | < 0.001 |
| Tricosanoic acid (23:0) | 28.0 (23.3, 33.0) | 28.0 (23.6, 33.0) | 26.3 (21.0, 31.4) | < 0.001 |
| Lignoceric acid (24:0) | 55.0 (46.8, 65.0) | 55.9 (47.0, 65.2) | 51.0 (41.0, 62.5) | < 0.001 |
Association between FFAs and all-cause mortality
In the USFA group, USFA positively associated with the all-cause mortality were myristoleic acid (14:1 n-5) (HR 1.02 [1.006–1.034]; P = 0.004), 16:1 n-7 (HR 1.001 [1.001–1.002]; P < 0.001), 18:1 n-7 (HR 1.006 [1.003–1.009]; P < 0.001), nervonic acid (24:1 n-9) (HR 1.007 [1.002–1.012]; P = 0.003), 20:3 n-9 (HR 1.027 [1.009–1.046]; P = 0.003), 22:4 n-6 (HR 1.024 [1.012–1.036]; P < 0.001), and 22:5 n-6 (HR 1.019 [1.006–1.032]; P = 0.005), while 22:6 n-3 had a statistically lower risk of all-cause mortality (HR 0.998 [0.996–0.999]; P = 0.007) (Model 4) (Table 3). Among the SFA group, 16:0 demonstrated a higher risk of all-cause mortality (HR 1.00 [1.00–1.00]; P = 0.022), while 23:0 (HR 0.975 [0.959–0.991]; P = 0.002) and 24:0 (HR 0.992 [0.984–0.999]; P = 0.036) were linked to a lower risk of all-cause mortality in the fully-adjusted model (Model 4) (Table 3). After adjusting for HOMA-IR, the findings did not change significantly (Supplementary Table S4).
Table 3.
Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis of serum fatty acids associated with all-cause mortality
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | P | HR (95%CI) | P | HR (95%CI) | P | HR (95%CI) | P | |
| Unsaturated fatty acids (N = 3719) | ||||||||
| Myristoleic acid (14:1 n-5) | 1.006 (0.998–1.015) | 0.134 | 1.013 (1.005–1.021) | 0.002 | 1.006 (0.993–1.019) | 0.373 | 1.020 (1.006–1.034) | 0.004 |
| Palmitoleic acid (16:1 n-7) | 1.001 (1.000-1.001) | < 0.001 | 1.001 (1.000-1.001) | < 0.001 | 1.001 (1.000-1.001) | 0.030 | 1.001 (1.001–1.002) | < 0.001 |
| cis-Vaccenic acid (18:1 n-7) | 1.002 (1.002–1.003) | 0.002 | 1.003 (1.002–1.004) | < 0.001 | 1.003 (1.001–1.006) | 0.013 | 1.006 (1.003–1.009) | < 0.001 |
| Oleic acid (18:1 n-9) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | < 0.001 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.005 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.908 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.153 |
| Eicosenoic acid (20:1 n-9) | 1.016 (1.005–1.027) | 0.006 | 1.014 (1.001–1.028) | 0.042 | 0.998 (0.973–1.024) | 0.907 | 1.013 (0.987–1.039) | 0.337 |
| Nervonic acid (24:1 n-9) | 1.002 (0.997–1.007) | 0.388 | 1.002 (0.997–1.007) | 0.368 | 1.002 (0.998–1.007) | 0.294 | 1.007 (1.002–1.012) | 0.003 |
| Linoleic acid (18:2 n-6) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.002 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.212 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | < 0.001 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.213 |
| α-Linolenic acid (18:3 n-3) | 1.000 (0.998–1.002) | 0.791 | 1.000 (0.998–1.002) | 0.776 | 0.996 (0.993-1.000) | 0.027 | 0.998 (0.995–1.002) | 0.294 |
| γ-Linolenic acid (18:3 n-6) | 1.002 (0.998–1.005) | 0.334 | 1.002 (0.999–1.006) | 0.211 | 0.999 (0.995–1.003) | 0.749 | 0.999 (0.995–1.004) | 0.800 |
| Stearidonic acid (18:4 n-3) | 1.015 (0.994–1.037) | 0.165 | 1.013 (0.998–1.040) | 0.308 | 0.990 (0.957–1.025) | 0.577 | 0.998 (0.962–1.035) | 0.912 |
| Eicosadienoic acid (20:2 n-6) | 1.007 (0.996–1.019) | 0.185 | 1.009 (0.998–1.022) | 0.181 | 0.995 (0.997–1.013) | 0.578 | 1.013 (0.995–1.032) | 0.166 |
| Dihomo-γ-Linolenic acid (20:3 n-6) | 0.999 (0.997–1.001) | 0.174 | 1.000 (0.998–1.002) | 0.982 | 0.998 (0.996–1.001) | 0.148 | 1.000 (0.998–1.002) | 0.947 |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (20:3 n-9) | 1.036 (1.024–1.048) | < 0.001 | 1.033 (1.018–1.049) | < 0.001 | 1.027 (1.010–1.045) | 0.002 | 1.027 (1.009–1.046) | 0.003 |
| Arachidonic acid (20:4 n-6) | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.021 | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.145 | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.675 | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.834 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5 n-3) | 1.001 (0.999–1.002) | 0.330 | 0.998 (0.997-1.000) | 0.107 | 0.998 (0.996-1.000) | 0.093 | 0.999 (0.997–1.001) | 0.245 |
| Docosatetraenoic acid (22:4 n-6) | 1.013 (1.006–1.020) | < 0.001 | 1.020 (1.013–1.028) | < 0.001 | 1.021 (1.009–1.033) | < 0.001 | 1.024 (1.012–1.036) | < 0.001 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-3) | 1.007 (1.003–1.012) | < 0.001 | 1.002 (0.997–1.007) | 0.424 | 0.998 (0.992–1.004) | 0.563 | 1.000 (0.995–1.006) | 0.902 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-6) | 1.009 (0.999–1.019) | 0.089 | 1.019 (1.008–1.030) | < 0.001 | 1.013 (1.000-1.026) | 0.045 | 1.019 (1.006–1.032) | 0.005 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 n-3) | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.886 | 0.998 (0.996–0.999) | 0.002 | 0.997 (0.996–0.999) | 0.001 | 0.998 (0.996–0.999) | 0.007 |
| Saturated fatty acids (N = 3900) | ||||||||
| Capric acid (10:0) | 1.012 (0.997–1.028) | 0.120 | 1.027 (1.012–1.043) | < 0.001 | 1.017 (0.996–1.039) | 0.114 | 1.020 (0.999–1.042) | 0.056 |
| Lauric acid (12:0) | 1.000 (0.995–1.004) | 0.913 | 1.002 (0.997–1.006) | 0.448 | 0.998 (0.992–1.003) | 0.435 | 1.000 (0.994–1.005) | 0.956 |
| Myristic acid (14:0) | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.321 | 1.001 (1.000-1.002) | 0.034 | 1.000 (0.998–1.002) | 0.910 | 1.002 (1.000-1.003) | 0.111 |
| Pentadecanoic acid (15:0) | 1.004 (0.995–1.013) | 0.354 | 1.005 (0.996–1.015) | 0.290 | 0.996 (0.984–1.009) | 0.589 | 1.008 (0.994–1.022) | 0.251 |
| Palmitic acid (16:0) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.029 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.013 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.506 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.022 |
| Margaric acid (17:0) | 1.010 (1.001–1.019) | 0.022 | 1.006 (0.996–1.016) | 0.222 | 0.996 (0.982–1.011) | 0.630 | 1.006 (0.991–1.022) | 0.429 |
| Stearic acid (18:0) | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.185 | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.084 | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.722 | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.275 |
| Arachidic acid (20:0) | 0.987 (0.969–1.006) | 0.176 | 0.993 (0.974–1.012) | 0.475 | 0.978 (0.958–0.998) | 0.033 | 0.992 (0.972–1.013) | 0.468 |
| Docosanoic acid (22:0) | 0.983 (0.977–0.990) | < 0.001 | 0.990 (0.984–0.997) | 0.005 | 0.988 (0.981–0.995) | < 0.001 | 0.994 (0.987-1.000) | 0.060 |
| Tricosanoic acid (23:0) | 0.960 (0.945–0.974) | < 0.001 | 0.964 (0.949–0.980) | < 0.001 | 0.961 (0.945–0.977) | < 0.001 | 0.975 (0.959–0.991) | 0.002 |
| Lignoceric acid (24:0) | 0.976 (0.968–0.984) | < 0.001 | 0.985 (0.977–0.993) | < 0.001 | 0.984 (0.976–0.992) | < 0.001 | 0.992 (0.984–0.999) | 0.036 |
Unsaturated fatty acids: model 1 unadjusted; model 2 adjusted by age, gender, and education level; model 3 adjusted by model 2 and increasing exercise, reducing salt diet, protein, sugar, dietary fiber, and triglycerides; model 4 adjusted by model 3 and diabetes, hypertension, congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, angina, heart attack, stroke, and cancer. Saturated fatty acids: model 1 unadjusted; model 2 adjusted by age, gender, and education level; model 3 adjusted by model 2 and increasing exercise, reducing salt diet, protein, carbohydrate, sugar, dietary fiber, total monounsaturated fatty acids, total polyunsaturated fatty acids, and triglycerides; model 4 adjusted by model 3 and diabetes, hypertension, congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, angina, heart attack, stroke, and cancer. Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval
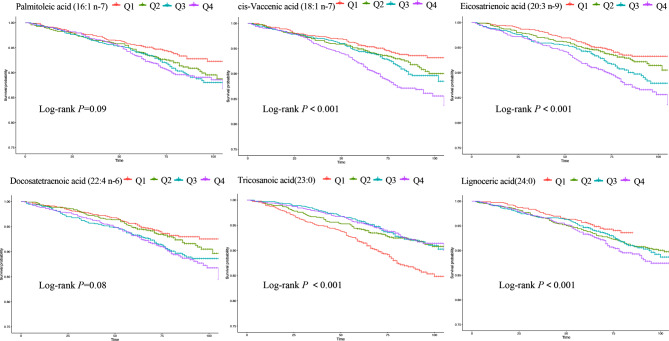
To explore the different risk of all-cause mortality in different FFAs concentration, we divided the FFAs into quartiles (Table 4). In USFA, comparing with Q1, 16:1 n-7, 18:1 n-7, 20:3 n-9, and 22:4 n-6 in Q3 and Q4 had significantly elevated risk of all-cause mortality (P < 0.05). In SFA, comparing with Q1, serum 23:0 and 24:0 in Q2, Q3 and Q4 had significantly reduced risk of all-cause mortality (P < 0.05).
Table 4.
Association of quartile percentages of serum fatty acids with all-cause mortality in different gender population
| All-cause mortality | All | Male | Female | P for interaction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | P | HR (95%CI) | P | HR (95%CI) | P | ||
| Unsaturated fatty acids (N = 3719) | |||||||
| Myristoleic acid (14:1 n-5) | 0.123 | ||||||
| Q1 (< 3.34) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | ||||
| Q2 (3.34–5.99) | 0.921 (0.674–1.260) | 0.607 | 0.995 (0.682–1.451) | 0.977 | 0.867 (0.495–1.518) | 0.617 | |
| Q3 (6.00-9.99) | 1.101 (0.813–1.490) | 0.534 | 0.973 (0.662–1.431) | 0.889 | 1.451 (0.878–2.398) | 0.146 | |
| Q4 (≥ 10.00) | 0.905 (0.662–1.236) | 0.529 | 0.629 (0.414–0.956) | 0.030 | 1.515 (0.921–2.491) | 0.102 | |
| Palmitoleic acid (16:1 n-7) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 135) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.030 | |||
| Q2 (135–198) | 1.351 (0.964–1.895) | 0.081 | 1.487 (1.008–2.195) | 0.046 | 1.404 (0.707–2.787) | 0.332 | |
| Q3 (199–297) | 1.507 (1.083–2.098) | 0.015 | 1.213 (0.803–1.834) | 0.359 | 2.707 (1.458–5.026) | 0.002 | |
| Q4 (≥ 298) | 1.581 (1.140–2.193) | 0.006 | 1.085 (0.716–1.645) | 0.699 | 3.275 (1.779–6.030) | <0.001 | |
| cis-Vaccenic acid (18:1 n-7) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 115) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | <0.001 | |||
| Q2 (115–140) | 1.319 (0.926–1.878) | 0.125 | 1.195 (0.787–1.814) | 0.403 | 1.736 (0.884–3.410) | 0.109 | |
| Q3 (141–176) | 1.488 (1.050–2.107) | 0.025 | 1.240 (0.816–1.883) | 0.313 | 2.273 (1.186–4.358) | 0.013 | |
| Q4 (≥ 177) | 2.125 (1.555–2.978) | <0.001 | 1.216 (0.808–1.831) | 0.348 | 5.113 (2.812–9.297) | <0.001 | |
| Nervonic acid (24:1 n-9) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 73.0) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.073 | |||
| Q2 (73.0-86.2) | 0.977 (0.712–1.340) | 0.886 | 0.866 (0.596–1.259) | 0.451 | 1.487 (0.801–2.759) | 0.209 | |
| Q3 (86.3-101.9) | 0.997 (0.725–1.370) | 0.985 | 0.986 (0.667–1.457) | 0.943 | 1.471 (0.807–2.680) | 0.208 | |
| Q4 (≥ 102.0) | 1.165 (0.861–1.577) | 0.323 | 1.059 (0.706–1.588) | 0.783 | 2.026 (1.159–3.539) | 0.013 | |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (20:3 n-9) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 5.00) | 1(ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.318 | |||
| Q2 (5.00-6.99) | 1.207 (0.846–1.722) | 0.300 | 1.332 (0.855–2.074) | 0.205 | 0.937 (0.511–1.717) | 0.833 | |
| Q3 (7.00-9.44) | 1.598 (1.140–2.240) | 0.007 | 1.443 (0.931–2.236) | 0.101 | 1.768 (1.040–3.006) | 0.035 | |
| Q4 (≥ 9.44) | 2.044 (1.479–2.824) | <0.001 | 1.559 (1.020–2.385) | 0.040 | 2.742 (1.663–4.521) | <0.001 | |
| Docosatetraenoic acid (22:4 n-6) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 20.0) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.004 | |||
| Q2 (20.0-25.2) | 1.180 (0.837–1.665) | 0.344 | 1.117 (0.740–1.685) | 0.598 | 1.280 (0.684–2.396) | 0.440 | |
| Q3 (25.3–32.4) | 1.511 (1.086–2.102) | 0.014 | 1.008 (0.664–1.530) | 0.970 | 2.673 (1.522–4.696) | <0.001 | |
| Q4 (≥ 32.5) | 1.652 (1.195–2.285) | 0.002 | 0.987 (0.656–1.487) | 0.951 | 3.292 (1.891–5.734) | <0.001 | |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-6) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 15.0) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.427 | |||
| Q2 (15.0-19.6) | 0.863 (0.620–1.199) | 0.379 | 0.945 (0.631–1.414) | 0.783 | 0.794 (0.448–1.408) | 0.430 | |
| Q3 (19.7–25.8) | 1.185 (0.873–1.608) | 0.276 | 1.015 (0.688–1.496) | 0.941 | 1.533 (0.928–2.534) | 0.095 | |
| Q4 (≥ 25.9) | 1.190 (0.876–1.617) | 0.265 | 1.068 (0.717–1.590) | 0.748 | 1.519 (0.928–2.486) | 0.097 | |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 n-3) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 109) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.233 | |||
| Q2 (109–143) | 0.820 (0.593–1.132) | 0.227 | 0.750 (0.502–1.121) | 0.161 | 1.121 (0.637–1.975) | 0.692 | |
| Q3 (144–198) | 1.065 (0.790–1.437) | 0.679 | 0.982 (0.677–1.425) | 0.926 | 1.469 (0.864–2.498) | 0.155 | |
| Q4 (≥ 199) | 0.970 (0.714–1.318) | 0.846 | 0.936 (0.630–1.391) | 0.745 | 1.354 (0.800-2.291) | 0.259 | |
| Saturated fatty acids (N = 3900) | |||||||
| Palmitic acid (16:0) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 2159) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.142 | |||
| Q2 (2160–2629) | 1.173 (0.856–1.607) | 0.320 | 0.970 (0.667–1.410) | 0.873 | 2.099 (1.123–3.921) | 0.020 | |
| Q3 (2630–3229) | 1.184 (0.865–1.621) | 0.291 | 0.785 (0.530–1.162) | 0.227 | 2.801 (1.533–5.121) | <0.001 | |
| Q4 (≥ 3230) | 1.331 (0.979–1.808) | 0.068 | 0.764 (0.518–1.126) | 0.174 | 3.609 (1.998–6.520) | <0.001 | |
| Tricosanoic acid (23:0) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 23.3) | 1(ref) | 1(ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.620 | |||
| Q2 (23.3–27.9) | 0.691 (0.513–0.930) | 0.015 | 0.461 (0.310–0.684) | <0.001 | 0.807 (0.474–1.376) | 0.432 | |
| Q3 (28-32.9) | 0.730 (0.539–0.989) | 0.042 | 0.542 (0.354–0.830) | 0.005 | 0.947 (0.581–1.543) | 0.826 | |
| Q4 (≥ 33.0) | 0.724 (0.528–0.992) | 0.045 | 0.572 (0.402–0.815) | 0.002 | 0.852 (0.531–1.368) | 0.507 | |
| Lignoceric acid (24:0) | |||||||
| Q1 (< 46.8) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 0.170 | |||
| Q2 (46.8–54.9) | 0.705 (0.534–0.931) | 0.014 | 0.500 (0.348–0.718) | <0.001 | 1.295 (0.814–2.062) | 0.275 | |
| Q3 (55.0-64.9) | 0.451 (0.332–0.613) | <0.001 | 0.333 (0.224–0.496) | <0.001 | 0.792 (0.477–1.316) | 0.368 | |
| Q4 (≥ 65.0) | 0.569 (0.427–0.758) | <0.001 | 0.365 (0.246–0.541) | <0.001 | 1.153 (0.726–1.831) | 0.546 | |
Abbreviations Q1, below 25th percentile; Q2, between 25th percentile and 50th percentile; Q3, between 50th percentile and 75th percentile; Q4, above 75th percentile; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; ref, reference
Kaplan–Meier survival curves for all-cause mortality were shown in Fig. 2, which displayed similar trends as in Cox regression. However, subgroup analysis in USFA, indicated only 16:1 n-7, 18:1 n-7 and 22:4 n-6, had interactions with gender. Meanwhile, in the SFA group, no interaction between FFA and gender was found. (Table 4).
Fig. 2.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves for all-cause mortality according to serum fatty acids quartiles. Q1, below 25th percentile; Q2, between 25th percentile and 50th percentile; Q3, between 50th percentile and 75th percentile; Q4, above 75th percentile
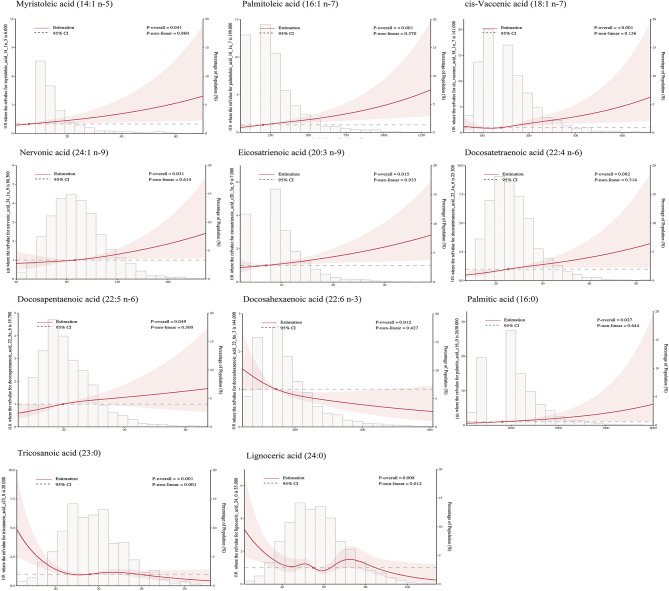
To evaluate the non-linear relationship between FFAs and all-cause mortality, we used RCS analysis. In the USFA group, serum 14:1 n-5 (P-linear = 0.041), 16:1 n-7 (P-linear < 0.001), 18:1 n-7 (P-linear < 0.001), 24:1 n-9 (P-linear = 0.031), 20:3 n-9 (P-linear = 0.015), 22:4 n-6 (P-linear = 0.002), and 22:5 n-6 (P-linear = 0.049) were linearly associated with higher risks of all-cause mortality, while, 22:6 n-3 were linearly associated with negative risk of all-cause mortality (P-linear = 0.012) (Fig. 3). In the SFA group, 16:0 (P-linear = 0.027) was linearly associated with higher risk of all-cause mortality, and the relationship between serum 23:0, 24:0 and risk of all-cause mortality showed L-shaped correlation curve which indicated that the lower concentration association with a higher all-cause mortality risk (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
Restricted Cubic Spline analysis for association of serum fatty acids with all-cause mortality
FFAs and cardiovascular mortality
Unlike the results between FFAs and all-cause mortality, in the USFA group, only 22:6 n-3 (HR 0.997 [0.994-1.000]; P = 0.035) had significant negative cardiovascular mortality risk while none of the SFA was found to be associated with cardiovascular mortality (Table 5). After adjusting for HOMA-IR, the findings did not change significantly (Supplementary Table S4). While, comparing with Q1, the level of 22:6 n-3 in Q2, Q3 and Q4 had no significantly associated with risk of cardiovascular mortality (Supplementary Table S5). The relationship between USFA, 22:6 n-3, and cardiovascular mortality was characterized by neither a linear nor nonlinear association (P-linear = 0.215; P-nonlinear = 0.260) (Supplementary Figure S1).
Table 5.
Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis of serum fatty acids and associated with cardiovascular mortality
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | P | HR (95%CI) | P | HR (95%CI) | P | HR (95%CI) | P | |
| Unsaturated fatty acids (N = 3719) | ||||||||
| Myristoleic acid (14:1 n-5) | 0.999 (0.977–1.022) | 0.936 | 1.007 (0.986–1.029) | 0.516 | 1.007 (0.985–1.030) | 0.534 | 1.006 (0.984–1.029) | 0.581 |
| Palmitoleic acid (16:1 n-7) | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.457 | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.541 | 1.000 (0.999–1.002) | 0.528 | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.603 |
| cis-Vaccenic acid (18:1 n-7) | 1.002 (1.000-1.004) | 0.043 | 1.002 (0.999–1.005) | 0.225 | 1.002 (0.999–1.005) | 0.196 | 1.001 (0.998–1.005) | 0.484 |
| Oleic acid (18:1 n-9) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.143 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.271 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.263 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.812 |
| Eicosenoic acid (20:1 n-9) | 1.011 (0.986–1.035) | 0.394 | 1.009 (0.979–1.041) | 0.555 | 1.010 (0.979–1.042) | 0.535 | 0.993 (0.959–1.027) | 0.668 |
| Nervonic acid (24:1 n-9) | 1.000 (0.990–1.009) | 0.921 | 0.997 (0.998–1.006) | 0.457 | 0.997 (0.988–1.006) | 0.453 | 1.004 (0.996–1.013) | 0.336 |
| Linoleic acid (18:2 n-6) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.215 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.773 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.817 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.863 |
| α-Linolenic acid (18:3 n-3) | 1.000 (0.996–1.004) | 0.977 | 1.000 (0.996–1.004) | 0.990 | 1.000 (0.996–1.004) | 0.989 | 0.999 (0.995–1.003) | 0.528 |
| γ-Linolenic acid (18:3 n-6) | 1.001 (0.995–1.008) | 0.661 | 1.001 (0.994–1.008) | 0.833 | 1.000 (0.993–1.007) | 0.947 | 0.997 (0.990–1.004) | 0.407 |
| Stearidonic acid (18:4 n-3) | 1.015 (0.972–1.059) | 0.502 | 1.008 (0.952–1.067) | 0.783 | 1.006 (0.948–1.068) | 0.832 | 0.975 (0.909–1.047) | 0.493 |
| Eicosadienoic acid (20:2 n-6) | 1.009 (0.988–1.031) | 0.412 | 1.008 (0.982–1.035) | 0.554 | 1.007 (0.981–1.034) | 0.604 | 1.006 (0.980–1.032) | 0.674 |
| Dihomo-γ-Linolenic acid (20:3 n-6) | 0.997 (0.993–1.001) | 0.157 | 0.998 (0.994–1.002) | 0.246 | 0.997 (0.993–1.001) | 0.193 | 0.998 (0.993–1.002) | 0.296 |
| Eicosatrienoic_acid (20:3 n-9) | 1.031 (1.005–1.059) | 0.021 | 1.021 (0.985–1.057) | 0.252 | 1.020 (0.984–1.056) | 0.281 | 1.003 (0.965–1.043) | 0.866 |
| Arachidonic_acid (20:4 n-6) | 1.001 (1.000-1.002) | 0.034 | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.260 | 1.000 (1.000-1.001) | 0.330 | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.605 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5 n-3) | 1.001 (0.998–1.004) | 0.613 | 0.998 (0.994–1.002) | 0.300 | 0.998 (0.994–1.002) | 0.257 | 0.998 (0.994–1.002) | 0.261 |
| Docosatetraenoic acid (22:4 n-6) | 1.014 (1.002–1.028) | 0.027 | 1.022 (1.008–1.037) | 0.003 | 1.023 (1.007–1.038) | 0.004 | 1.015 (0.998–1.031) | 0.079 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-3) | 1.009 (1.000-1.017) | 0.042 | 1.002 (0.993–1.011) | 0.666 | 1.002 (0.992–1.011) | 0.712 | 0.999 (0.991–1.008) | 0.909 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5 n-6) | 1.009 (0.988–1.029) | 0.414 | 1.013 (0.991–1.035) | 0.253 | 1.012 (0.989–1.035) | 0.306 | 1.007 (0.985–1.031) | 0.528 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 n-3) | 1.000 (0.997–1.002) | 0.752 | 0.997 (0.994-1.000) | 0.026 | 0.996 (0.994–0.999) | 0.017 | 0.997 (0.994–0.999) | 0.035 |
| Saturated fatty acids (N = 3900) | ||||||||
| Capric acid (10:0) | 1.009 (0.976–1.043) | 0.594 | 1.030 (0.997–1.064) | 0.075 | 1.029 (0.996–1.064) | 0.087 | 1.025 (0.992–1.059) | 0.134 |
| Lauric acid (12:0) | 1.000 (0.992–1.008) | 0.952 | 1.002 (0.994–1.011) | 0.592 | 1.002 (0.994–1.010) | 0.635 | 1.003 (0.994–1.011) | 0.547 |
| Myristic acid (14:0) | 1.001 (0.999–1.002) | 0.522 | 1.001 (0.999–1.003) | 0.148 | 1.001 (0.999–1.003) | 0.194 | 1.001 (0.999–1.003) | 0.419 |
| Pentadecanoic acid (15:0) | 1.004 (0.987–1.021) | 0.649 | 1.006 (0.988–1.025) | 0.521 | 1.005 (0.987–1.024) | 0.593 | 1.005 (0.988–1.022) | 0.573 |
| Palmitic acid (16:0) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.213 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.148 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.173 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.504 |
| Margaric acid (17:0) | 1.016 (1.001–1.031) | 0.041 | 1.013 (0.995–1.030) | 0.158 | 1.012 (0.994–1.029) | 0.194 | 1.007 (0.991–1.024) | 0.390 |
| Stearic acid (18:0) | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.745 | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.610 | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.665 | 1.000 (0.999–1.001) | 0.812 |
| Arachidic acid (20:0) | 0.968 (0.931–1.006) | 0.094 | 0.977 (0.939–1.017) | 0.251 | 0.976 (0.938–1.016) | 0.234 | 0.992 (0.957–1.028) | 0.650 |
| Docosanoic acid (22:0) | 0.975 (0.962–0.989) | <0.001 | 0.985 (0.972–0.999) | 0.036 | 0.985 (0.972–0.999) | 0.035 | 0.994 (0.981–1.007) | 0.350 |
| Tricosanoic acid (23:0) | 0.961 (0.933–0.990) | 0.009 | 0.970 (0.940–1.001) | 0.057 | 0.970 (0.940–1.001) | 0.056 | 0.988 (0.958–1.019) | 0.445 |
| Lignoceric acid (24:0) | 0.965 (0.949–0.981) | <0.001 | 0.978 (0.963–0.994) | 0.006 | 0.979 (0.963–0.994) | 0.008 | 0.989 (0.974–1.005) | 0.175 |
Unsaturated fatty acids: model 1 unadjusted; model 2 adjusted by age and education level; model 3 adjusted by model 2 and abdominal obesity, and reducing salt diet; model 4 adjusted by model 3 and diabetes, hypertension, congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, angina, heart attack, stroke, and cancer. Saturated fatty acids: model 1 unadjusted; model 2 adjusted by age, gender, and education level; model 3 adjusted by model 2 and abdominal obesity, reducing salt diet, and triglycerides; model 4 adjusted by model 3 and diabetes, hypertension, congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, angina, heart attack, stroke, and cancer. Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval
Discussion
In this prospective cohort study utilizing data from NHANES, our results highlight the influence of various circulating FFAs on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Additionally, the risk associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality exhibited significant variations across different FFAs. Specifically, USFA, serum 22:6 n-3 demonstrated a reduced risk in terms of both all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Among SFA, lower concentrations of circulating 23:0 and 24:0 exhibited higher risk of all-cause mortality.
It is widely accepted that USFA are associated with protective effects on human health, in contrast to the recognized adverse impact of SFA on overall well-being and longevity. Dietary recommendations have emphasized on the reduction of SFA [33], yet the evidence remains inconclusive. Meta-analyses have yielded conflicting findings, with some indicating no association between SFA intake and risk of CAD [34]. Research has shown that diverse types of SFA, distinguished by variations in carbon bond length and parity, demonstrate different effects on cardiovascular risk factors [35]. The observed heterogeneity of effects across the circulating composition of specific SFA, may be attributed to the interplay of dietary intake and endogenous metabolism and synthesis [36]. This is indirectly supported by the positive yet nonsignificant associations observed for the circulating concentration of 16:0 and 18:0 which are synthesized in the body and only weakly with CAD [34]. Moreover, 16:0 may raise cholesterol levels to greater extends than 18:0 [4]; substituting 16:0 with 18:0 could lower LDL concentrations [37]. Remarkably, a recent study emphasized that, across the entire population, individuals exhibiting higher serum levels of very long-chain SFAs (specifically 22:0 and 24:0) as a proportion of total serum FFAs, experienced a reduction in risks associated with all-cause mortality, CHD, and CVD mortality [38]. In our study, we observed a similar association between 24:0 and all-cause mortality, but not 22:0. Notably, we identified another very long-chain SFA, 23:0, which was linked to reduced all-cause mortality risk. Given that the highest total very long-chain SFA are primarily derived from the intake of peanuts and macadamia nuts [39], we found a significant negative association with all-cause mortality, with a HR of 0.78 (95% CI 0.76–0.81) [40]. The EPIC-InterAct case-cohort study revealed an inverse association between incident type 2 diabetes and plasma levels of long-chain SFAs (23:0 and 24:0); a finding that remained robust across various sensitivity analyses [41]. In a previous cohort study, replacing SFA, particularly 16:0 and 18:0, with plant proteins led to decreased risk of myocardial infarction [42]. However, no risk reduction was observed when SFA were substituted with MUFA or PUFA [42].
A meta-analysis revealed that the consumption of omega-3 fatty acids, encompassing 20:5 n-3 (EPA), DHA, and plant-derived 18:3 n-3 (ALA), is linked to a decreased risk of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and CVD events among individuals with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [43]. In contrast, no significant association was observed between the omega-6 intake or total PUFA and these events [43]. Though guidelines recommend the augmentation of omega-3 fatty acids, recent trials have not confirmed this [44]; increase in omega-3 intake demonstrates minimal impact on both all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality [44]. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids supplementation may also not demonstrate significantly beneficial influence on cancer incidence, non-vascular mortality, or all-cause mortality [45].
In our study, only serum DHA (22:6 n-3) was associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality, and cardiovascular mortality. Conversely, 18:2 n-6 (LA), ALA, DHA (22:4 n-6), DHA (22:5 n-6), and EPA were associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality. These diverse outcomes could be attributed, in part, to variations in participant characteristics and the detection methods for circulating fatty acids, influencing the associations between self-reported intake and actual circulating levels of EPA and DHA [46]. Another source of variability among different studies could be attributable to the normalization process. Indeed, circulating fatty acids are often expressed as a percentage of total measured fatty acids [47–49]. As an example, Johnson and colleagues reported both absolute and percentage normalization for free fatty acids showing how different normalization approaches led to different results [50]. Factors such as BMI, alcohol intake, and the method of expressing circulating fatty acids may play an important role in shaping the associations between dietary and circulating FFAs [46]. Furthermore, long-term dietary habits influenced the fatty acid composition of adipose tissue, which is largely reflected in circulating FFAs [51]. Specific dietary factors (e.g. low intake of whole grains; high intake of refined carbohydrates or trans fat) significantly reduce metabolic stress, and lowering risk of cardiovascular events [52]. It is noteworthy that dietary intake was commonly assessed using food frequency questionnaires in epidemiological studies, a method that may generate approximately 50% inaccurate data [53]. Epidemiological investigations examining the association between blood levels of EPA and DHA with clinical events could reveal more robust correlations compared to studies assessing solely dietary intake [54, 55]. Nevertheless, as showed in our study, there are significant interactions between USFA (16:1 n-7, 18:1 n-7 and 22:4 n-6) and gender in terms of all-cause mortality. Gender influences circulating FFA levels due to differences in hormone levels, body fat percentage, and body fat distribution between males and females, which may further mediate the relationship between FFA and health outcomes [56, 57]. Therefore, future studies might consider sex-specific factors when assessing the mortality risk using FFA biomarkers.
Strengths and limitations
To our knowledge, this is the first study to examine how different FFAs associate with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in a large, diverse, nationally representative sample of adults.
Meanwhile, this study has many limitations. The disparities in the origins of individual FFAs, whether from dietary intake or endogenous metabolism, is unknown, which may have an impact on FFAs levels in blood serum, so the relationship between levels of FFAs and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality needs to be further verified. Then, we could not determine the exact impact of various FFAs and concentrations on overall mortality. Thirdly, only one baseline value was considered, and the individual FFAs levels and distribution may change over years. And the level of circulating FFAs is mainly affected by various factors, such as the lipolytic activity of the adipose tissue stores, obesity, visceral fat, insulin resistance etc., even we have adjustment for BMI, waist circumference, diabetes, HOMA-IR, the relationship between levels of FFAs and CVD end-points need more evidence.
Conclusions
In this nationally representative cohort of US adults, the different FFAs exhibited significant associations with risk of all-cause mortality. Achieving optimal concentrations of specific FFAs effectively lowered this risk of all-cause mortality, but this benefit was not observed in regards to cardiovascular mortality.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
The authors of this research thank the participants of the NHANES and the NHANES staff.
Abbreviations
- SFA
Saturated fatty acids
- USFA
Unsaturated fatty acids
- MUSFA
Monounsaturated fatty acids
- PUSFA
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- CVD
Cardiovascular disease
- FFAs
Free fatty acids
- CAD
Coronary artery disease
- CHD
Coronary heart disease
- NHANES
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- NCHS
National Center for Health Statistics
- CDC
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- FIP
Family income to poverty ratio
- BMI
Body mass index
- HR
Hazard ratio
- CI
Confidence interval
- RCS
Restricted cubic spline
- HOMA-IR
Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance
- CHF
Chronic heart failure
Author contributions
YC, and GY.H.L designed research; LJZ conducted research; BH and YL analyzed data; ML wrote the paper. GY.H.L had primary responsibility for final content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
None funding was received for this work.
Data availability
The data included in this study are publicly and freely available without restriction at:https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/continuousnhanes.
Declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The NHANES protocol has been approved by the NCHS Ethics Review Board, and written informed consent has been obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Change history
10/10/2024
Figure 3 was missing in the original publication. The article has been updated to rectify the error.
Contributor Information
Yang Chen, Email: yang.chen2@liverpool.ac.uk.
Gregory Y. H. Lip, Email: gregory.lip@liverpool.ac.uk
References
- 1.Roche HM. Unsaturated fatty acids. Proc Nutr Soc. 1999;58(2):397–401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.A ISS, C AB. Changes in plasma free fatty acids Associated with Type-2 diabetes. Nutrients. 2019;11(9):2022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Briggs M, Petersen K, Kris-Etherton P. Saturated fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: replacements for saturated fat to reduce cardiovascular risk. Healthcare. 2017; 5: 29. 2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Mensink RP, World Health Organization. Effects of saturated fatty acids on serum lipids and lipoproteins: a systematic review and regression analysis. World Health Organization; 2016.
- 5.Willett W. Nutritional epidemiology. Oxford University Press; 2012.
- 6.Cena H, Calder PC. Defining a healthy diet: evidence for the role of contemporary dietary patterns in health and disease. Nutrients. 2020;12(2):334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Roy VK, Kumar A, Joshi P, Arora J, Ahanger AM. Plasma free fatty acid concentrations as a marker for acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7(11):2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pirro M, Mauriège P, Tchernof A, Cantin B, Dagenais GR, Després JP, et al. Plasma free fatty acid levels and the risk of ischemic heart disease in men: prospective results from the Québec Cardiovascular Study. Atherosclerosis. 2002;160(2):377–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pilz S, Scharnagl H, Tiran B, Seelhorst U, Wellnitz B, Boehm BO, et al. Free fatty acids are independently associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in subjects with coronary artery disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(7):2542–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kleber ME, Delgado GE, Dawczynski C, Lorkowski S, Maerz W, von Schacky C. Saturated fatty acids and mortality in patients referred for coronary angiography—the Ludwigshafen Risk and Cardiovascular Health study. J Clin Lipidol. 2018;12(2):455–e633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Malik VS, Chiuve SE, Campos H, Rimm EB, Mozaffarian D, Hu FB, et al. Circulating very-long-chain saturated fatty acids and incident coronary heart disease in US men and women. Circulation. 2015;132(4):260–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lemaitre RN, McKnight B, Sotoodehnia N, Fretts AM, Qureshi WT, Song X, et al. Circulating very long-chain saturated fatty acids and heart failure: the cardiovascular health study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(21):e010019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kharazmi-Khorassani J, Zirak RG, Ghazizadeh H, Zare-Feyzabadi R, Kharazmi-Khorassani S, Naji-Reihani-Garmroudi S et al. The role of serum monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in cardiovascular disease risk. Acta Bio Medica: Atenei Parmensis. 2021;92(2). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Hu FB, Manson JE, Willett WC. Types of dietary fat and risk of coronary heart disease: a critical review. J Am Coll Nutr. 2001;20(1):5–19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Belfort R, Mandarino L, Kashyap S, Wirfel K, Pratipanawatr T, Berria R, et al. Dose-response effect of elevated plasma free fatty acid on insulin signaling. Diabetes. 2005;54(6):1640–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Suiter C, Singha SK, Khalili R, Shariat-Madar Z. Free fatty acids: circulating contributors of metabolic syndrome. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2018;16(1):20–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Boden G. Obesity and free fatty acids. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2008;37(3):635–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schembri Wismayer D, Laurenti MC, Song Y, Egan AM, Welch AA, Bailey KR, et al. Effects of acute changes in fasting glucose and free fatty acid concentrations on indices of beta-cell function and glucose metabolism in subjects without diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023;325(2):E119–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lu J, Varghese RT, Zhou L, Vella A, Jensen MD. Glucose tolerance and free fatty acid metabolism in adults with variations in TCF7L2 rs7903146. Metabolism. 2017;68:55–63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Poynten AM, Gan SK, Kriketos AD, Campbell LV, Chisholm DJ. Circulating fatty acids, non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and insulin-infused fat oxidation acutely influence whole body insulin sensitivity in nondiabetic men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(2):1035–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pankow JS, Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Ballantyne CM, Couper DJ, Hoogeveen RC, et al. Fasting plasma free fatty acids and risk of type 2 diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(1):77–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Khawaja O, Maziarz M, Biggs ML, Longstreth WT Jr., Ix JH, Kizer JR, et al. Plasma free fatty acids and risk of stroke in the Cardiovascular Health Study. Int J Stroke. 2014;9(7):917–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jouven X, Charles MA, Desnos M, Ducimetière P. Circulating nonesterified fatty acid level as a predictive risk factor for sudden death in the population. Circulation. 2001;104(7):756–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Charles MA, Fontbonne A, Thibult N, Claude JR, Warnet JM, Rosselin G, et al. High plasma nonesterified fatty acids are predictive of cancer mortality but not of coronary heart disease mortality: results from the Paris prospective study. Am J Epidemiol. 2001;153(3):292–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Akinbami LJ, Chen TC, Davy O, Ogden CL, Fink S, Clark J et al. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2017-March 2020 Prepandemic file: Sample Design, Estimation, and Analytic guidelines. Vital Health Stat. 2022(190):1–36. [PubMed]
- 26.Chen Y, Gue Y, Calvert P, Gupta D, McDowell G, Azariah JL et al. Predicting stroke in Asian patients with atrial fibrillation using machine learning: a report from the KERALA-AF registry, with external validation in the APHRS-AF registry. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024:102456. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Lagerstedt SA, Hinrichs DR, Batt SM, Magera MJ, Rinaldo P, McConnell JP. Quantitative determination of plasma c8-c26 total fatty acids for the biochemical diagnosis of nutritional and metabolic disorders. Mol Genet Metab. 2001;73:38–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.CDC. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Laboratory Data - Continuous NHANES. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/search/datapage.aspx?Component=Laboratory&CycleBeginYear=2011
- 29.Statistics NCfH. The Linkage of National Center for Health Statistics Survey Data to the National Death Index — 2019 Linked Mortality File (LMF): Linkage Methodology and Analytic Considerations. Hyattsville. 2022.
- 30.Brämer GR. International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems. Tenth revision. World Health Stat Q. 1988;41(1):32–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Moy E, Garcia MC, Bastian B, Rossen LM, Ingram DD, Faul M, et al. Leading causes of death in Nonmetropolitan and Metropolitan areas- United States, 1999–2014. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2017;66(1):1–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yoon PW, Bastian B, Anderson RN, Collins JL, Jaffe HW. Potentially preventable deaths from the five leading causes of death–United States, 2008–2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63(17):369–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products N, Allergies. Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for fats, including saturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, trans fatty acids, and cholesterol. Efsa J. 2010;8(3):1461. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chowdhury R, Warnakula S, Kunutsor S, Crowe F, Ward HA, Johnson L, et al. Association of dietary, circulating, and supplement fatty acids with coronary risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(6):398–406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zheng Y, Fang Y, Xu X, Ye W, Kang S, Yang K, et al. Dietary saturated fatty acids increased all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in an elderly population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr Res. 2023;120:99–114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Parks EJ, Hellerstein MK. Carbohydrate-induced hypertriacylglycerolemia: historical perspective and review of biological mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71(2):412–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.van Rooijen MA, Mensink RP. Palmitic acid versus stearic acid: effects of interesterification and intakes on cardiometabolic risk markers—A systematic review. Nutrients. 2020;12(3):615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tao X, Liu L, Ma P, Hu J, Ming Z, Dang K, et al. Association of Circulating Very Long-Chain Saturated Fatty acids with Cardiovascular Mortality in NHANES 2003–2004, 2011–2012. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024;109(2):e633–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lemaitre RN, King IB. Very long-chain saturated fatty acids and diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2022;33(1):76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Amba V, Murphy G, Etemadi A, Wang S, Abnet CC, Hashemian M. Nut and peanut butter consumption and mortality in the National Institutes of Health-AARP Diet and Health Study. Nutrients. 2019;11(7):1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Forouhi NG, Koulman A, Sharp SJ, Imamura F, Kröger J, Schulze MB, et al. Differences in the prospective association between individual plasma phospholipid saturated fatty acids and incident type 2 diabetes: the EPIC-InterAct case-cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(10):810–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Praagman J, Vissers LE, Mulligan AA, Laursen ASD, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, et al. Consumption of individual saturated fatty acids and the risk of myocardial infarction in a UK and a Danish cohort. Int J Cardiol. 2019;279:18–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Luo S, Hou H, Wang Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Zhang H, et al. Effects of omega-3, omega-6, and total dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Funct. 2024;15:1208–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Abdelhamid AS, Brown TJ, Brainard JS, Biswas P, Thorpe GC, Moore HJ et al. Omega-3 fatty acids for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018(11):1465–858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 45.Zhang Y-F, Gao H-F, Hou A-J, Zhou Y-H. Effect of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on cancer incidence, non-vascular death, and total mortality: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Public Health. 2014;14(1):1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wanders AJ, Alssema M, De Hoon SE, Feskens EJ, van Woudenbergh GJ, van der Kallen CJ, et al. Circulating polyunsaturated fatty acids as biomarkers for dietary intake across subgroups: the codam and hoorn studies. Ann Nutr Metab. 2018;72(2):117–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Imamura F, Lemaitre RN, King IB, Song X, Lichtenstein AH, Matthan NR, et al. Novel circulating fatty acid patterns and risk of cardiovascular disease: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;96(6):1252–61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang Q, Imamura F, Ma W, Wang M, Lemaitre RN, King IB, et al. Circulating and dietary trans fatty acids and incident type 2 diabetes in older adults: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(6):1099–107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fretts AM, Imamura F, Marklund M, Micha R, Wu JH, Murphy RA, et al. Associations of circulating very-long-chain saturated fatty acids and incident type 2 diabetes: a pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019;109(4):1216–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Johnston LW, Liu Z, Retnakaran R, Zinman B, Giacca A, Harris SB, et al. Clusters of fatty acids in the serum triacylglyceride fraction associate with the disorders of type 2 diabetes. J Lipid Res. 2018;59(9):1751–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hodson L, Skeaff CM, Fielding BA. Fatty acid composition of adipose tissue and blood in humans and its use as a biomarker of dietary intake. Prog Lipid Res. 2008;47(5):348–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mozaffarian D. Free fatty acids, cardiovascular mortality, and cardiometabolic stress. Eur Heart J 28(22):2699–700. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 53.Archer E, Hand GA, Blair SN. Validity of US nutritional surveillance: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey caloric energy intake data, 1971–2010. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(10):e76632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Harris WS, Tintle NL, Etherton MR, Vasan RS. Erythrocyte long-chain omega-3 fatty acid levels are inversely associated with mortality and with incident cardiovascular disease: the Framingham Heart Study. J Clin Lipidol. 2018;12(3):718–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.von Schacky C. Importance of EPA and DHA blood levels in brain structure and function. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Giltay EJ, Gooren LJ, Toorians AW, Katan MB, Zock PL. Docosahexaenoic acid concentrations are higher in women than in men because of estrogenic effects. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80:1167–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhao L, Hao F, Huang J, Liu X, Ma X, Wang C, et al. Sex-and age-related metabolic characteristics of serum free fatty acids in healthy Chinese adults. J Proteome Res. 2020;19:1383–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data included in this study are publicly and freely available without restriction at:https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/continuousnhanes.